Esme Stallard is a reporter for the British Broadcasting Corporation.
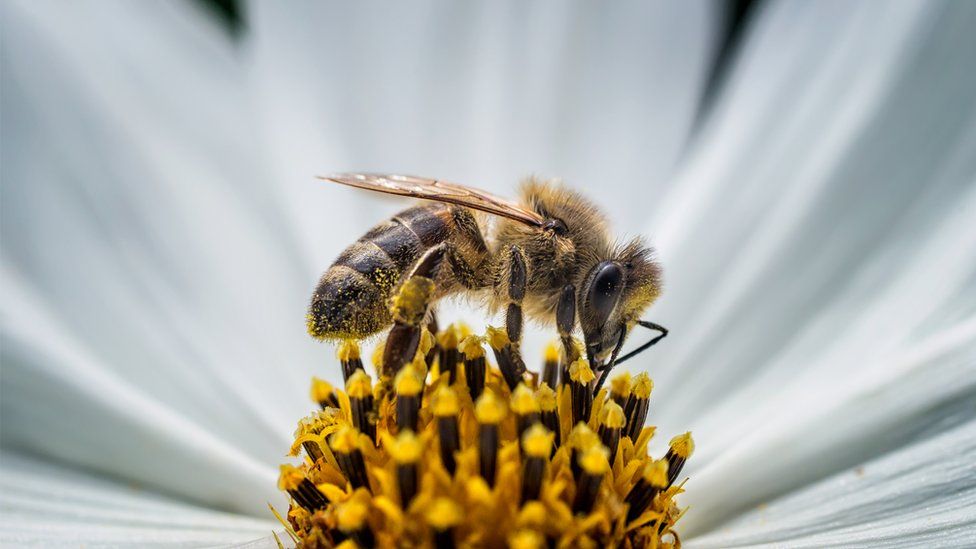 Image source, Getty Images
Image source, Getty ImagesGovernments from around the world will meet later this year to discuss how to stop human activities from causing the extinction of animal and plant species.
They hope to come up with a long-term plan to reverse the threat to life on Earth at the United Nations Biodiversity Conference in China.
The variety of life on Earth is called biodiversity.
Humans rely on animals and plants for food, water, and medicines.
We need a variety of animals and plants to thrive in order to get these benefits. In other words, we need a lot of different things.
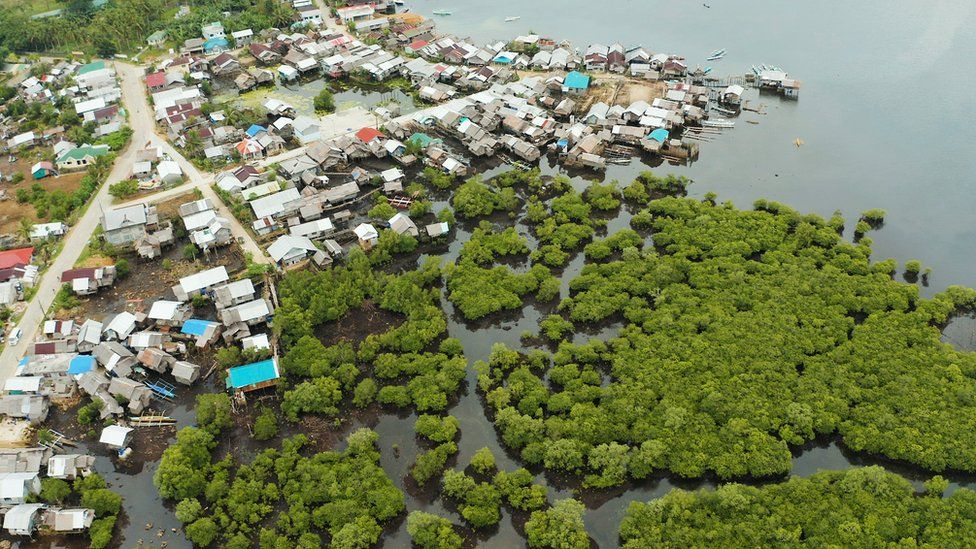 Image source, Getty Images
Image source, Getty ImagesTo grow wheat, we need insects to pollinate the plant and microorganisms to balance the soil.
Plants help improve the environment by cleaning the air and providing protection against climate change.
Mangrove swamps and coral reefs act as a barrier to erosion. Common trees in cities such as the London plane or the tulip tree are good at absorbing carbon dioxide and removing pollutants from the air.
98% of the species that have ever existed are now extinct.
The red list of threatened species has been kept by the International Union for the Preservation of Nature. More than 142,000 species have been assessed and 29% are considered to be in danger of extinction.
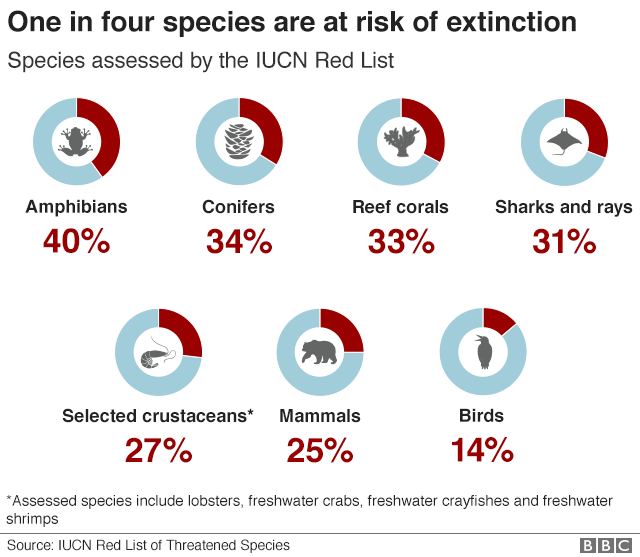
It is hoped that an agreement can be reached to stop the sixth mass extinction event.
The post-2020 Biodiversity Framework is a long-term action plan that governments will try to agree on.
The main aim is to slow down the rate of biodiversity loss by 2030.
According to a United Nations report, harvesting, logging, hunting and fishing had an impact.
The world lost 411 million hectares of tree cover between 2001 and 2020. These forests have taken a long time to develop. The destruction of rich environments can have a serious impact on the environment.
The Natural History Museum in London has found that pollution, rapid industrialisation and over use of water have caused the biggest changes in Australia, Brazil and the UK.
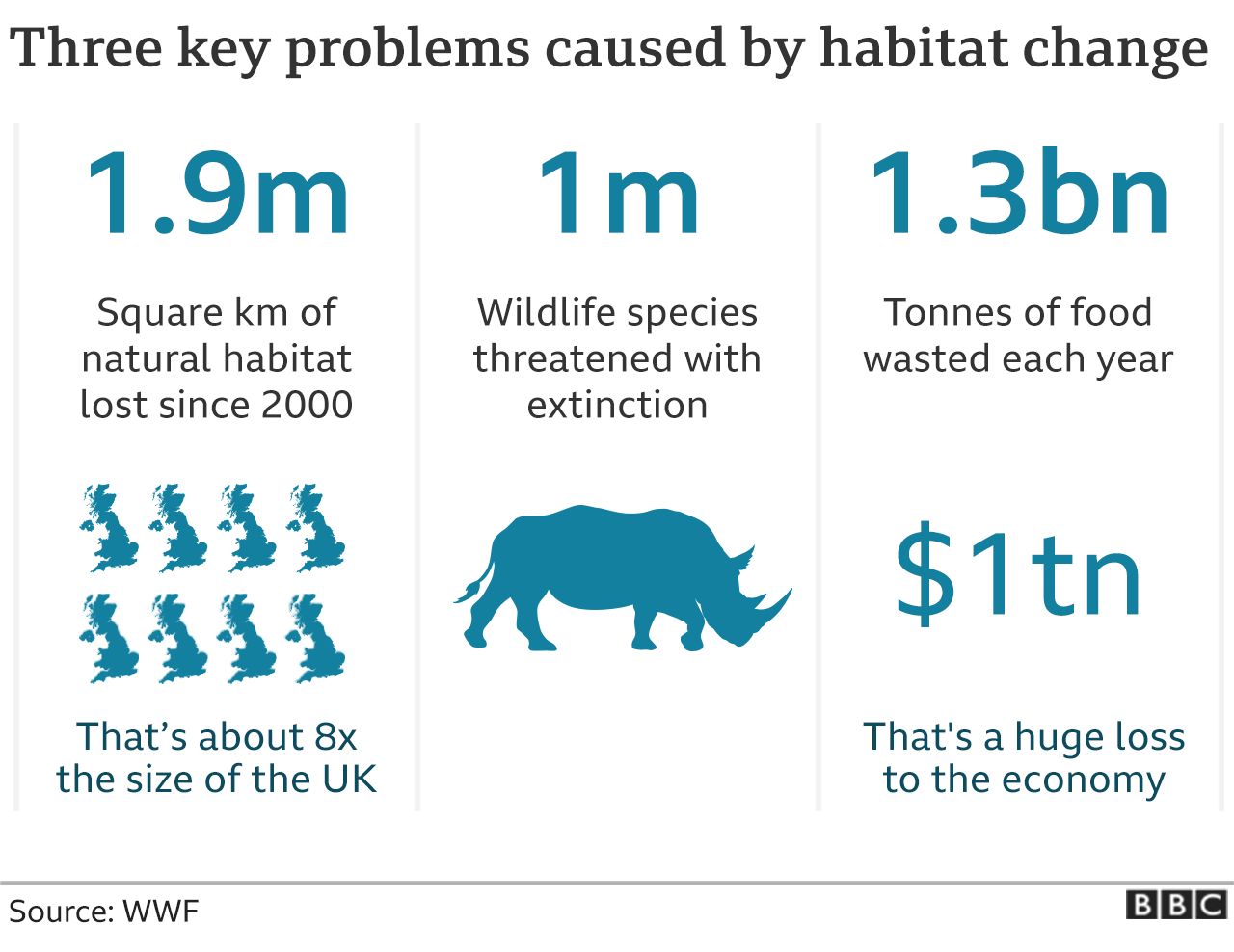
If global warming was limited to 1.5 degrees Centigrade, the extinction of species would be lower.
The framework has four goals.
It wants to use trees and plants to absorb carbon dioxide.
The UN warns that planting trees on landscapes where they have never been before can have a negative impact on the environment.
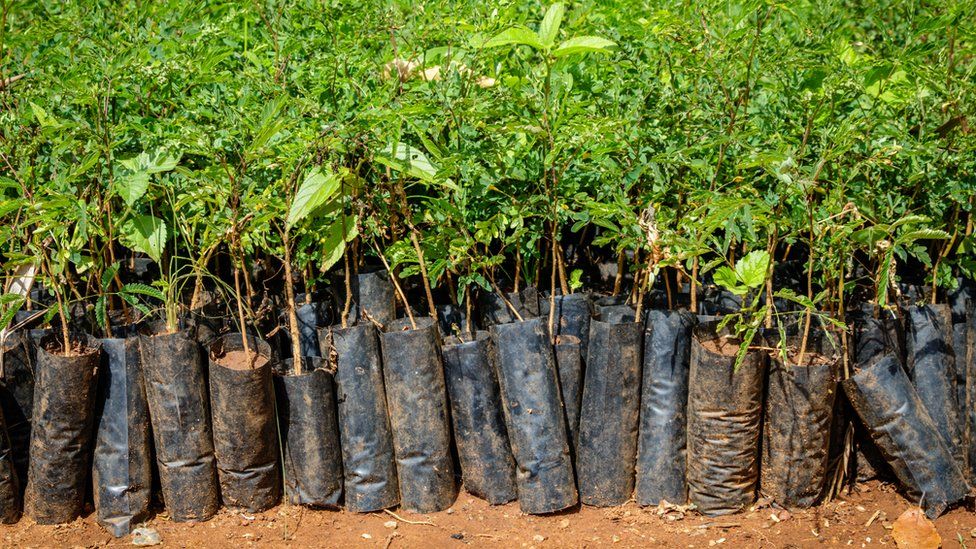 Image source, Getty Images
Image source, Getty ImagesIn order to achieve these targets governments and private organizations are promising to give at least 200 billion dollars per year by the year 2030.