The Conversation published this article as part of the Curious Kids series. Space.com's expert voices: op-ed and insight was contributed by the publication.
Ian Whittaker is a senior lecturer in physics.
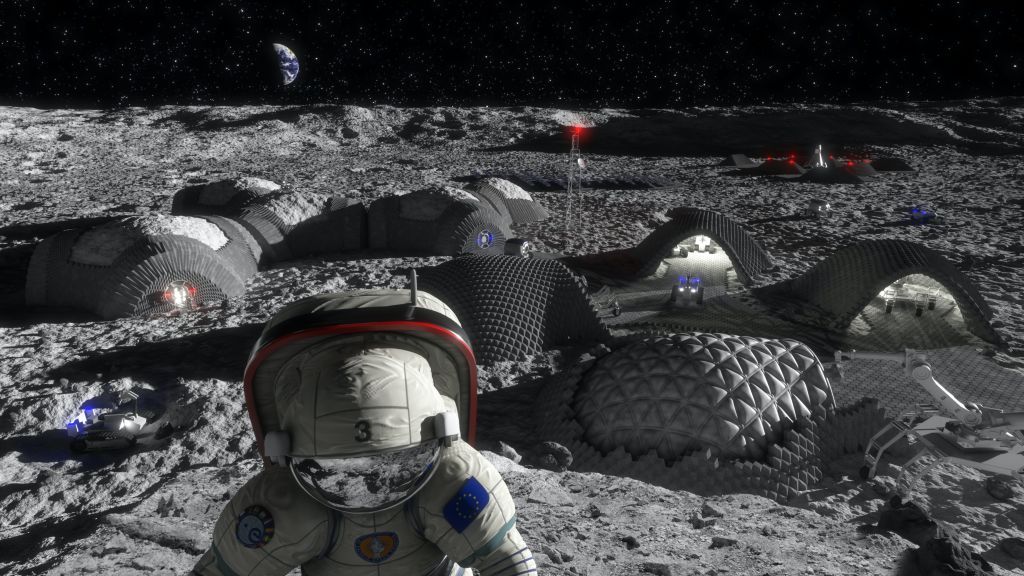
A space station on the moon could be useful. Future space missions would have a stopping point between leaving the Earth and reaching further into the solar system.
We don't send people to the moon very often, which is one reason we haven't built a space station. We've only put astronauts on the moon six times. Between 1969 and 1972 the moon landings were part of a series of space missions called the Apollo missions.
The type of rocket used to get the astronauts to the moon is no longer produced. We don't have a rocket powerful enough to get people to the moon at the moment.
The Gateway moon-orbiting space station is explained in pictures.
We are building rockets again. The weight of astronauts can be taken to the moon by newer and bigger rockets being created by the company. New missions are being planned by NASA to take astronauts to the moon.
It is very difficult to build a space station on the moon, which is a big difference from a short trip. One way to build it would be to take the pieces from Earth and put them on the moon. The International Space Station was built like this: pieces were taken into space and put together by astronauts on the space shuttle.
The International Space Station is only 250 miles from the surface of Earth. The moon is over three times larger than the Earth. Each trip to the moon would take about three days and would require a lot of fuel.
It would be better to build as much of the base as possible from the moon's materials.
You would make concrete from gravel, sand, cement and water. We don't have those things on the moon, but we do have lunar dust and sulphur. They can be melted and mixed together. The solid material produced by this mixture is stronger than many of the materials we use on Earth.
Power and food.
We need to think about what the astronauts would need. The most important things are a food supply and electricity to power equipment.
Scientists are working on growing food in space. On the International Space Station, astronauts are growing vegetables using soil pillows. Hydroponics means that the plants grow in water, not soil.
It would be more difficult to get power on the moon. The best way to use the sun's rays is to use solar energy. The moon rotates every 28 days. A space station on the moon would be in the sun for 14 days and then darkness for 14 days, and without light, solar-powered equipment wouldn't work without a big improvement in battery storage.
The space station can be built at either the north or south pole of the moon, and the solar panels can be raised above the surface. The panels would get constant sunlight because they can rotation and not be blocked by the planet.
We might not need a base on the moon at all. NASA is planning to build a satellite that will go to the moon. It would not be as difficult to launch a rocket from the moon than it would be from a satellite. It would be better than a base on the moon for missions to go further into the solar system.
The Conversation's article is a Creative Commons licensed one. The original article can be found here.
Become a part of the discussion and follow the issues and debates of Expert Voices on social media. The views expressed are those of the author and do not represent the views of the publisher.
