Tomasz Nowakowski is a writer for Phys.org.
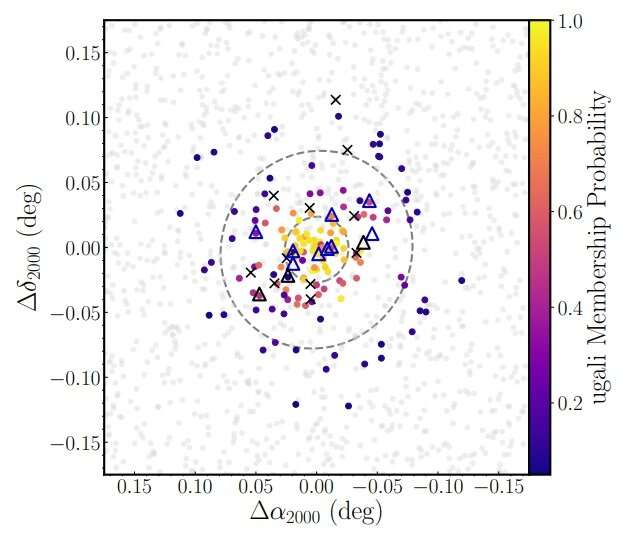
An international team of astronomy has discovered a new dwarf galaxy as part of a survey. The new galaxy, called Pegasus IV, has an absolute magnitude of -4. The paper was published on arXiv.org.
The ultra-FAint dwarf galaxies are the most dark matter dominated and least chemically evolved of all the galaxies. They are thought to be the best candidate fossils from the universe's early stages.
A group of astronomer led by William Cerny of the University of Chicago have found a satellite of the Milky Way. The data from the Dark Energy Camera was used to make the discovery.
In this work, we present the discovery and characterization of another ultra-FAint Milky Way satellite by DELVE. The Dark Energy Camera (DECam) is accessible to the northern edge of the sky, which was previously covered by the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System 1 survey.
The UFD Pegasus IV is a compact, old, ultra-FAint stellar system. The results show that the UFD is at least 12.5 billion years old, has a half-light radius of 133.7 light years, and has an absolute V-band magnitude of -4. The stellar mass of the system was 4,400 solar mass.
According to the paper, the heliocentric velocity of Pegasus IV is -273.6 km/s, while the velocity dispersion is 3.3 km/s. The results show that the UFD is on an elliptical, retrograde path and is currently near the apocenter.
The iron abundances for five stars of Pegasus IV yielded a metallicity of approximately - 2.67. One of the most metal-poor ultra-FAint dwarfs is the newly found galaxy. The astronomer said that the metallicity spread of Pegasus IV confirms its nature as a dwarf galaxy.
The researchers were able to constrain the distance to the system using a metallicity-absolute magnitude relation for two stars. They found that the location of Pegasus IV is 293,000 light years away from the Earth.
The authors of the paper said that their discovery shows how incomplete the census is. They think that many of the faint systems may still be undetected.
More information: W. Cerny et al, Pegasus IV: Discovery and Spectroscopic Confirmation of an Ultra-Faint Dwarf Galaxy in the Constellation Pegasus. arXiv:2203.11788v1 [astro-ph.GA], arxiv.org/abs/2203.11788The Science X Network will be launched in 2022.
Citation: Astronomers discover a new ultra-faint dwarf galaxy (2022, March 29) retrieved 29 March 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-03-astronomers-ultra-faint-dwarf-galaxy.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.