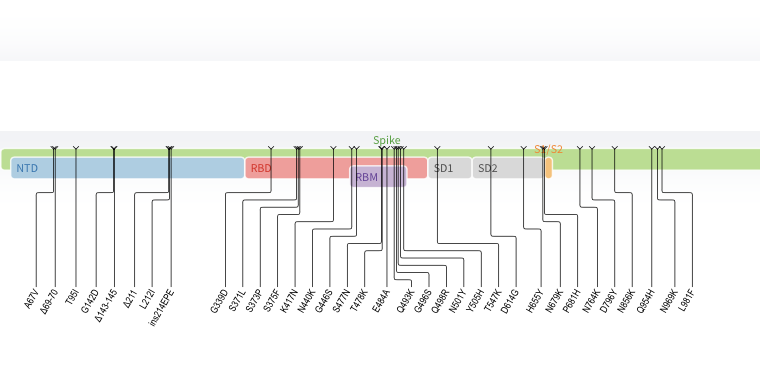
That's a lot of changes.
The World Health Organization attached the Greek letter omicron to the designation of the new version of the disease. The Omicron variant has a lot of changes in the spikeProtein of the virus. While Omicron appears to have started spreading in Africa, it has already appeared in European countries like Belgium and the UK, which are working to limit its spread through contact tracing.
The data on the variant is very limited and we don't know how much protection is offered by vaccines or past infections. The new designation will likely help focus resources on studying Omicron's behavior.
There are many changes.
The Delta variant's version of spike has nine changes compared to the Omicron variant's 30. A number of these have been seen in other strains, where they have a variety of effects. The increase infectiveness of the virus is due to the fact that a number of the changes increase the affinity between the spike protein and the cell wall that it targets.
The spike can change in areas of theProtein that are frequently targeted by antibodies that neutralizing the virus. Changes here can mean that the immune response generated by vaccines or earlier versions of the virus is less able to target Omicron.
Advertisement
Understanding how these and the previously un described Omicron mutations change its behavior will depend on getting real-world data on its spread. We don't have much of that right now.
It's relatively easy to detect Omicron. The WHO says that some of the large collection of mutations in the gene that encodes the spikeProtein interfere with the test's recognition. The tests continue to recognize the presence of the virus by targeting other areas of the genome. The presence of Omicron can be confirmed by the presence of a spike-negative but virus-positive test.
Omicron is spreading quickly in a number of countries in southern Africa, although the total cases in Botswana and South Africa are relatively low, so the significance of this spread is unclear. Vaccination rates in these countries are low, making it difficult to determine how much of a risk Omicron poses to those who have been immunized.
There are some constants.
Travelers who spent time in this region have been the ones who have identified the cases outside of southern Africa. Public health authorities in those countries are trying to limit the spread of the variant's outside of the people who are already sick.
Public health measures such as testing and contact tracing can be used to limit the impact of Omicron while we learn more about it. The CDC provides a reminder of the rest, including social distance, mask when indoors, and get a vaccine if you are eligible. It is certain that the effectiveness of the vaccines against Omicron is greater than zero.
The image is by Aurich Lawson.
