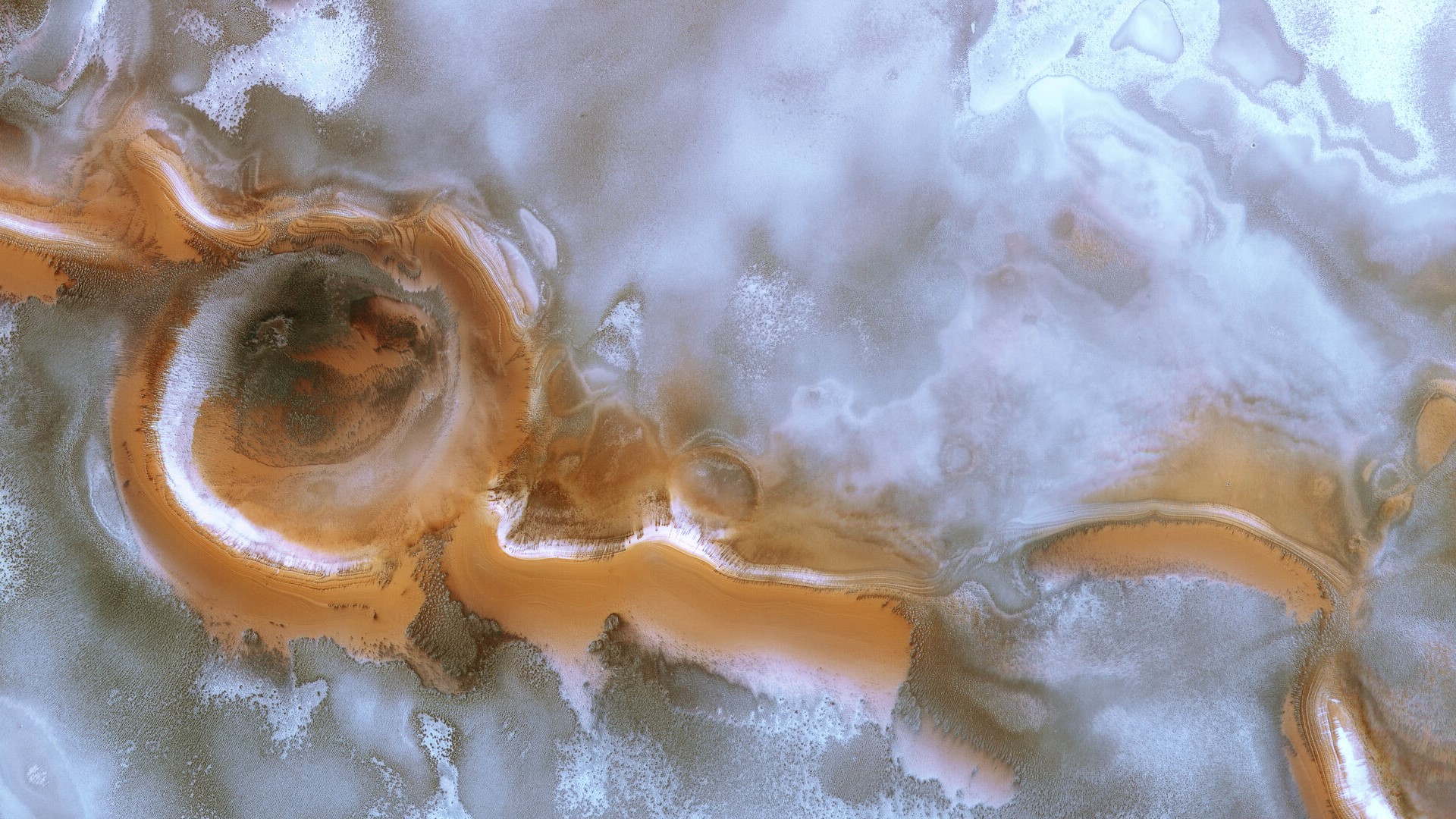
There are ribbons of red and white dancing across a landscape near the planet's south pole in a new picture of Mars.
The snowy scene was captured by the European Space Agency's Mars Express in May. The image shows a spring in the southern hemisphere and the ice is starting to fall.
The Red Planet will begin its own new year on December 26th, which will last over 700 Earth days. The Red Planet has four seasons, winter, spring, summer and autumn, and just like on Earth, the winter is cold and the summer is warm.
There is a crater near the north pole of Mars.
Nineteen years have passed since Mars Express arrived on the red planet.
Two massive impact craters, banded with alternating layers of water ice and sediments, are the most prominent features in the newly released image. There are deposits in the ridge between the craters.
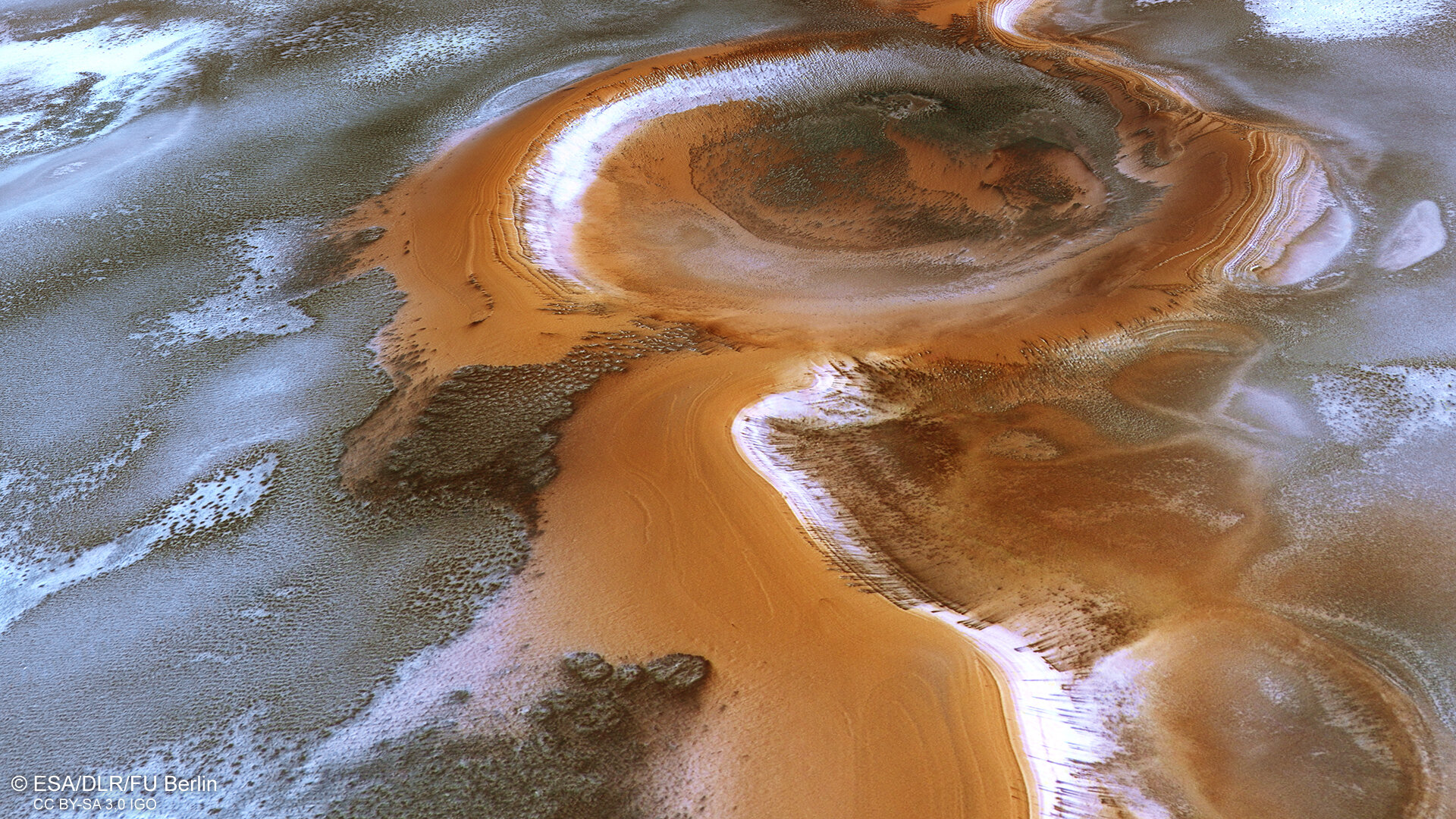

Dark dunes poke through the surface frost in other areas when the ice is gone. Dune fields look like ridges that run parallel to the most prevalent wind direction.
Scientists think that the dust that fills these dunes is dark because it comes from buried volcanic material that was exposed to strong Martian winds that easily carried it across the Red Planet's surface.
The dust and jets that erupt through the icy surface when carbon dioxide ice is transformed into gas are depicted in other dark spots. The jets cause geysers of dust to launch into the atmosphere and then settle on the surface.
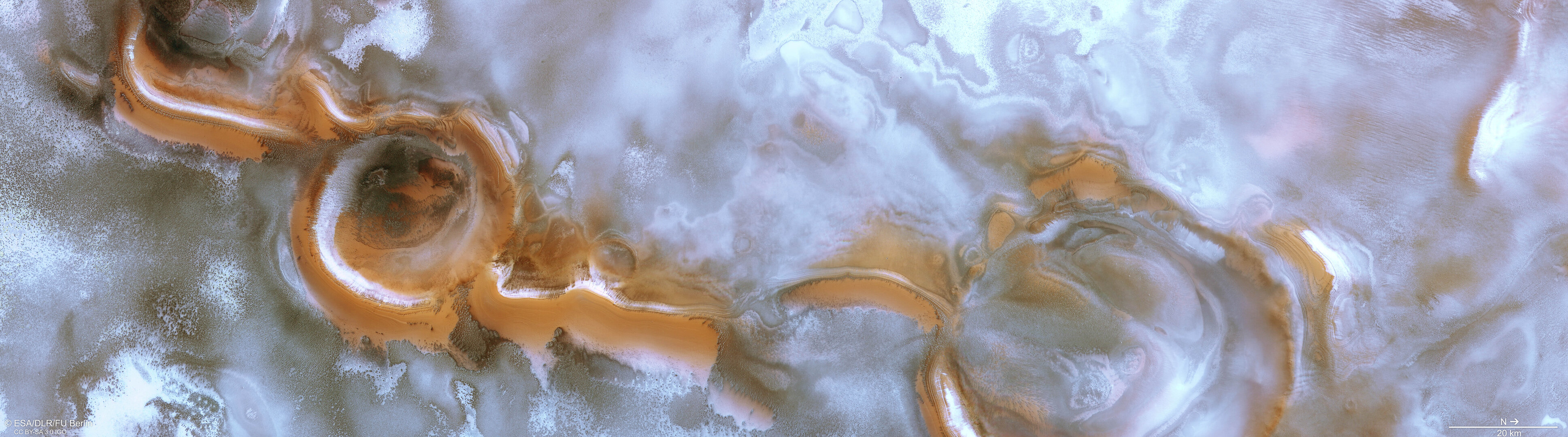

The other elements in the image are caused by the same thing. There are a number of irregularly shaped features in the polar region. There is an example of this in the upper left-hand corner of the new image.
Scientists can observe the processes that are shaping the Martian surface and change the appearance of the polar regions by monitoring these features.
There's more to the picture of spring in the southern hemisphere of Mars. There are clouds on the surface of Mars. Water ice can be seen across the center of the image and is influenced by the terrain beneath them.
During the Martian winter, carbon dioxide is deposited at the poles as ice and thaws in the spring. Strong winds are caused by the release of gas into the atmosphere.
The exchange of material between the surface and atmosphere of Mars is driven by the winds.
We encourage you to follow us on social networking sites.