Logistical issues will have to be solved for humans to venture out among the stars.
The travel time is not the most important thing. It would take a long time to travel to another star because of the size of space and limited technology.
The closest star to the Sun would take 73,000 years to be reached by the Voyager 1 probe.
Even so, the journey would still take thousands of years with our current technology, even if the newer ships were expected to travel quicker.
Generation ships would allow multiple generations of space travelers to live and die at the same time. Artificial hibernation is possible if it could be implemented.
This is what scientists from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences are investigating in monkeys, because of a chemical reaction.
The researchers wrote in their paper that they have shown that a subpopulation of POA neurons can be activated by a Chemgenetic strategy.
The central regulation of body temperature in primates is demonstrated by our findings.
Hibernation and its less comatose state, torpor, allow animals to survive in adverse conditions.
metabolism slows to a crawl and the body temperature lowers, keeping the body in a bare-bones maintenance mode.
This can be found in many animals but very few primate. Wang Hong and Dai Ji of SIAT wanted to see if they could induce a state of hypometabolism, or even hibernation, in monkeys by manipulating the preoptic neurons.
The research was done on three young males. In both anesthetized and non-anesthetized states, the researchers applied drugs that activated specific modifiedreceptors in the brain.
The scientists studied the results using various methods.
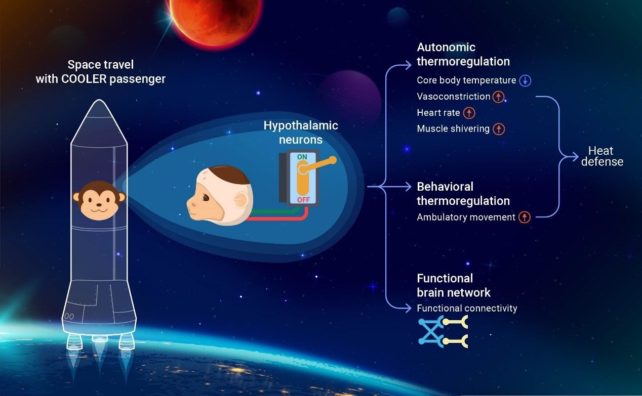
In order to investigate the brain-wide network as a consequence of preoptic area activation, we performed fMRI scans.
The first fMRI study to investigate the brain-wide functional connections is taking place.
The researchers found that a synthetic drug called Clozapine N-oxide reliably induce hypothermia in the anesthetized and awake macaques.
In anesthetized monkeys, the drop in core body temperature was prevented by the CNO-Induced Hypothermia. The researchers say that this shows the critical role POA neurons play.
The researchers compared the behavioral changes in the awake monkeys to those of the mice that had been hypoxic. The heart rate of mice is usually lowered in an attempt to conserve heat.
The monkeys showed an increase in activity and a decrease in activity. If it can be done at all, humans will need to consider the complexity of thermoregulation in primates.
The first successful demonstration of hypothermia in a primate is provided by this work.
The hypothermic monkey model is a milestone on the path to artificial hibernation because of the growing passion for human spaceflight.
The innovation has published the research.