There are thread-like structures of deoxyribonucleic acid DNA that carry hereditary information for everything from height to eye color. They are found in the nucleus of a cell and help ensure that the DNA is divided evenly during cell division. There is a single molecule of DNA in chromosomes. We are who we are because of chromosomes.
The nucleus of each cell has a scroll tightly rolled up in it. Your genes are divided into 46 chapters called chromosomes from each parent. The 23 chromosomes from each parent form the 23 chromosomes in each cell.
Without chromosomes, DNA wouldn't fit inside cells. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, histones are coiled around DNA. If you put all the DNA from a single human cell end-to-end, it would stretch 6 feet.
Some chromosomes are created differently. Some have a lot of genetic material while others have less. According to Medline Plus, chromosome 1 contains eight percent of your total DNA. A collection of chromosomes is called a karyotype. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, the Greek word for color and body is soma, which means strongly stained by dyes.
The number of chromosomes an organisms possesses is not related to the complexity of the organisms or the amount of DNA it possesses. A potato has 48 chromosomes while most humans have 46. A fruit fly has eight chromosomes, a rice plant has 24 and a dog has 78.
Some organisms have a lot of chromosomes. According to the Guinness World Records, there is a world record for the highest number of chromosomes.
The number of chromosomes can affect growth and development in humans. Aneuploidy is when an organisms has more than one chromosomes. Down's Syndrome is an example of a condition caused by trisomy. People with Down's Syndrome have three copies of the same chromosome.
The reproductive cells are the only cells that do not have a pair of chromosomes. When egg and sperm cells unite, they become a single cell with a pair of chromosomes.
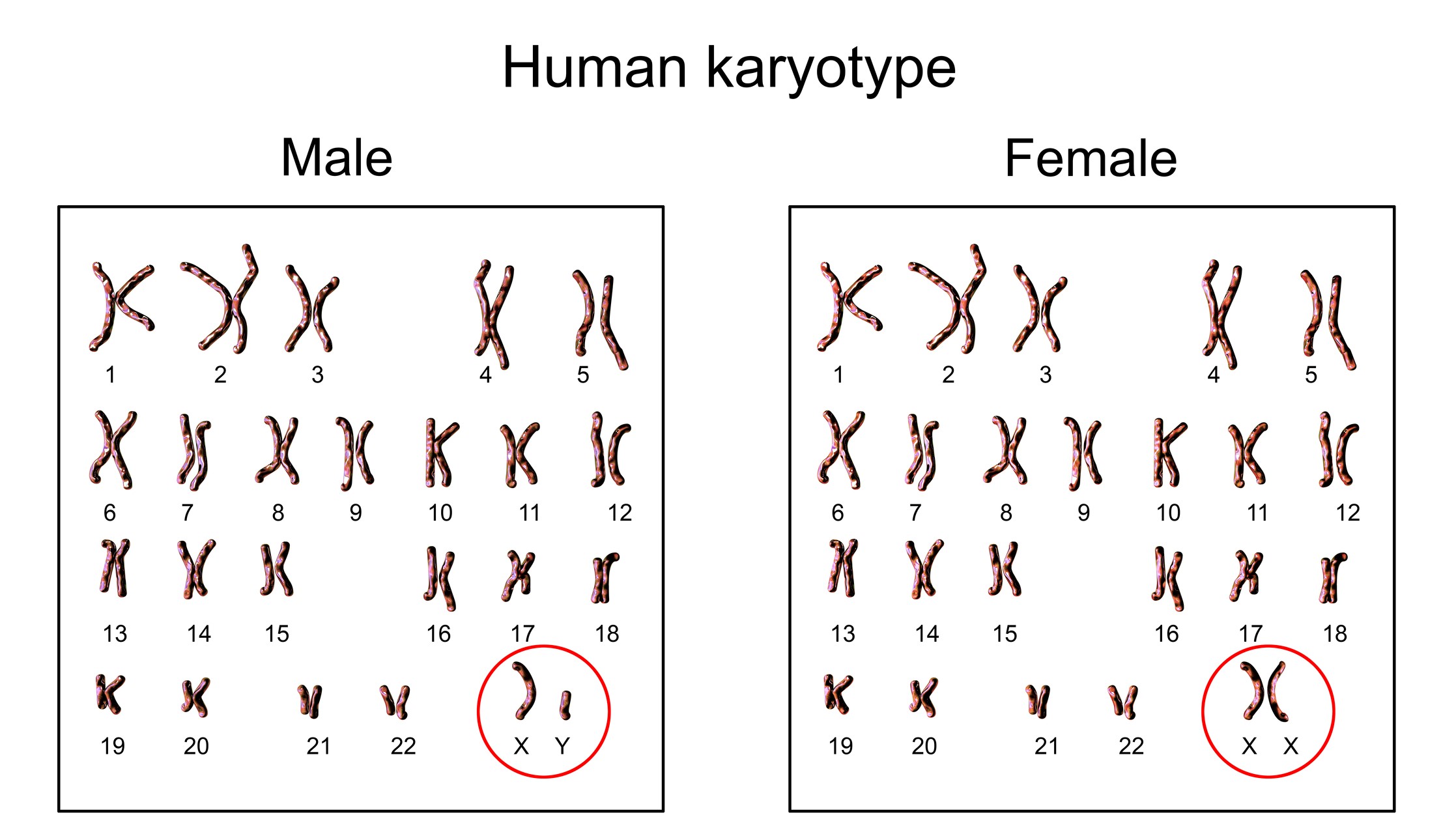
Sex chromosomes are referred to as X and Y and determine a person's sex. Human females and males have two X chromosomes. Most mammals as well as some reptiles and plants have the XY sex-determination system.
When a spermfertilizes an egg, it is determined whether a person has XX or XY chromosomes. The cells in the egg and sperm are called gametes or sex cells because they only have one chromosomes. Gametes are produced by meiosis cell division, in which the divided cells have half the number of chromosomes as their progenitor cells. The parent cells of humans have two chromosomes, known as diploid and gametes.
The gametes in the mother's eggs have X chromosomes. The father has X and Y chromosomes in his sperm. The sex of the baby is determined by sperm. If the sperm carries an X chromosomes, it will combine with the egg's X chromosomes to form a female embryo. If the sperm carries a Y chromosomes, it will result in a male.
Gametes from the sperm are combined with gametes from the egg to form a new cell. There are two sets of 23 chromosomes in the zygote.
There are some differences in the number of sex chromosomes. Recent research has shown that a person can have a variety of sex chromosomes and genes. According to a study in the journal Psychological Medicine, a certain X chromosome called Xq28 and a gene on the same part of the chromosomes seem to be found in men who are gay.
Sex and gender have different definitions and many cultures include more labels than simply "male" and "female" to identify others.
The X and Y chromosomes have different structures, which makes them different from the other parts of the body.
The Y and X chromosomes have a lot of genes. The X genes are dominant because they have no counterpart in the Y genes. The X will be expressed in males even if there is a female in it. These genes are referred to as X-linked genes. Y-linked genes are those found on the Y chromosomes and expressed in males. Sex-linked genes can be found on either sex chromosomes.
Most of the X-linked genes are not for female characteristics. Many are linked to disorders such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy and fragile-X syndrome. Red-green color blindness is the most common genetic disorder and is found most often in males. Male pattern baldness is caused by the non-sex feature X-linked genes.
The Y chromosome is one-third the size of the X chromosome, according to the National Human Genome Research Institute. The Y chromosome contains a male-determining gene. If there is a change in this gene in the embryo, it will develop female genitalia despite having XY chromosomes.
There are a variety of gender-specific conditions that are rarely lethal. The abnormality can be caused by deletions or duplicated sex chromosomes.
Turner syndrome is caused by missing or partially missing an X chromosomes. Turner Syndrome can cause a variety of medical and developmental problems, including short stature, failure in the development of ovaries and heart defects.
One in 1000 females are affected by Trisomy X syndrome, also known as Triple X syndrome, which is caused by three X chromosomes instead of two. Most people with Trisomy X don't have any symptoms or have mild symptoms. More significant symptoms may occur which can delay the development of speech and language skills.
According to Medicine Plus, one of the most common sex chromosome disorders is Klinefelter syndrome, which affects one in 650 males and is caused by an extra X chromosome. In some cases, the symptoms can be so mild that many go undetected until they reach puberty, and some researchers believe up to 75% of affected males may never know they have the condition. Small testes that produce lower amounts of testosterone can lead to delayed puberty, breast development, infertility and decreased muscle mass, all of which can be symptoms of Klinefelter syndrome.
You can find more information about chromosomes from this material. You can learn more about gender identity with the organization. The Intersex Society of North America has an article about whether having a Y chromosome makes you a man. Discover more about modes of inheritance and genetic basics in animals with this article.