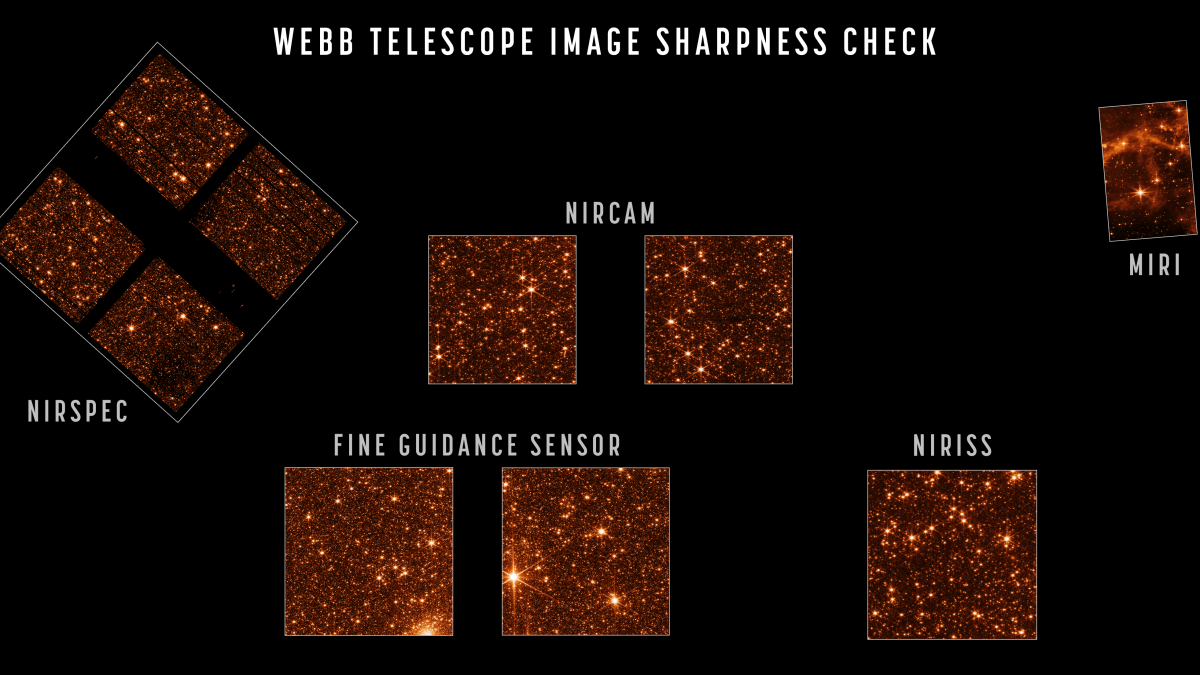
NASA's view of deep space has gotten sharper.
The agency announced that the James Webb Space Telescope can capture crisp, well-focused images with all four of its science instruments.
The milestone allows the mission team to proceed with science instrument commissioning. After several months of mirror and instrument alignments, the telescope will enter a new phase of preparation. If everything goes to plan, the next step will take roughly two months, with Webb finishing in June.
The images have profoundly changed the way I view the universe, according to the NASA statement. It is my hope that everyone can see them.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
Live updates: NASA's James Webb Space Telescope mission
Related: How the James Webb Space Telescope works in pictures
Since its launch, the $10 billion telescope has been busy. It took almost a month to get to deep space, and then it had a seven-step alignment process to get through. Each milestone has been mapped out, with only minor changes required along the way.
The 18 hexagonal segments of the scope's primary mirror were almost completely cooled to the deep-space temperatures they need to see objects sharply. The mirrors appear to be ready, as they are sending fully focused light into every instrument, which in turn is rendering images.
NASA officials said in the statement that the optical performance of the telescope continues to be better than the engineering team's most optimistic predictions. Minor adjustments will be required from here on, the agency said.
The next phase of work will include telescope calibration. To make sure they can perform science work, equipment needs to work in different configurations.
Before it is declared operational, there is a list of milestones that Webb will need to hit.
The total amount of solar radiation hitting the observatory will vary to confirm thermal stability when changing targets, according to NASA officials.
Maintenance observations every two days will monitor the mirror alignment, and when needed, apply corrections to keep the mirrors in their aligned locations.
Follow Elizabeth on social media. Follow us on social media.