Dinosaurs are usually in the headlines. Every year, many important non-dino fossil discoveries are dug up. The same thing happened in 2022. Some of our favorites include mangled "dragon bones" and a 3D fish face.
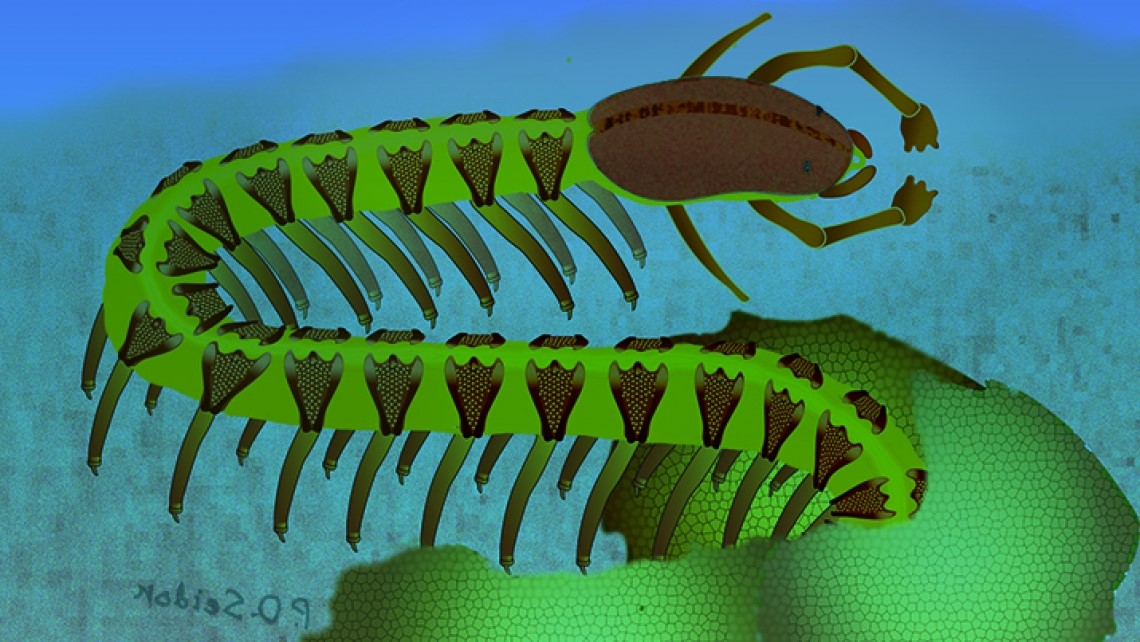
The oldest example of a brain ever discovered is believed to be a 525 million-year-old worm.
The ancient worm-like creature, known as Cardiodictyon catenulum, is part of a group of arthropod ancestors that were abundant during the Cambrian period.
The specimen was discovered in 1984 but the original researchers wouldn't look at it in hopes of finding a brain. The whole nervous system was found when the new team analyzed the fossil.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
There is a longstanding debate about the evolution of brains in arthropods.
The brain of a 525 million-year-old deep sea worm was found.
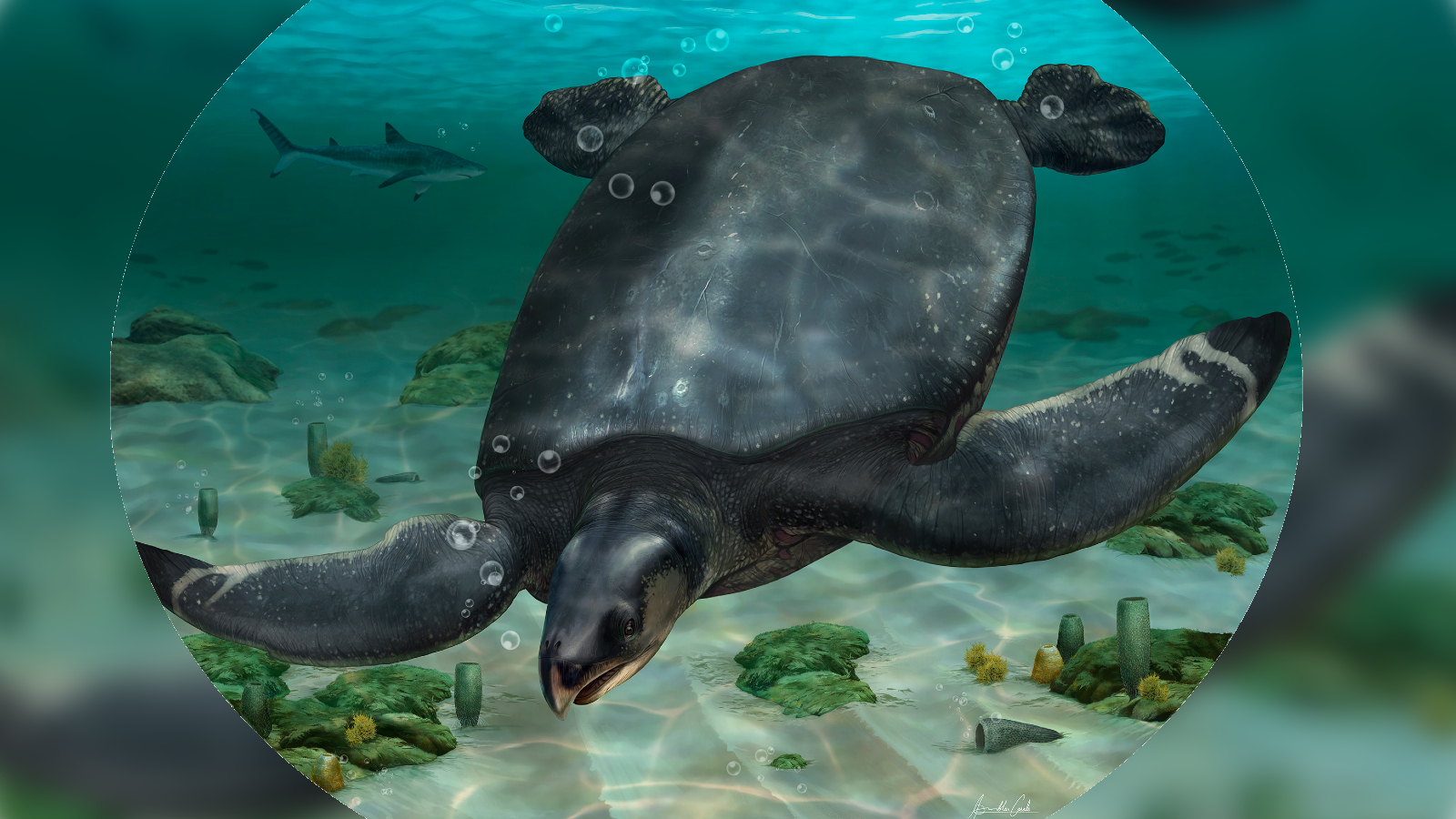

A species of giant sea turtle has never been seen before. The largest turtle species ever discovered in Europe is thought to have a body length of more than 12 feet.
A complete pelvis fossil and fragments of a shell were used to identify the new species. Europe's ancient oceans are thought to have been between 83.6 million and 72.1 million years old.
The Archelon ischyros was the world's largest turtle and had a maximum body length of 15 feet. It has been found that gigantism in turtles evolved in at least two different evolutionary lines.
A turtle cruises the ocean 80 million years ago.

More than 150 frog fossils were found in Germany between the 1930s and 1950s. Scientists were puzzled by the fact that all the frog seemed to be in good health when they died.
Researchers theorize that the frog may have died while having sex underwater. Females can sometimes drown if males hold them under the surface as they mount them in some species of modern frog. The fossil site is thought to have been a marshy swampland 45 million years ago when the frog are thought to have died.
Extreme environmental changes, such as flooding, are some of the past explanations for the extinction of the frog. The study researchers think their theory is the only explanation that makes sense.
Hundreds of ancient frog fossils that drowned during sex were preserved.

A species of panda that was probably the last of its kind to roam Europe was identified after researchers rediscovered a pair of teeth that had been lost.
It was most likely that the new species was similar in size to the living giant pandas in Asia. The tooth structure suggests that the teeth were less strong than giant panda teeth.
The oldest panda in Europe is around 10 million years old. The fossils are around 6 million years old and suggest that the pandas were on the planet more recently than previously thought.
Extreme ancient climate change is believed to have wiped out A.
Europe's last panda were weaklings who couldn't eat bamboo.

The remains of a 439 million-year-old shark-like fish were unearthed by researchers in China.
The new species, Fanjingshania renovata, is the oldest jawed animal ever found. The team recreated the ancient fish using thousands of fossils.
The species is part of a group of shark-like creatures called acanthodians, which are similar to chondrichthyans and osteichethyans. The researchers think that F. renovata was related to an undiscovered common ancestor.
The primeval sharklike fish is unlike any other fish.
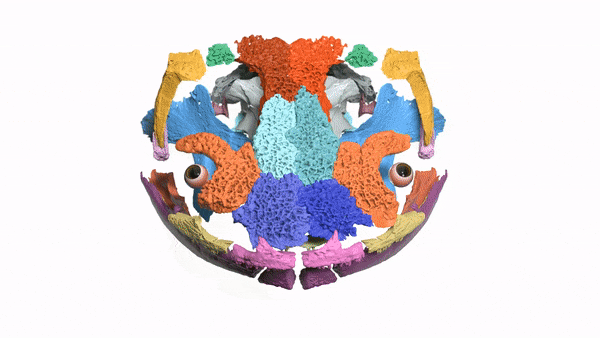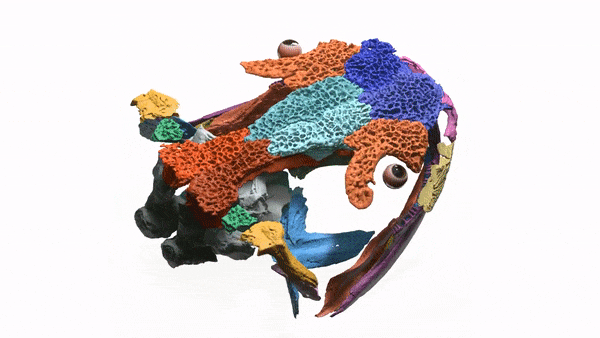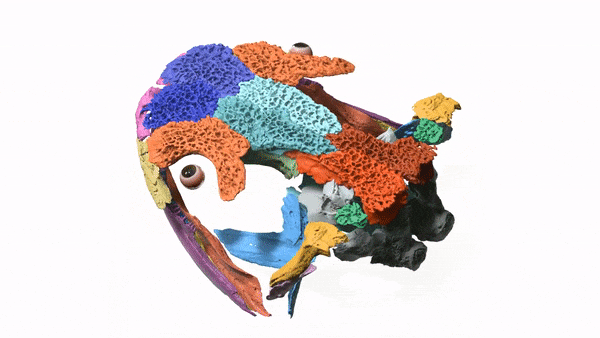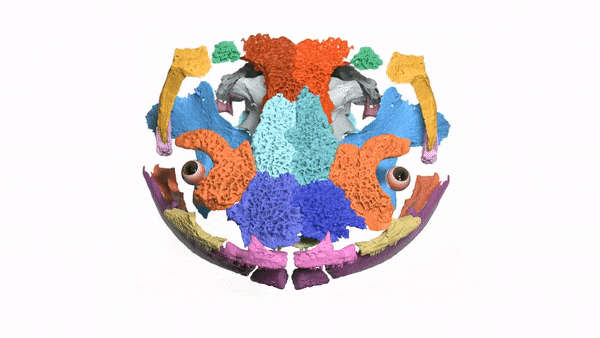
Researchers used X-ray images to create a 3D model of the salamander's skull, which had been trapped in a rock for more than 50 years.
The Mamorerpeton wakei is an ancient lizard that dates back to 166 million years ago during the Period of the Dinosaurs. It is believed that it was an aquatic species that swam around ancient ponds and lakes, slurping up smaller creatures.
The skull is trapped inside a rock that was unearthed in Scotland in the 1970s. It was put in storage because paleontologists thought it was less important than other fossils. A team of researchers were able to see inside the rock without having to open it.
Stunning reconstruction of a dinosaur fossil shows skull's weird quirks.
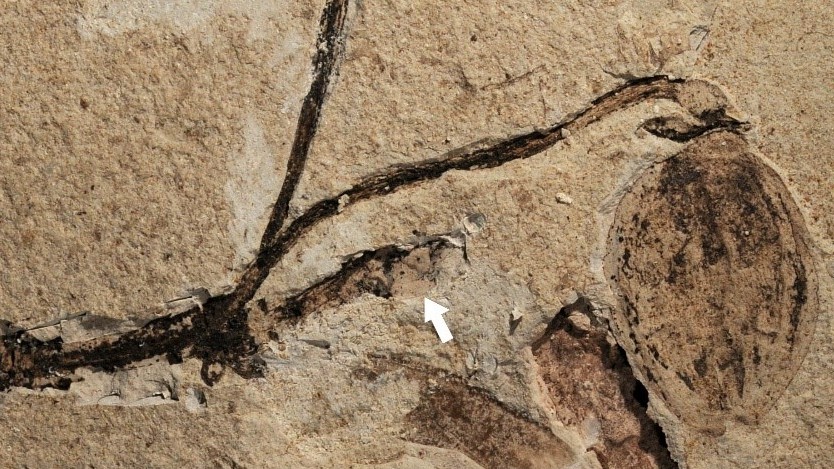

The earliest example of a flowering plant ever found was unearthed by researchers in China.
The fossil is long and wide. There is a stem, a leafy branch, a fruit and a flower bud in this picture.
The new discovery pushes the emergence of the group firmly back into the dinosaur era. A new species was named after it.
The oldest example of a flower is a plant fossil.
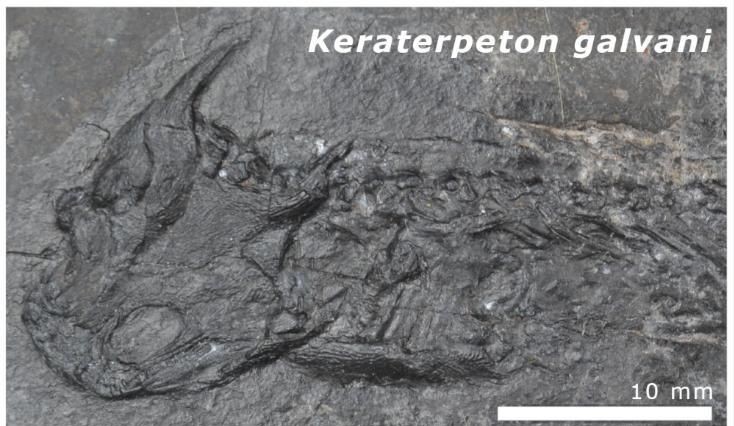

A group of mangled fossils in Ireland are thought to have been altered when continents collided to form Pangaea.
The fossils are from an extinct group of small, amphibian-liketetrapods with dragon-like horns. The remains have mostly been replaced by coal. Around 320 million years ago, they were discovered. Scientists used to think that the fossils had been degraded by acidic soils.
The remains were reanalyzed and found that the apatite was only around 300 million years old. The researchers believe that the apatite comes from the superheated fluids that came to the surface during the continental collision.
Dinosaur fossils were cooked by ancient continents to form Pangaea.
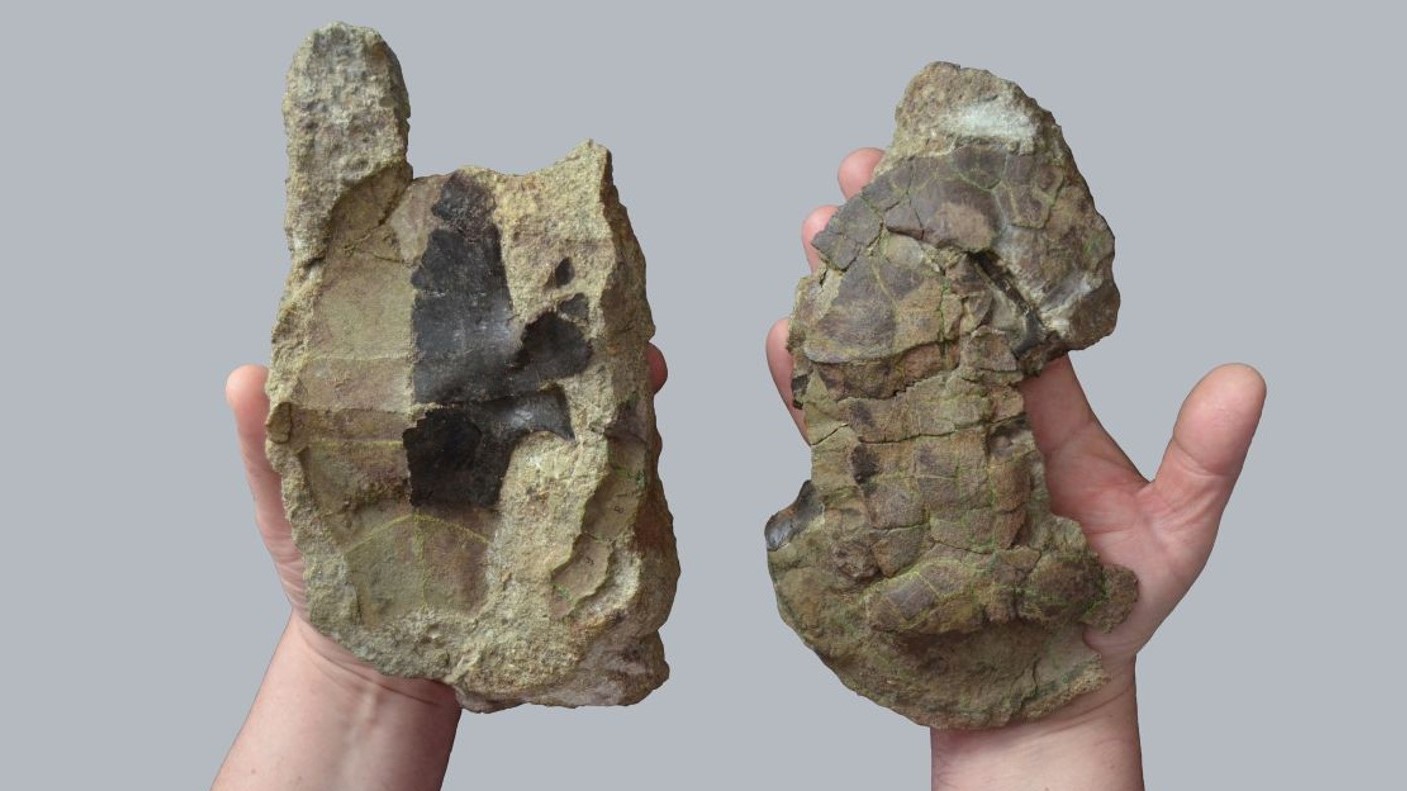

The remains of a 70 million-year-old turtle were found in the Transylvania region of Romania.
There are 16 living species of Dortoka vremiri. The extinct side-necked turtle is related to D. vremiri. The extinction event that wiped out 75% of life on Earth is thought to have survived the new species.
The turtles are thought to have lived in freshwater habitats on an ancient island which may have sheltered them from the worst damage caused by the asteroid 66 million years ago.
The extinction of the dinosaurs did not end the existence of the ancient Transylvanian turtle.
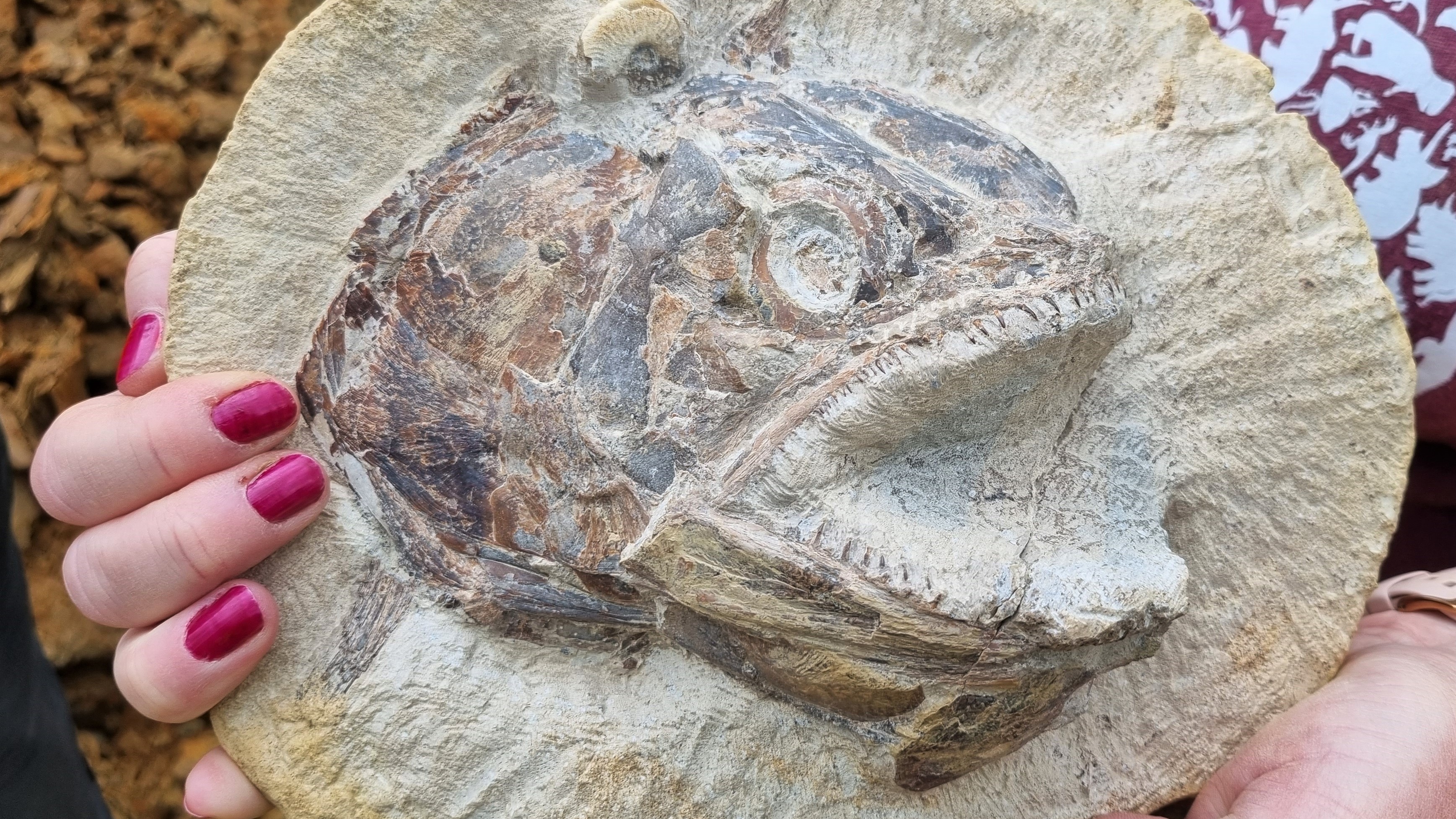

There is a treasure trove of 183 million-year-old fossils, including Ichthyosaurs, squids and insects, found on a farm in England. There was a fish head that was 3D.
Scales, teeth, and an eye sockets are some of the rare fossils found in the head of a fish from an extinct group of ray-finned fishes. The orientation of the fossil astounded researchers.
The site was discovered with his wife by a field geologist with the University of Birmingham. It looked like the fish was leaping out of the rock because it was preserved in more than oneDIMENSION.
Impeccably preserved fish fossils were found on a UK farm.