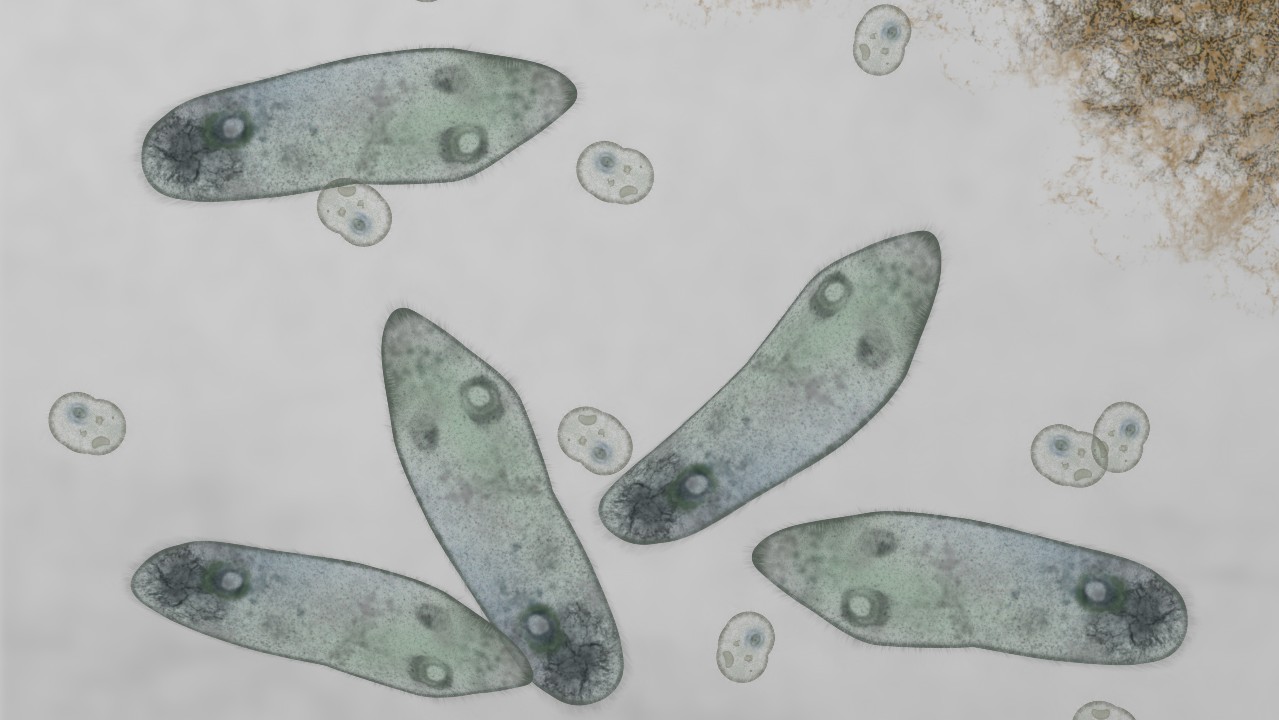
Paramecia are single-celled protists that are found in aquatic habitats. They are oblong or slipper-shaped and covered with hairy structures called cilia. Paramecia can be cultured in labs and serve as useful model organisms.
According to The Biology of Paramecium, 2nd Ed., aurelia and bursaria were divided into two groups based on the shape of the cells. The aurelia type is oblong and has a slightly curved end. Bursaria represents cells that are shaped. They are shorter and have a rounded end.
According to the California Institute of Technolog y, paramecium are part of a group of organisms. Their bodies are covered in short hairs. Cilia are important to a paramecium. The structures whip back and forth in the water.
Paramecia can move forward at a rate of up to 2 millimeters per second. Sometimes the organisms will perform avoidance reactions by reversing the direction in which the cilia beat. After the paramecium stops swimming, it stops spinning or turning. It is possible for a paramecium to swim backwards if multiple avoidance reactions follow one another.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
Cilia helps in feeding by pushing food into the oral grooves. Paramecia are known to eat yeast, unicellular algae and even some non-living substances such as milk powder, starch and powdered charcoal, according to theBiology of Paramecium.
Eukaryotes include paramecium. Eukaryotes have cells that are well-organized. According to Washington University, the nucleus is a compartment that holds DNA and is the defining feature of eukaryotic cells. The energy-generating mitochondria is one of the organelles characteristics of Paramecia. The organisms also have some unique parts.
Under the pellicle is a layer of cytoplasm called the ectoplasm. The region has a organelles called trichocysts. They become long, thin and spiky when they discharge their contents.
According to Cell Biology magazine, the paramecium is protected from predatory attacks and propelled in unpredictable directions by a network of telescopic Trichocysts. Two of the three predator species that were tested were found to be defeated by the trichocysts of Paramecium tetraurelia.
The endoplasm is a more fluid type of cytoplasm. The majority of the cell components are in this region. According to the National Human Genome Research institute, these are pockets in plants and animals that hold waste product, store water and offer structural support for cells. According to the University of Chicago, food vacuoles contain food. The lysosomes break apart food and conduct a form of digestion. The discharge of excess water from the cell is caused by contractile vacuoles. Water can be fed into the contractile vacuoles via canals or smaller water-carrying vacuoles. Excess water leaves the paramecium body through the pellicle when the contractile vacuole collapses.
James Forney, a professor of biochemistry at Purdue University, said that paramecia has two types of nuclei.
According to the Encyclopedia of Microbiology, the two types of nuclei are the micronucleus and macronucleus. The micronucleus has two copies of each paramecium chromosome. He said that the DNA that is present in the organisms is passed from one generation to the next. According to Forney, the macronucleus has a subset of DNA from the micronucleus.
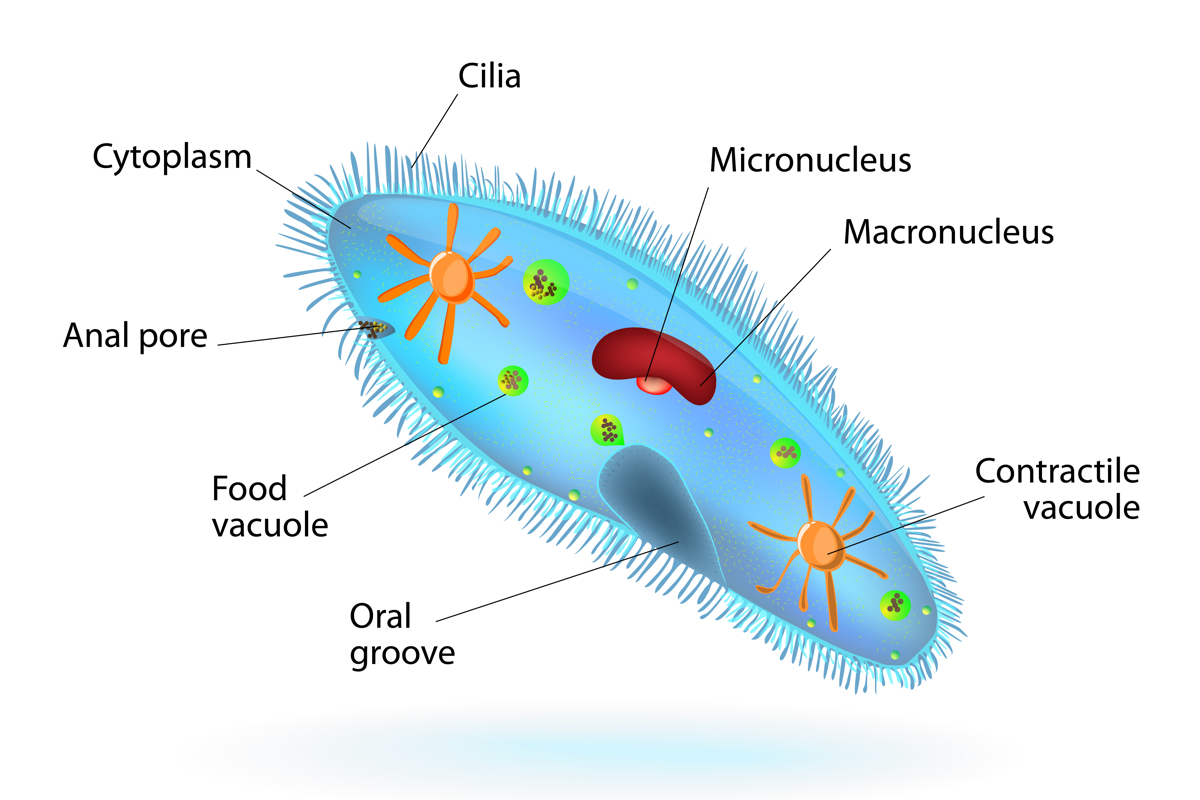
According to Forney, all paramecium species have one macronucleus. The number of micronuclei can vary by species. The Paramecium aurelia species complex has two micronuclei and Paramecium multimicronucleatum.
There are two distinct nuclei. It is a mechanism by which paramecium and other ciliates can protect themselves from genetic invaders.
Depending on their environment, Paramecia can reproduce either asexually or sexually. Sexual reproduction takes place under conditions of starvation, while asexual reproduction takes place when there is ample nutrition. Paramecia can also undergo autogamy or self-fertilization under certain conditions.
Asexual reproduction.
One paramecium cell divides into two genetically identical offspring. According to Forney, the macronucleus divides into two parts, 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609- 888-609-
Sexual reproduction.
Paramecia conjugating is similar to sex. According to Forney, there are two types of paramecia, which are referred to as odd and even. The mating types for various paramecium species are either an odd or even number. If you are the same type as the other one, you cannot mate, according to Forney. Only cells within a single Paramecium species can mate.
Under laboratory conditions, the process is easily distinguishable. They can form clumps of cells when they are mixed.
The paramecium is used in the conjugate. Antonio Guill, CC BY 3.0.
During sexual reproduction, the micronuclei of each paramecium undergo meiosis, halving the genetic content to create a haploid nucleus. The two connected mates exchange these. A new, genetically varied, micronucleus can be created from the haploid nuclei from each mate. The new micronucleus give rise to a new macronucleus.
Self-fertilization is autogamy.
Forney said that autogamy is essentially the same thing as conjugation, but it is only happening with a single cell. The micronucleus replicate multiple times. One of the new micronuclei undergoes a genetic change. According to the journal, some DNA is fragmented and some are removed.
The term "paramecium" refers to a single organisms within the Paramecium. A group of organisms that share the same characteristics are referred to as a genera. The Paramecium is divided into groups called subgenera, which each contain one or more species.
The methods of classification have changed over time. The earliest methods were based on visual observation and used to describe all paramecia as either aurelia or bursaria. The combination of observation and information has been used in classification. A family tree is a representation of evolutionary relationships, according to Berkeley University.
The understanding of relationships within the Paramecium genus and species diversity has been affected by the shift from morphology to molecular phylogenetics, according to Michaela Strüder-Kypke, manager of advanced light microscopy at the University of Guelph in Ontario. According to the journal Diversity, there are five subgenera of paramecia.
The method of identifying species based on the sequence of a particular fragment of DNA has been used for Paramecium.
Strüder-Kypke says there are 19 recognized morphospecies of Paramecium. She said that amorphospecies is a species defined by its unique characteristics, not by genetics or the ability to produce offspring. The Paramecium aurelia species complex has 15 sibling species. Sibling species can't conjugate with one another because they differ in biochemical and genetic aspects. The Paramecium aurelia complex is a single morphospecies.
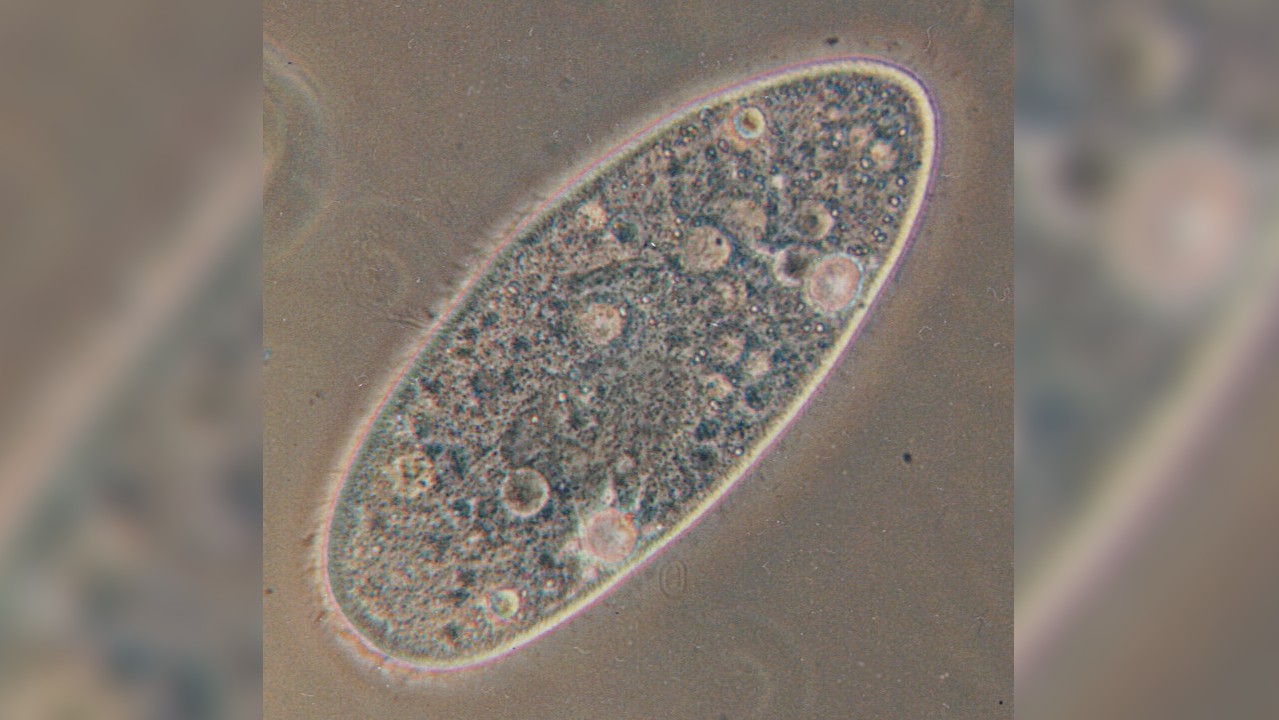
Even today, new insights into Paramecium taxonomy and the existence of new species are described. The 19th morphospecies,Paramecium buetschlii, was discovered in a freshwater pool in Norway and described in a research published in the journal Organisms Diversity & Evolution. There are three new cryptic species found in Germany, Hungary and Brazil. The authors say that they were treated as cryptic species because they were difficult to distinguish from other members of theParamecium genus. They are a separate species according to their DNA barcodes.
StrFC;der-Kypke told LiveScience that the idea is that if we look in unusual habitats or regions of this world, we may still find new species.
Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design discovered that paramecium can be used to monitor water quality. The researchers tracked the movement of paramecia because they are ubiquitous in water bodies and large enough to be seen with a normal camera. Researchers were able to detect the quality and presence of water pollutants by tracking swimming speeds and movements. Paramecium swimming speeds declined when pollutants such as heavy metals zinc chloride and copper sulfate were present.
It is possible to assess the drinkability of water without the need for specialized equipment or chemicals by taking a sample of water and measuring paramecia.
Brock Biology of Microorganisms is a good source of information about paramecium. Take a look at the video produced by the channel Journey to the Microcosmos.
Iwona, Rzeszutek, et al., "Programmed genome rearrangements in ciliates", Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, Volume 77, May 2020, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03555-2
Anne-Marie Tassin, et al., "Paramecium tetraurelia basal body structure", Cili, Volume 5, Feburary 2016
Van Houten was the author of "Evo-Devo: Non-model Species in Cell and Developmental Biology."
Secretory mechanisms in paramecium The April 2020 edition of the Masterclass in Neuroendocrinology can be found here.
There is a person named Edna s. The Cell Physiology Source Book, Academic Press, 1995 contains Kaneshiro's Amoeboid Movement, Cilia, and Flagella.