The nervous system is made up of nerves and specialized cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is the electrical wiring of the body.
The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system are part of the nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that connect to one another and to the central nervous system.
The nervous system has two main subdivisions: the voluntary component and the involuntary component. The rate of breathing and blood pressure are regulated by the autonomic nervous system. The brain and spine are connected by nerves that go to the skin and muscles.
According to the University of Michigan Medical School, nerves are cylindrical bundles of fibers that start at the brain and central cord.
Stimulating chemicals known as neurotransmitters are released at junctions called synapses when signals are sent to other cells through thin fibers called axons. The average human brain has over 100 trillion neural connections. A study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that highly creative people have more connections in their brains than less creative people.
Lead study author Roger Beaty said that the three different systems that are located in different parts of the brain are all activated at the same time.
The entire communication process takes a fraction of a second when a sphinx gives a command. According to Discover magazine, signals travel along an alpha motor neuron at the fastest rate in the human body.
According to the American Psychological Association, sensory neurons send feedback to the central nervous system when they respond to physical stimuli.
Motor neurons are located in the central nervous system or peripheral ganglia. According to the Oregon Institute of Health and Science University, glial cells are specialized cells that support, protect or nourish nerve cells.
Over thousands of years of evolution, the brain grew. The genetic code of four-limbed animals can still be found in the brains of humans, according to two papers published in the Cell journal. A very important process in the brain is when genetic information is sent from nerve cells to other nearby nerve cells.
Our thoughts go to the brain when we think of the nervous system. The brain is a hive of activity, with billions of interwoven neurons firing to preserve and recall memories, coordinate thoughts and speech, and plan future actions. The central nervous system is made up of the spine and bone-clad parts.
The majority of our cells are behind protective fluid and bone, where they receive signals from and dictate to organs around the body. The signals from the central nervous system must reach their targets. They need to connect to the nerves in the central nervous system all the way to the body. The peripheral nervous system is made up of two networks of nerves. According to the National Cancer Institute, the central and peripheral are the major divisions of the nervous system.
The peripheral nervous system is responsible for many functions, and there are many sub-divisions that specialize in different tasks. The afferent division carries signals from the peripheral to the central nervous system. The signals from the central nervous system to the peripheral organs and muscles are transmitted by the motor. There are two forms of motor functions. According to the medical library, somatic functions are the easiest concept to grasp, as they dictate all our voluntary actions, such as jumping on the bed or picking up a cup.
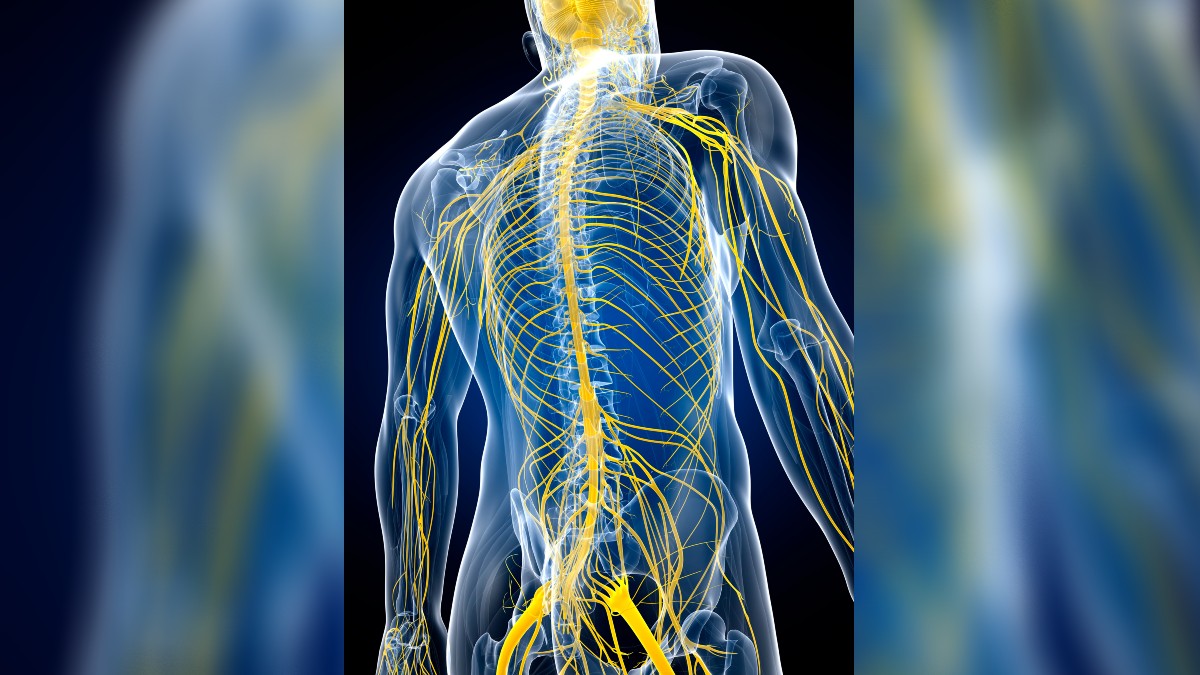
Some motor functions are not voluntary. Our bodies have pre-programmed responses that help us cope with danger. When you accidentally touch a hot stove, step on a sharp object, or something flies toward your eye, you will notice that your body reacts before you are aware of it. Your eyelid slams shut as you hop onto the other foot. This is all the work of reflexes that do not require input from the brain. Pulling your hand away from danger is known as a flexor or withdrawal reflex, whereas stepping on a sharp object is known as a crossed-extensor. The latter reflex causes multiple motor functions, as one leg pulls the other leg down, preventing us from falling over.
The peripheral nervous system helps keep us safe from danger, but it's not the only automatic function it performs. Actions that are not voluntary, or somatic, are considered to be autonomic, which means they operate independently of conscious thought. The heart beat, the food churned out of the bicyle, and the respiration are some of the processes. Our brain can assume control of a few of these processes, but our autonomic functions will continue to function even if we are knocked unconscious or fall asleep.
The processes that we can't control are not unchanging. The organs are regulated by a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. These systems help to ensure our body is always ready to respond to the challenge by increasing or decreasing activity of our internal organs.
The founder and CEO of a medical device company said that the most common difficulty that people have is pain.
Parkinson's disease is a disease.
The brain's central nervous system is responsible for controlling movement. Dopamine is important in coordinating many functions, including executive functions and motor control. The cause is not yet clear, but sometimes the basal ganglia can become impaired and die. Parkinson's disease is caused by the loss of dopamine in the brain, which affects key functions such as walking, talking, and memory recall. These effects are compounded by the loss of the sympathetic nervous system's ability to regulate heart rate and blood pressure. According to the National Institute of Aging, medicines that increase the amount of dopamine in the brain can help combat symptoms of the disease.
Bell's palsy.
Major nerves travel from the central nervous system to various organs and tissues. The facial nerve is known as the cranial nerve and it controls many of the muscles on our face. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, Bell palsy can occur when the nerve is damaged or disrupted. This affects only one side of the face, causing symptoms such as droop of the mouth on one side and a loss of eyelid, giving the affected side a slack appearance. Some or total recovery of the affected areas is possible with six months. Scientists believe that Bell's palsy and the swelling of the cranial nerve are caused by a recurring viral infection of the nervous system.
Multiplesclerosis is a disease.
The agents of signalling in our bodies are Neurons. The axons are covered in a sheaf of myelin. The function of protecting and facilitating nerve conductivity is achieved by myelin sheaves, which are produced in the central nervous system. Multiplesclerosis is caused by an abnormal immune response within the central nervous system that strips away the protective myelin and causes lots of nerve scarring. Research is underway to treat the disease.
There is peripheral neuropathy.
There are a number of diseases that impact the peripheral nervous system instead of the central nervous system. The diseases are referred to as peripheral neuropathies. Loss of sensation and regulatory control of the limbs are caused by neuropathies in the peripheral nervous system. According to the University of Michigan Health, these include a loss of coordination and feeling in fingers and toes. Diabetes is one of the primary causes of peripheral neuropathy, despite the fact that the causes are not fully understood.
There are a number of tests and procedures that can be used to diagnose conditions in the nervous system. A specialized X-ray called a fluoroscopy can be used to look at the body in motion, such as blood flowing through arteries.
Other standard neurological exams include anEEG, which records the brain's electrical activity. Positron emission tomography is a procedure that can be used to detect tumors or diseases of the brain.
A small amount of cerebral spinal fluid that is tested for infections or other problems can be drained with a spinal tap.
The branch of medicine that studies and treats the nervous system is called neurology, and doctors who practice in this field are called neurologists. Once they have completed medical training, neurologists are certified by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Periodontalists are physicians who work to rehabilitate patients who have experienced disease or injury to their nervous systems that impact their ability to function.
Neurological surgeons are certified by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
The Human Nervous System by Juergen K. Mai and The Big Book of the Human Body are both good sources of information about the nervous system.