
The age of the impact crater is known.
According to a study published in the journal Science Advances, the Hiawatha crater was formed 58 million years ago. The new finding means that the impact occurred much earlier, at a time when the island was truly green and full of life.
According to study co-author Michael Storey, a researcher at the Natural History Museum of Denmark who specializes in dating geological materials, greenland was covered with a rainforest when the asteroid hit.
The asteroid hit the ground at a distance of about 1.5 km. There is no evidence that it had an effect on the global climate.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
The age of a crater.
The crater was discovered using ice-penetrating radar instruments. There was no way to know the age of the impact because of the huge slab of ice covering the crater.
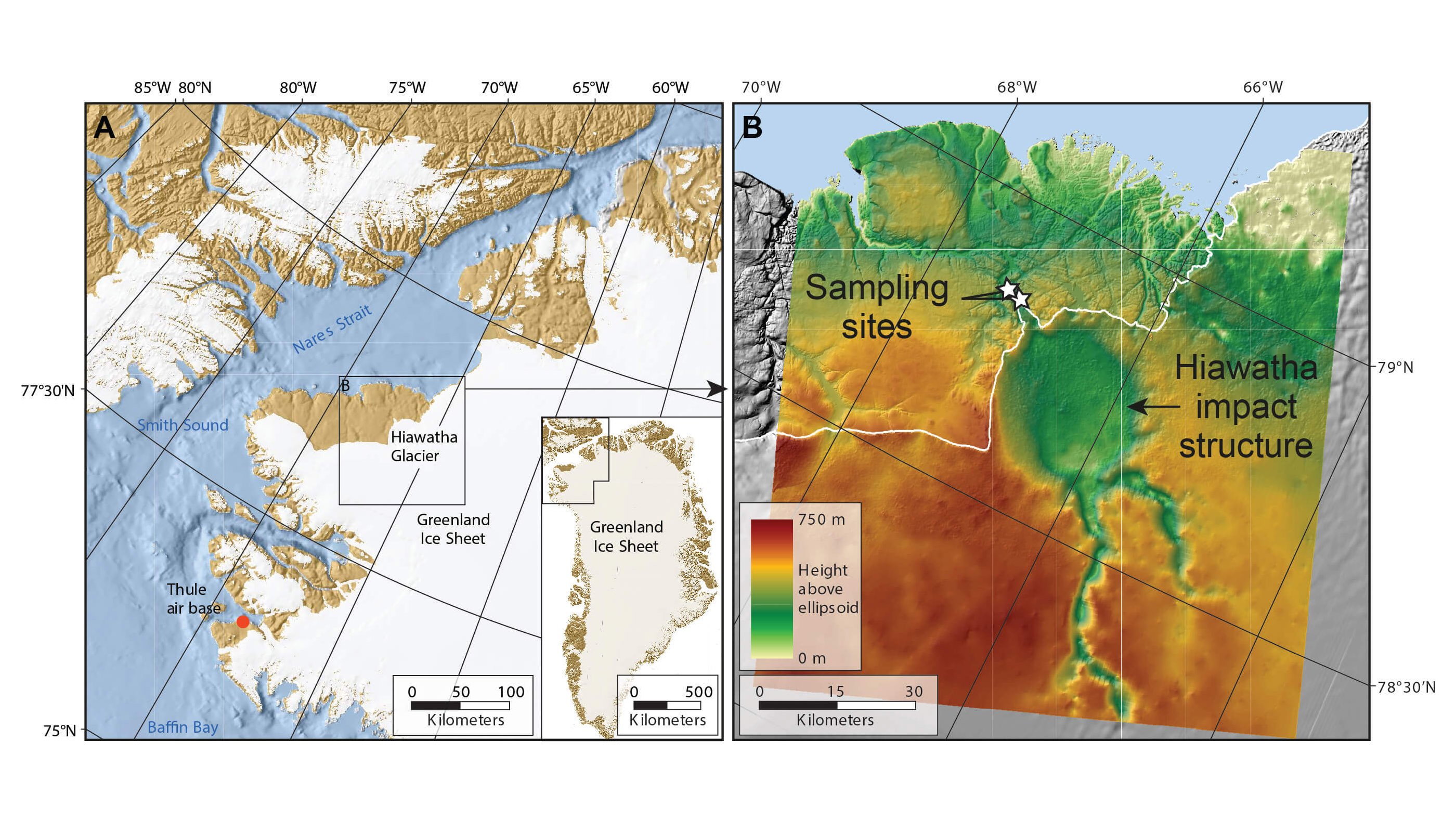
The Hiawatha impact crater is related in photos.
The crater is at the edge of the ice sheet. There is a stream from under the ice that carries sediments just 3 miles from the crater rim. Researchers found that many of the sand grains and larger pebbles had signs of melting and shock after examining them.

Storey and his colleagues used a method called argon-argon dating to determine the ages of 50 grains of sand. The method relies on the decay of the element potassium 40, which has a half-life of 1.251 billion years. A gas trapped within the rock is called argon 40. Researchers can use the ratio between the two isotopes to figure out how long the decay has been. This method is useful for measuring very old ages because of the slow rate of decay. The heat of an impact resets the molecular clock to zero, so he and his team could use the numbers to determine when the sand grains were hit.
The Swedish Museum of Natural History's research fellow,Gavin Kenny, used a similar method to measure the decay of the radioactive element uranium to lead in minerals called zircons.
The grains and pebbles had been hit by a large impact about 58 million years ago.
The Younger Dryas cooling event, a global cold shift that occurred about 13,000 years ago, had nothing to do with this age. There is a theory that the cooling event was kicked off by an asteroid impact, but no crater of the right age has ever been found.
There is no indication that the impact of the Hiawatha impact caused any global climate hiccup, as there is a very detailed record of the climate dating back 58 million years. The impact would have had a devastating effect on the local flora and fauna. Massive forest fires could have been sparked by an earthquake of magnitude 8 or 9 nearby. Evidence of old charcoal deposits has been found beneath the ice sheets.
I think that Hiawatha is somewhere in the middle, on a sliding scale for asteroid impacts. He said that a space rock the size of the one that made the crater is expected to hit Earth once every million to 2 million years, with a 75% chance that it will land in the ocean.
Now that the age of the crater has been known, it will be possible to look for evidence of the consequences nearby.
It was originally published on Live Science.