NASA crews are sent to the International Space Station by the private spaceflight company, SpaceX. The founder of Musk is testing a system for lunar landings that he hopes will lead to future crewed Mars missions.
The company sent its first two astronauts to the International Space Station on May 30, 2020, aboard the SpaceX Crew Dragon and has sent several more crews aloft on behalf of NASA and other entities.
It is the only company that can send astronauts to space, although it may soon face competition from Boeing.
There are 8 ways that SpaceX has changed spaceflight.
Musk is a South African born businessman. The New York Times reported that at age 30, Musk made his initial fortune by selling his two successful companies, Zip2 and PayPal, for a total of $307 million. Musk decided his next venture would be a space company.
Musk had the idea of sending a greenhouse to the Red Planet. He wanted to provide a science base on Mars and drum up public interest in exploration. The cost was too high and Musk started a new company called Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
He spent a third of his fortune to get the company up and running. There was skepticism that he would succeed.
The craft was unveiled in 2006 under the name Dragon. The folk group Peter, Paul and Mary wrote the song "Puff, the Magic Dragon" in the 1960s. He said that he chose the name because he thought his aims were impossible.

When he started the company, Musk believed that more frequent and reliable launches would bring down the cost of exploration. He wanted a stable customer that could fund the early development of a rocket. He wooed launch clients from different sectors to broaden his customer base. He wanted to develop the first privately built booster to make it into space, which he called the Falcon 1.
A steep learning curve was experienced by the company. It took four tries to get Falcon 1 flying, with previous attempts derailed by problems such as fuel leaks and a rocket-stage collision. On Sept. 28, 2008, and July 14, 2009, Falcon 1 made two successful flights. The Malaysian RazakSat satellite was placed into space by the 2009 launch.
See the evolution of the rockets in pictures.
The COTS demonstration program was created to spur the development of systems that could transport cargo commercially to the International Space Station. The contract value was boosted by a few more milestones. The contract of Rocketplane Kistler was terminated after the company failed to meet the requirements.
The COTS program had multiple companies participate in its early stages. NASA awarded two contracts for commercial-resupply services in 2008. Orbital ATK received a contract for eight flights, worth $1.9 billion.

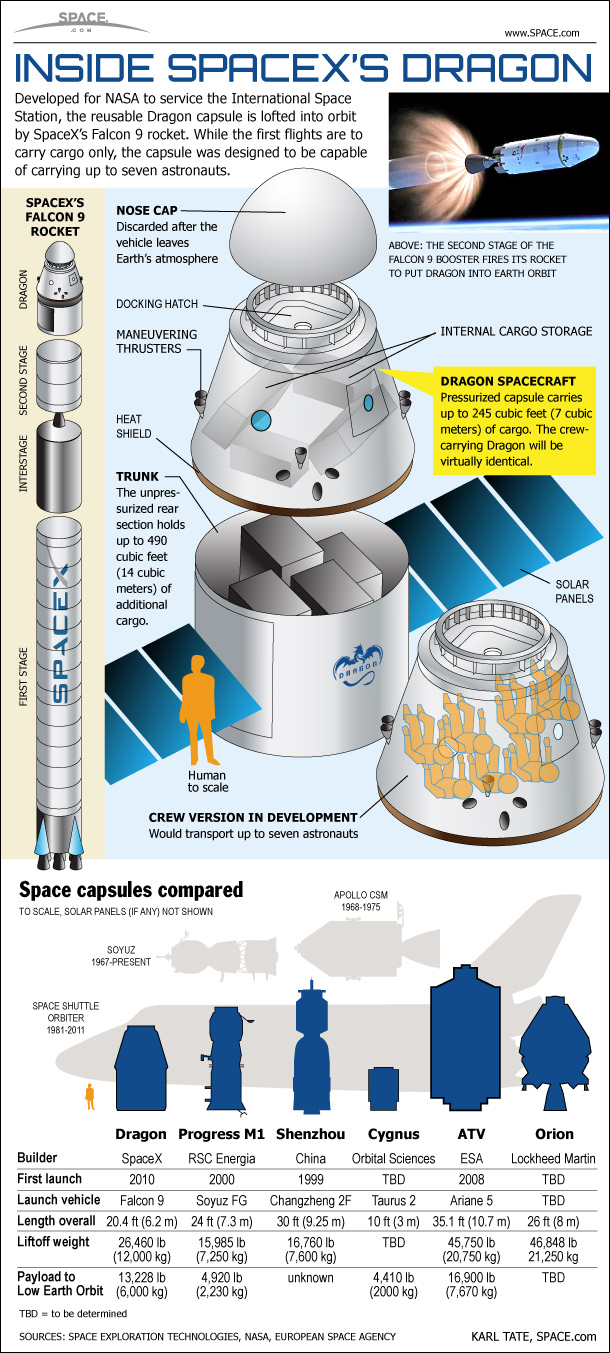
One of the features of the Falcon 9 is reusability. The cargo of Falcon 9 is more than that of Falcon 1. The capacity of Falcon 1 was 1,480 lbs. There is 670 kilogrammes.
The first Falcon 9 booster landing took place in December of 2015, and now the company wants to make its boosters retrievable. They usually land on a robotic ship. Many of the Falcon 9 boosters have been used multiple times.
The Falcon Heavy rocket made its debut in February of last year. A spacesuit mannequin called Starman and an electric car made by another company owned by Musk were carried on the Falcon Heavy. The live stream of the launch and the first few hours in space attracted attention from all over the world.
The core stage of the rocket failed to survive the impact and hit the ocean at 300 mph, which was too fast. The engine burn in space that is expected to bring the Roadster to Mars is performed by the Falcon Heavy.
A test of the crewed Dragon spacecraft, intended to bring NASA astronauts to space, experienced a malfunction while on the ground. There was a smoke cloud visible for miles around Cape Canaveral, Florida. The company had a plan to bring people to the International Space Station. Since the debut crewed mission in 2020, the company has brought people to space with few issues.
The space station delivery was the most important milestone for the company. In May 2012 the Dragon cargo ship delivered its first cargo to the space station under a test flight for the COTS program. The launch was delayed for a few days because of an engine problem, but the rocket lifted off safely.
Spaceflight observers praised the ability of the company to send a cargo ship to the International Space Station. When the space station was developed in the 1980s and 1990s, private spaceflight was not considered.
The first commercial flights to the space station took place in October of 2012. The flight achieved most of its objectives, but it experienced a partial rocket failure. The Orbcomm-OG2 satellite was stranding in an abnormal low altitude when the mission failed.
The first version of the Dragon spaceship ran 20 flights to the space station through 2020, with all but one of them arriving successfully. The next successful launch was on April 8, 2016 and brought the inflatable Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) to space.
A new version of Dragon's cargo variant began flying in December 2020 and has executed all five of its planned missions successfully to date.
The Crew Dragon was going to be flown to space. One set, called DragonFly, performed a pad abort test at Florida's Cape Canaveral Air Force Facility, as well as tethered hover tests at the SpaceX Rocket Development and Test Facility in Texas.
The company used a pressure vessel qualification module and an environmental control and life support system module to test out key systems. After eight days in space, the Crew Dragon splashed down in the ocean after completing its uncrewed test on March 2, 2019. The Crew Dragon was destroyed during a set of tests to evaluate the abort system.
On May 30, 2020, the first crewed test flight by the company, called Demo-2, safely delivered astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to the International Space Station. The two men returned safely to Earth on August 2, 2020.
On Nov. 15, 2020, the first successful operational flight, Crew-2, used a Falcon 9 rocket to safely launch four astronauts to the International Space Station aboard a Crew Dragon craft that the astronauts had named "Resilience."
NASA and international astronauts have been sent to the International Space Station by the SpaceX company. There is room in the current contract for more missions to be ordered as required for space station needs.
Helping the case of the Boeing Starliner has been ongoing issues in developing the vehicle, but Boeing plans to conduct a second uncrewed test flight in 2022.
There are amazing launch photos of the Crew-4 mission.

Musk has a plan to head to Mars. NASA chose the lander to send Artemis astronauts to the moon no earlier than 25 years from now. NASA's selection had to overcome legal protests by Blue Origin after the agency pivoted to a sole-sourced contract over multiple vendors, citing a lack of money.
The testing program began with a small vehicle called Starhopper, which performed a series of tethered and untethered flight tests. The first test of a series of Starship vehicles in high altitude flights was in August 2020. One of the greatest challenges of the program was executing flip maneuvers in mid-air, which led to the demise of several Starships before the soft landing on May 5, 2021.
The Super Heavy booster holds 3.6 tons of liquid oxygen and methane and is designed to launch to deep space. Super Heavy is expected to be re-usable. Four grid fins will assist in controlling the booster.
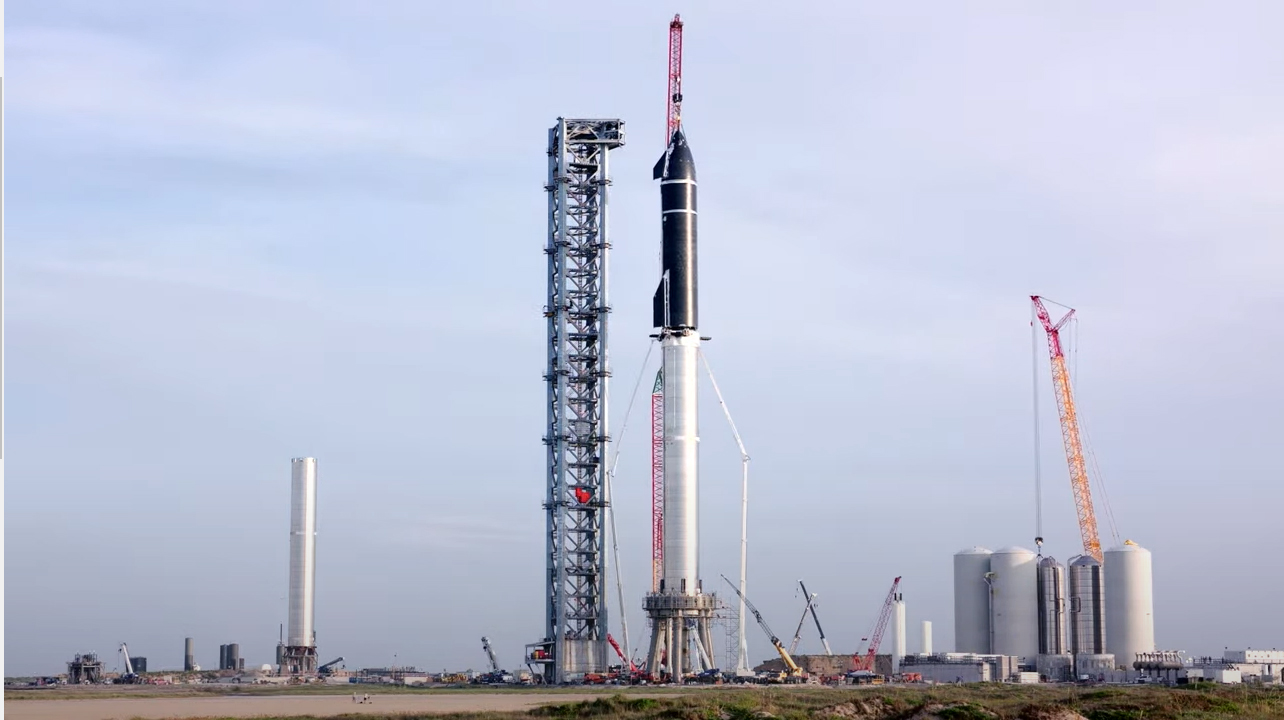
The Super Heavy and Starship were put together on a launchpad for the first time in August of 2021. That is more than 30 feet taller than the moon rocket.
A delayed environmental review of the Federal Aviation Administration of the launch facilities in Boca Chica, Texas will delay the orbital test of the Starship-Super Heavy version. The public response to the review added more data points than the FAA anticipated.

The success of the Crew Dragon missions to the space station attracted other companies to use similar craft to run missions to the moon.
The first Crew Dragon was used by non-professionals. Four people rode to the moon on a mission to raise money for St. Jude Children's Research Hospital. The crew used a variant of Crew Dragon with a large cupola window, flown in place of a docking mechanism, as they didn't need to reach the International Space Station.
The success of Inspiration4 inspired a billionaire to start a private space program. The Polaris Program will run missions for charity and research in space. He is expected to participate in all three missions. The first mission is called Polaris Dawn.
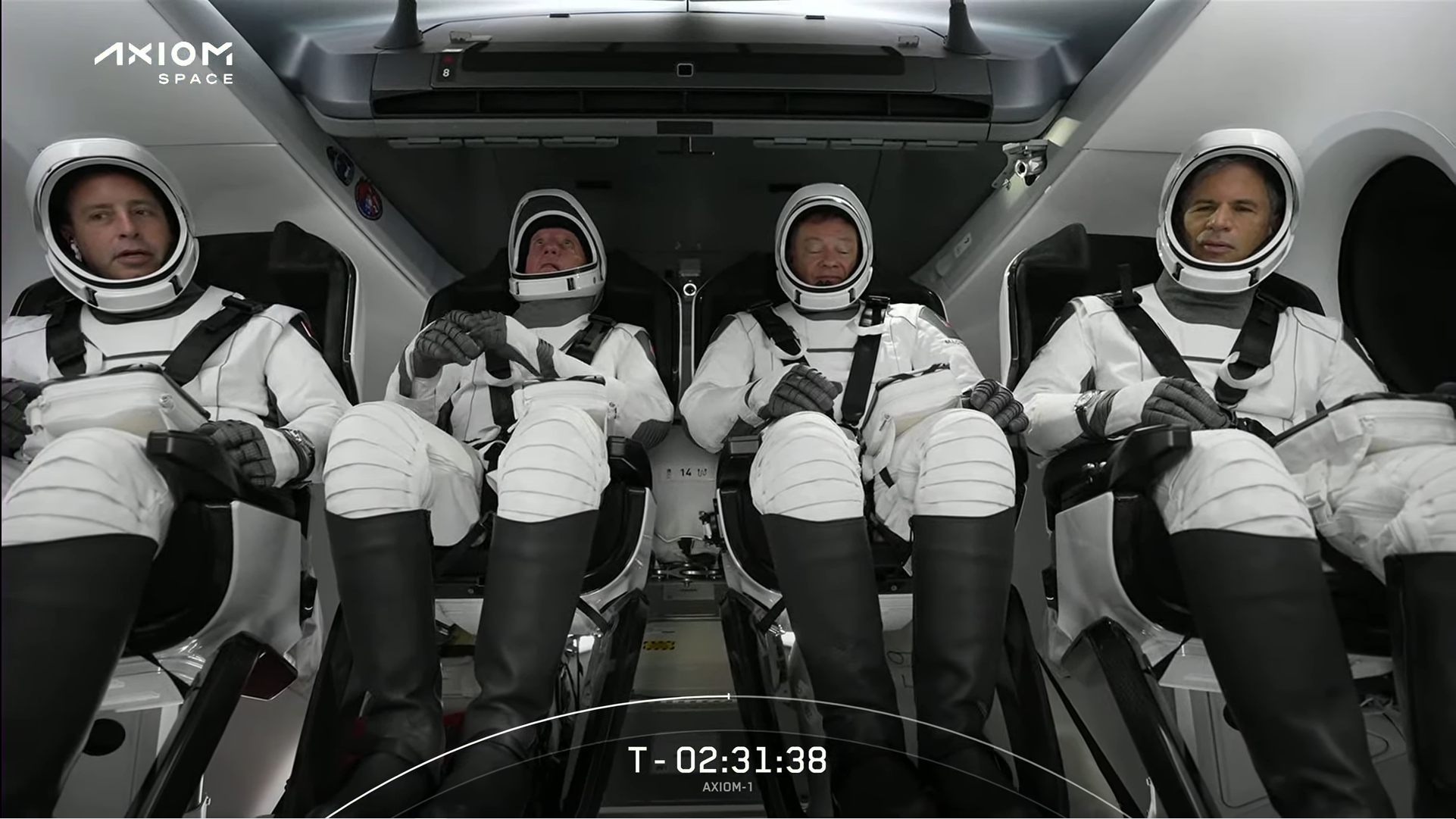
A company called Axiom Space plans to use the Crew Dragons from the SpaceX company to carry out research on the International Space Station. The first mission in the series was in April of 2022. The company should launch a research module to the International Space Station that will allow for a film studio, according to the manifest.
There are moon missions in the future. Musk announced that Yusaku Maezawa, an artist and billionaire founder of the Japanese e-commerce giant Zozo, and a few other artists will launch a trip around the moon in the 2020s. How much Maezawa paid for that trip was not disclosed. Maezawa is looking for crewmates for the trip who have an artistic bent.

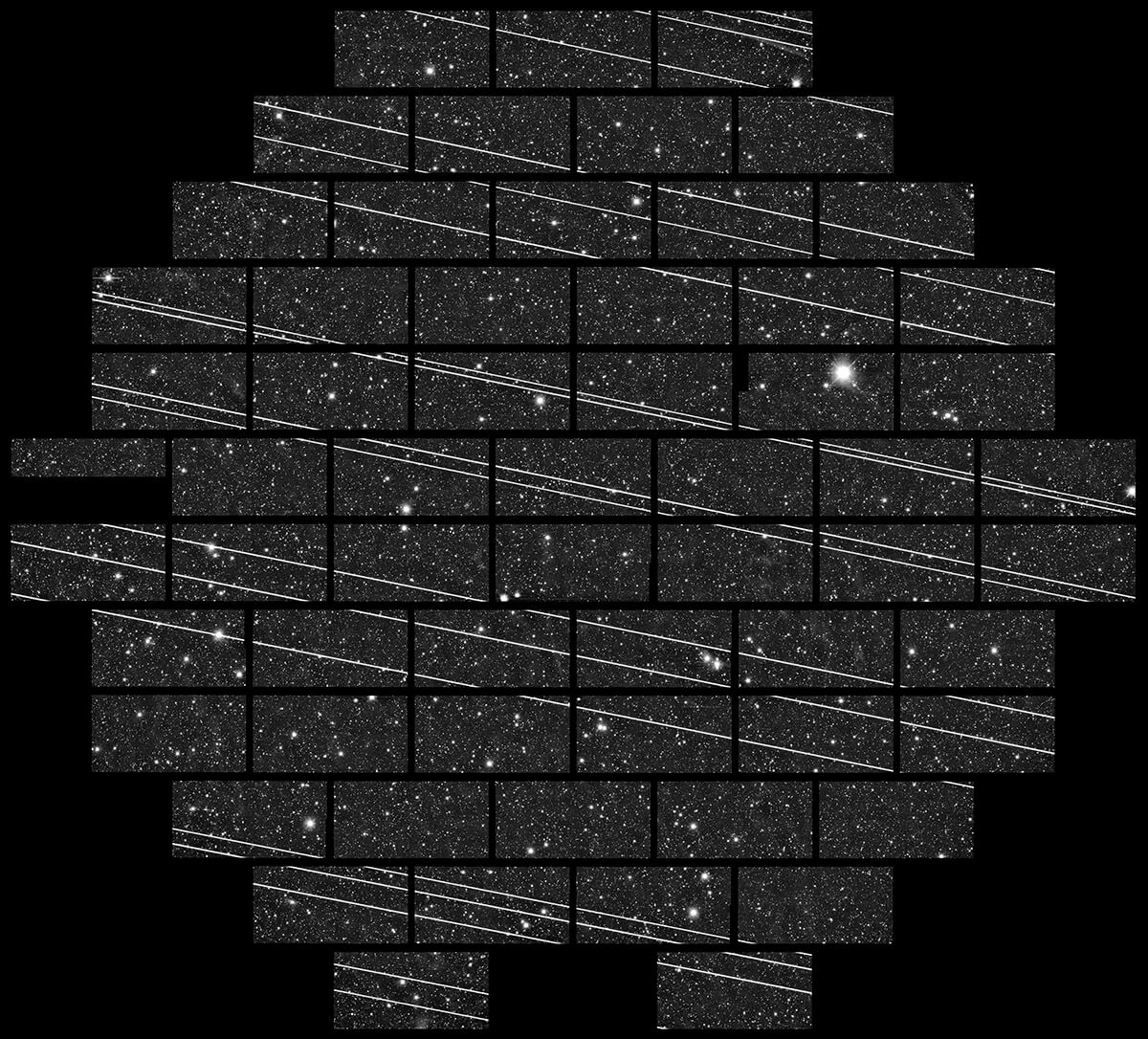
Musk and the company he founded, SpaceX, sparked controversy in the field of astronomy over their plans to place a constellation of 12,000 small satellites around the Earth in order to provide reliable internet access to remote places. Sixty of the Starlink satellites have been launched, but they have left trails in the telescope observations of the night sky. Many researchers fear that an increased number of satellites will cause problems.
The next round of Starlink satellites could be coated with a special coating that would make them less reflective and less obtrusive in the night sky. Astronomers continue to warn about the potential of intrusions in telescopic images. Satellite streaks appear to affect wide-field imagery at dawn and dusk.
Studies continue to show the impact of Starlink on observations. A research paper in the Astrophysical Journal shows that the images of the wide-field Zwicky Transient Facility are becoming more affected by time as more satellites are deployed.
The number of satellites passing overhead may interfere with launch windows and affect ground observations if a proposal to place 30,000 more Starlink internet satellites into orbit is approved. The agency noted that the risk of space debris collision is increasing.
The private sector, military and nongovernmental entities pay the company to launch cargo into space. Although it makes money from launch services, the company is also focused on developing technology for future space exploration.
Musk told delegates at theAIAA in San Diego that he planned to take people to Mars. He said at the International Space Development Conference that the reuse of the rocket stage would be a step in getting to the Red Planet.
Musk said at the time that the purpose of the company was to accelerate the development of rocket technology and establish a permanent base on Mars.
Musk's plan to create a Red Planet colony in the next 50 to 100 years includes a technological plan for Martian transport. The Interplanetary Transport System is a larger version of the Falcon 9. The spaceship is larger than the Dragon and will carry at least 100 people per flight. The crewed version of the Dragon is expected to carry four people.

Musk followed up his announcement by publishing a paper describing a future Red Planet city of a million people and providing more details about how the ITS would transport cargo and people.
In Australia, Musk updated his Mars plans. He talked about a system called the Big Falcon Rocket during the talk. The spaceship that BFR will carry is likely to have a capacity of 100 people and will be over 48 meters tall.
In September, Musk unveiled an update to his Mars plans, which included changing the outer coating on the first BFR to STAINLESS STEEL. Photos of the shiny, sci-fi-looking craft being assembled at the South Texas facilities of the space company were circulating on the internet.
The name of the spaceship has changed.
Musk has plans for Mars. Musk said in February that it could be possible to reach a launch rate of one Starship vehicle every six to eight hours, and one Super Heavy rocket every hour, on missions that would send up to 150 tons of cargo to space. Musk said that a high launch rate is expected to bring down costs.
You can follow the company on social media. There are videos on the company's YouTube channel of successful and failed launches. The latest news on collaborations between the two entities can be found on NASA's website. Stay up to date with the series of collaborations.
The SpaceX Starship Super Heavy Project will be held at the Boca Chica launch site in March of 2022, according to the Federal Aviation Administration.
The Government Accountability Office has a decision matter.
The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Volume 924, Number 2, is about the impact of the SpaceX Starlink Satellites on the Zwicky Transient Facility Survey Observations. There is a new year on Jan. 14.
There is a link to the Starlink website.
There is a website called "SpaceX." It is available at: https://www.spacex.com/