
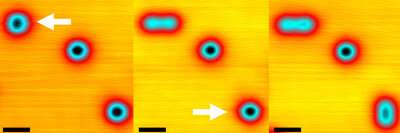
RIKEN chemists have determined how a molecule of oxygen on a silver surface separates into two oxygen atoms. Scientists can use this knowledge to improve their reactions.
Industrial processes use silver surfaces to break down oxygen molecule into their atoms. The exact reaction pathway remained unknown while this reaction was investigated.
It's hard to believe we don't know how oxygen molecule disassociates on a silver surface. The mechanism of the reaction seems simple and it has been used in industry.
The team led by Yousoo Kim used a scanning tunneling microscope to study the dissociation mechanism in detail.
Oxygen can be absorbed onto a silver surface. The researchers used the STM to investigate reactivity. They used the STM tip to inject electrons into the molecule, or to inject holes with negative voltages. The processes broke the oxygen bond and resulted in two separate oxygen atoms on the surface.
Understanding how the dissociation yield depends on the energy of electrons/holes helps illuminate the channels at work. The molecules were excited to higher-order excited states before they were able to break apart.
Lee explains that the reaction pathway is an excitation from the ground state to higher excitations of the vibrational states. We were able to identify the overtones involved in the reaction after comparing the experimental data with calculations.
The next step is to investigate the molecule slightly.
More information: Minhui Lee et al, Dissociation Mechanism of a Single O2 Molecule Chemisorbed on Ag(110), The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (2021). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02456 Journal information: Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters Citation: Dissociation mechanism of oxygen molecules on a silver surface unveiled (2022, January 27) retrieved 27 January 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-01-dissociation-mechanism-oxygen-molecules-silver.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.