The progression of events from the past to the future is called time. The nature of time is hard to define, but we all share many experiences that are bound by time: causes lead naturally to effects, we remember the past but not the future, and the evolution of time appears to be continuous and irreversible.
The experience of the flow of time is related to the observer and their situation according to Einstein. The master clock that kept synchronized time throughout the universe was assumed to exist by the work of IsaacNewton. The concept of the clock allowed it to work. According to the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, all observers could agree on a single moment of time.
Einstein discovered that the passage of time is relative. The faster you move in space, the slower you progress through time. The closer you get to the light's speed, the bigger the effect becomes.
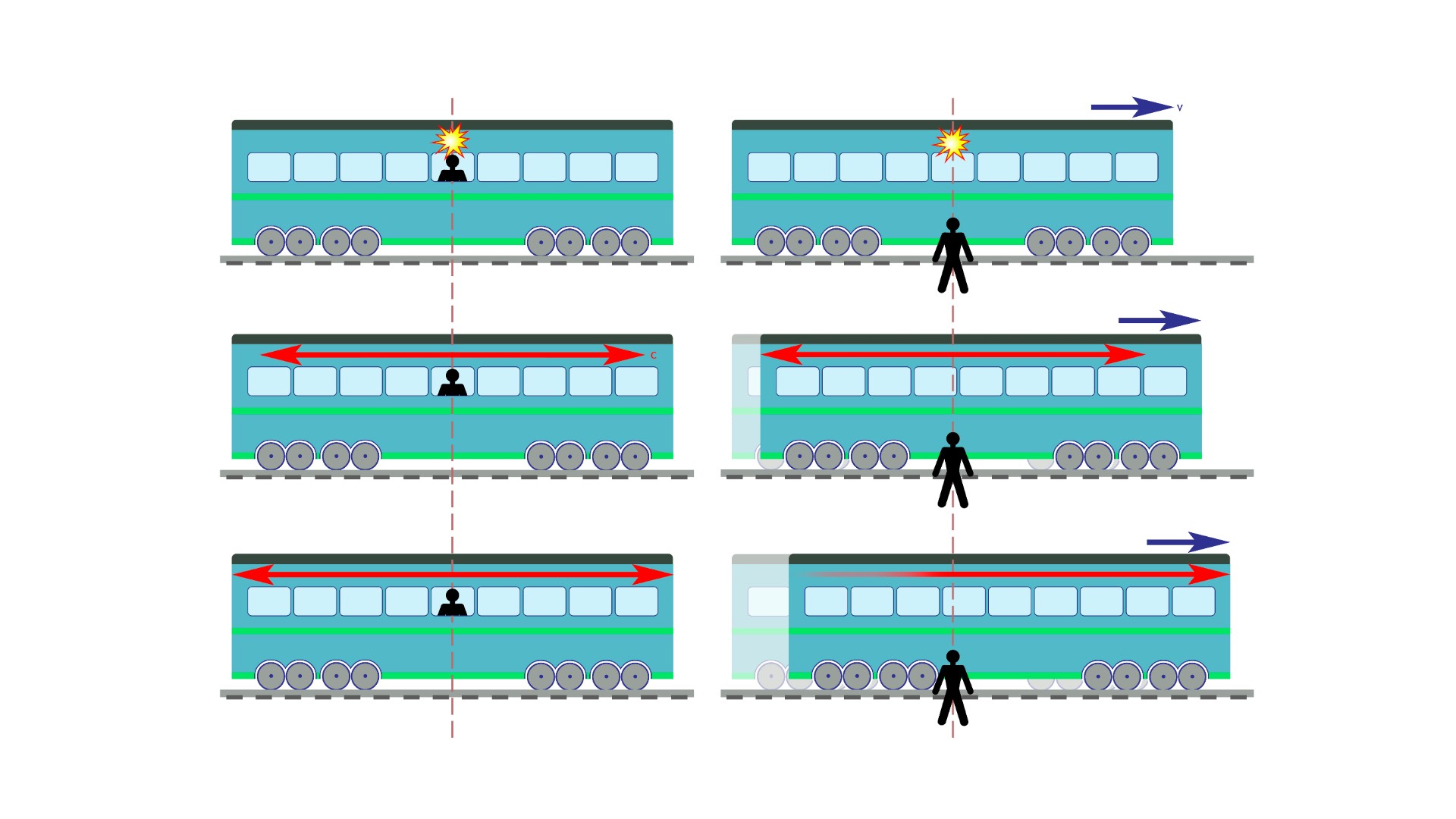
Physicists have made multiple measurements that show this effect since Einstein first proposed it. An atomic clock on a jet airplane will tick at a slower rate than one on the ground. A muon is a particle that doesn't exist long enough to travel from the atmosphere to the ground. Muons travel at close to the speed of light, which allows them to complete their journey.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
When Einstein developed his theory of general relativity, he extended it to situations involving gravity. The passage of time is slowed by the presence of strong gravity, so a clock on the surface of Earth or near a black hole will tick at a slower rate than a clock in the middle of space.
9 ways you can see Einstein's theory of relativity in real life
Time travel into the future is mandatory. All of us are moving forward into our futures. It is impossible to escape the future. It is clear that jumping forward in time is acceptable.
If a twin sets off in a rocket ship and travels for a few years, they will have aged less than their Earthbound twin. If the rocket traveled quickly, decades or even centuries could have passed on Earth. Scott Kelly has spent more time in space than his twin Mark, which has resulted in a few milliseconds less time being spent.

Time travel into the past is not allowed in all experiments and observations. The grandfather paradox asks what would happen if you killed your grandfather and then traveled back in time to commit the crime, it raises a lot of uncomfortable issues.
There is no known way to travel backwards in time. Some time-traveling situations can be constructed in general relativity, but they require entities that don't seem to exist in our universe, like matter with negative mass or infinitely long cylinders.
Physicists don't know why time travel into the past is forbidden.
Symmetric laws and equations are used by physicists to understand the natural world. That means they can be reversed. Without any other context, you wouldn't be able to tell if the video was being played in reverse or forward.
One aspect of physics that seems to respect a flow of time is the concept of entropy, which is a measure of the disorder in a system. The evolution of the system can't be reversed according to the second law of thermodynamics.
Physicists don't know if the growth of entropy gives rise to thearrow of time or if it's just a coincidence, according to the Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
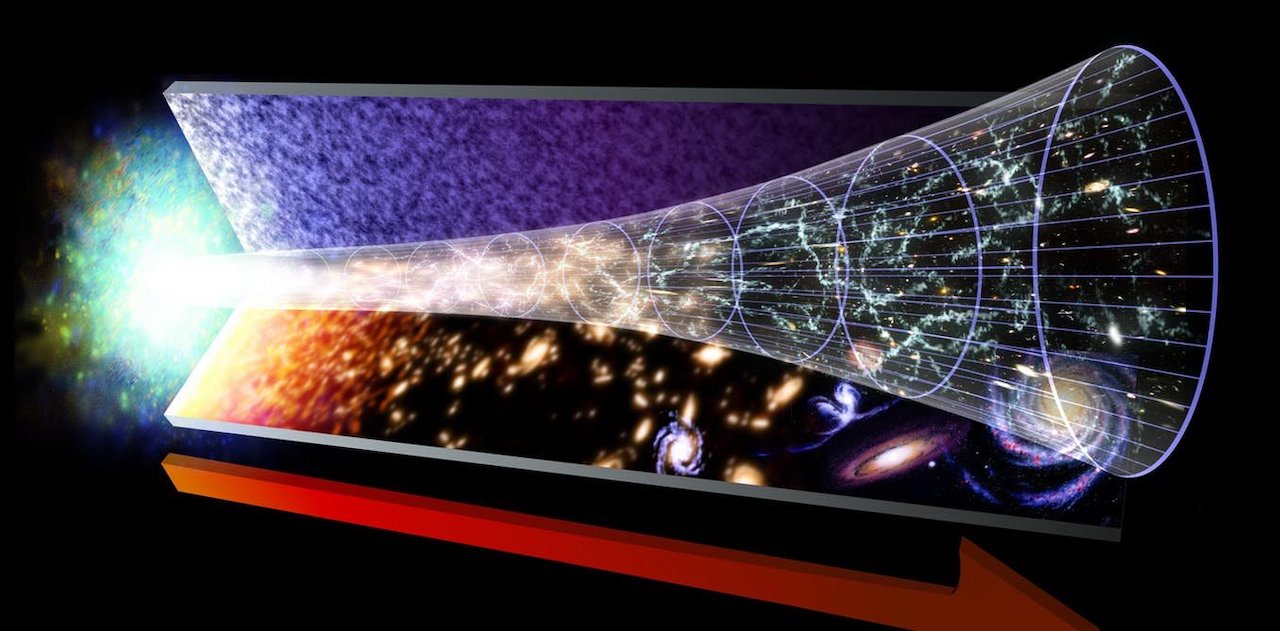

Most physical theories treat time as a continuum, which is how we perceive the flow of time. There is no smallest unit of time. All events go smoothly into the next.
One theory of quantum gravity, called loop quantum gravity, postulates the existence of a smallest possible unit of space-time. The smallest possible extension of space and time would be represented by this unit. The theory says that what we think is smooth, continuous time is really a stop- motion progression from past to future. The frames of a movie blend together like this when it happens for an incredibly brief duration, according to an article by Carlo Rovelli in the journal Living Reviews of Relativity.
Scientists, philosophers and others have pondered the nature of time. We haven't been able to come up with a complete description of what time is because we haven't learned a lot about it.
Physicists and philosophers argue that what we experience as time is just an illusion. The past and future are the same as the entire space already exists in this view. The way our brains process sensory information from our environment is what makes us sense the flow of time.
C.S. Baird was published on June 24. Does time go quicker at the top of a building? Does time go faster at the top of a building compared to the bottom?
C. Callender was published on June 8. There is asymmetrical symmetry in time. The Encyclopedia of Philosophy is available at theplato.stanford.edu.
The article was published on October 18. Is time real? is open in a new tab.
J. Hunter was a man. Time travel. The internet encyclopedia of philosophy. The timetrav is from April 5, 2022, in the new tab.
O&Connell, C. was published on August 3. There are five ways that we could do time travel. Fiveways to travel through time is a new article in the science section of the magazine.
C. Rovelli was born in 1998. You can loop quantum gravity. The article is titled Living Reviews in Relativity.