The cooling off season is between the blazing summer and chilly winter. The night time arrives earlier and the temperatures start to drop. Animals begin to prepare for the lack of food that comes during the winter, gathering supplies or traveling to warmer climates.
Earth's tilt on its axis and the planet's position around the sun cause the cycle of seasons. The hemisphere experiences summer when the axis points toward the sun. The hemisphere is tilted away from the sun. After Earth travels a quarter of the way around the sun, the axis is parallel to the star.
The sun travels along an imaginary line called the ecliptic, which marks the plane in which the planets are located. The celestial equator is a projection of the equator into space. During the summer season in the Northern Hemisphere, the sun appears to move north of the equator. It appears to be south of the equator during the other half of the year.
When the sun appears to arrive at the intersection of the ecliptic and the equator is when autumn begins. The sun is overhead at noon at the equator.
The length of daylight and nighttime are roughly the same, according to the National Maritime Museum. The Latin words aequus and nox are what inspired the wordequinox.
Day and night are not the same. We can see the sun for a few minutes before its disk rises and for a few minutes after it sets because of the way the sun's light reflects in Earth's atmosphere. Daylight lasts roughly six or seven minutes longer than it seems.
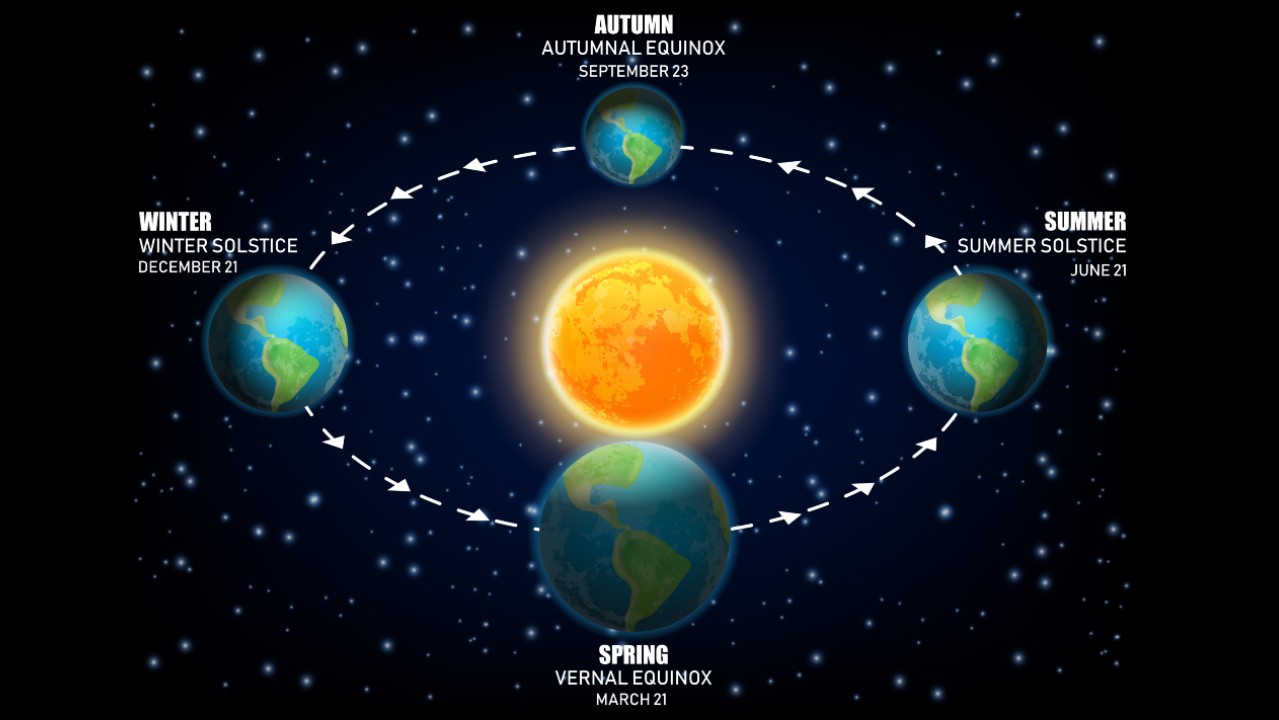
The autumnal equinox is the beginning of autumn and the beginning of winter. It varies from year to year in the Northern Hemisphere. The season in the Southern Hemisphere runs from March 20 to June 21.
The season is defined by the three months in which the weather changes. This is September, October, and November in the Northern Hemisphere. The meteorological autumn in the Southern Hemisphere is in March, April, and May.
The air gets a bit cooler in the Autumn. The location of the area on Earth affects how much a change is felt. The regions near the equator experience constant temperatures throughout the year, while those farther north or south experience more variation. The equator gets a consistent amount of sun. The southern and northern regions get less sun due to the sun's shape.
The average temperature for the continental United States in autumn is 55.9 degrees. The 20th-century average increase is 2.1 percent.

In the United States, autumn is also known as fall. The third season of the year is a relatively new concept. Many cultures only recognize two seasons, winter and summer.
The Latin word for harvest first appeared in English in the 14th century and gained on it in the 17th century.
In response to chilly temperatures and the changes in daylight, leaves stop producing green-tinted chlorophyll, which allows them to capture sunlight and make energy. Early frosts are sensitive to the cold and will turn off production more quickly.
The leaves of orange carrots were washed out green. According to the State University of New York College of Environment, the red color in some leaves is due to anthocyanins, which are produced in the fall. They give color to strawberries, red apples, and plums.
Red leaves are a sign of distress. If you see leaves of a tree turning red early in the month of August, it's most likely due to a disease or a reckless driver.
Autumn is the end of the growing season. The harvest season is a time of celebration for many farming cultures when they gather in their crops.
Autumn, or fall, is rich with different festivals which celebrate the return of light, harvest, and rebirth through death, according to an anthropologist at a college in London. The harvest festival in the United Kingdom is a time when people give thanks for the fruits of the land and collect food to donate to those in need.
Harvest celebrations tend to combine giving thanks with prayers for future abundance, to propitiate the god and ensure successful crops. Thanksgiving is celebrated in the United States. It's a historical commemoration, but it has a spiritual aspect to it and gives praise for what has been bestowed upon us.
These celebrations are examples of fall's ties with giving thanks and rebirth.
The State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry has a page on the science of autumn.