Tomasz Nowakowski is a member of the physics.org community.
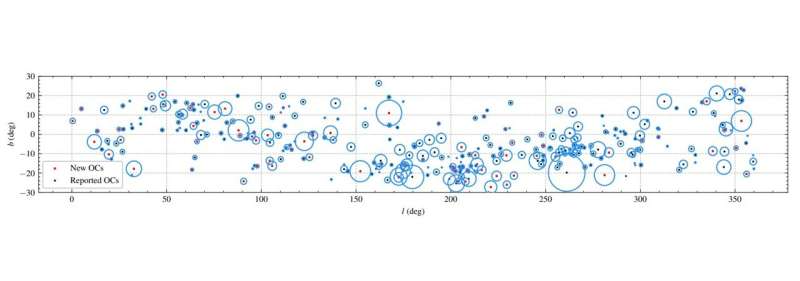
Astronomers from the SAO in China have found 101 new open clusters in the Milky Way. A paper on the discovery was published in December.
A group of stars are bound to each other by a giant cloud of atoms. More than a thousand of them have been found in the Milky Way, and scientists are still looking for more. Studying them in detail could help us understand the formation and evolution of our universe.
The finding of 101 new OCs in the solar neighborhood was reported by a team of astronomer. The data from DR3 was used to create the discovery.
We did a blind search for OCs within 500 pc of the solar neighborhood by using different slicing box sizes in different distance grids. The researchers said that the classification based on manual inspection combines some duplicate or partially reported clusters.
Songmei's team was able to identify more than 300 open clusters. The discovery increased the number of known nearby OCs by 45%. The parameters of the known 223 clusters were updated by comparing the spatial distribution with the previous catalog.
There are 19 OC pairs with a common origin that are less than 30 million years old. There are three groups with triple OCs and age differences of less than 10 million years. The triplets formed from the same cloud, according to the astronomer.
Many OCs with large spatial scales were discovered for the first time by the researchers. The technique they use is very effective for searching nearby OCs. Many open clusters have an outer structure.
The authors of the paper said that more detailed analyses are needed in order to shed more light on the properties of the OCs. The evolution of these clusters will be determined by the amount of data for the member stars.
There are 101 new open clusters within 500 percent of each other. There is a book titled "arxiv.2212.11034."
Journal information: arXiv
There is a science network.