Click here to watch more Space.com videos.
The European Southern Observatory took a photo of the Flame Nebula in the constellation of Orion.
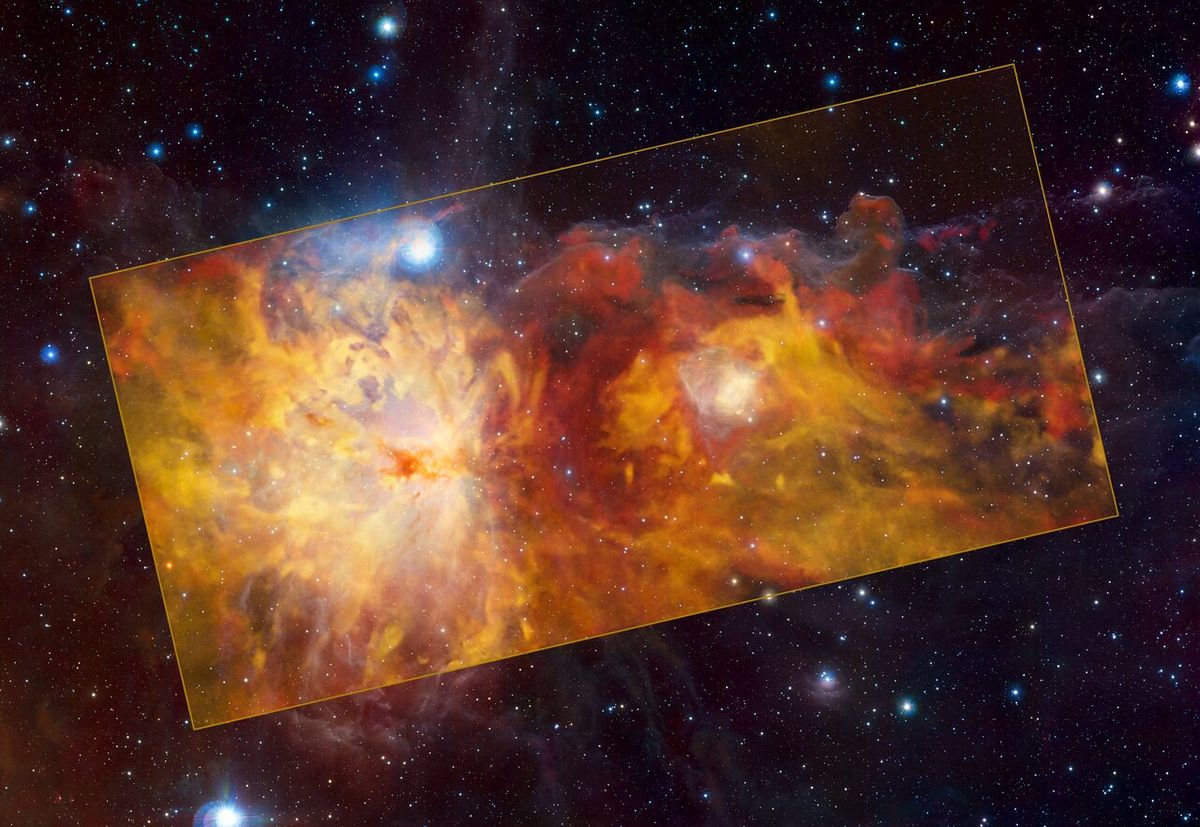
In the new telescope view, the "Orion's fireplace" is a colorful cloud of dust and gas and a nursery for new star formation. According to the statement from the ESO, the cluster of young stars emit high-energy radiation that causes the surrounding gases to glow brightly.
"Wherever there is a new telescope or instrument around, you should always look for something new and interesting to discover!" Thomas Stanke is a former astronomer and lead author of a new study on the region.
There are pictures of nebulas in deep space.
The large Cosmic feature on the left and its surroundings are captured in a new image from the APEX radio telescope. The image is from the ESO/Th. Stanke and J.Emerson are both employed by Visa. The Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit is known as Acknowledgment.
One of the most famous regions in the sky is the Flame Nebula, which is located in the constellation of the same name. The constellation is located between 1,300 and 1,600 light-years away from Earth's neighborhood and is home to the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which is where new stars and planets are formed.
The clouds are very cold, with temperatures just a few degrees above absolute zero, which is equivalent to about minus 459 degrees Fahrenheit. The new image was taken using the SuperCam instrument on the APEX radio telescope, which is located at the Llano de Chajnantor Observatory in the Atacama desert in northern Chile.
The large formation on the left is the Flame Nebula. The image features reflection nebulas, which reflect the light of nearby stars, and the Horsehead Nebula, which is located in the top right. A new, small, almost circular Cosmic cloud has been named the Cow Nebula.
The radio waves emitted by carbon monoxide in the clouds were observed by the instrument as part of the large CO Heterodyne Orion Legacy Survey.
The different colors indicate the speed of the gas. The red clouds in the background are moving faster than the yellow ones in the foreground, as the Flame Nebula and its surroundings are moving away from us.
A paper about the new research was accepted for publication in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Follow SamAshley13. Follow us on social media.
