There are various concepts of how computing using the properties of the quantum world can be implemented, as the development of quantum computers is being pursued worldwide. Many of these have advanced into areas that are not possible on classical computers. The technologies have not yet reached the point where they can be used to solve bigger problems. Rick van Bijnen of the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences says that researchers are looking for applications that can be implemented on existing platforms. A team around Van Bijnen and the Lechner research group is working on a method to solve problems using neutral atoms.
There is a software solution.
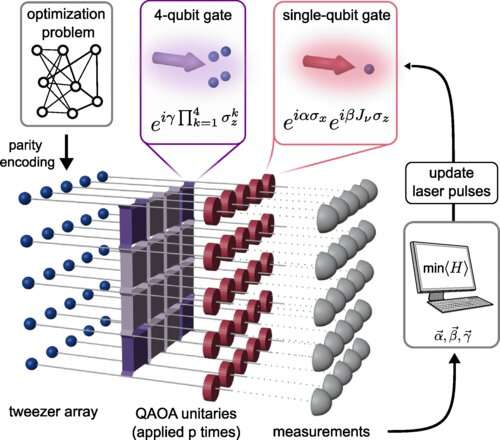
To develop scientifically and industrially relevant applications for existing quantum hardware in the near future, researchers are looking for special algorithms that match the strengths of a quantum platform. Physicists envision neutral atoms being trapped and arranged in optical tweezers. They can be programmed by the interaction of highly excited states. Wolfgang Lechner, Philipp Hauke, and Peter Zoller developed a hardware design called the parity architecture, which they used to avoid the limitations of previous approaches.
Only problem- dependent single-qubit operations and problem-independent four-qubit operations are required. The biggest challenge for the researchers was to find a simple and direct implementation of these four-qubit operations. The special quantum gate was designed for this purpose.
Scalable.
The performance of existing quantum hardware can be investigated for problem-sizes that are impossible to simulation on classical supercomputers with the proposed concept. The hardware platform and the software solution can be extended to a large extent without modifications, which is an important advantage of the new method.
The Innsbruck team has presented a new concept.
More information: Clemens Dlaska et al, Quantum Optimization via Four-Body Rydberg Gates, Physical Review Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.120503 Journal information: Physical Review Letters Citation: Researchers develop quantum gate enabling investigation of optimization problems (2022, March 25) retrieved 25 March 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-03-quantum-gate-enabling-optimization-problems.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.