Tomasz Nowakowski is a member of the physics.org community.
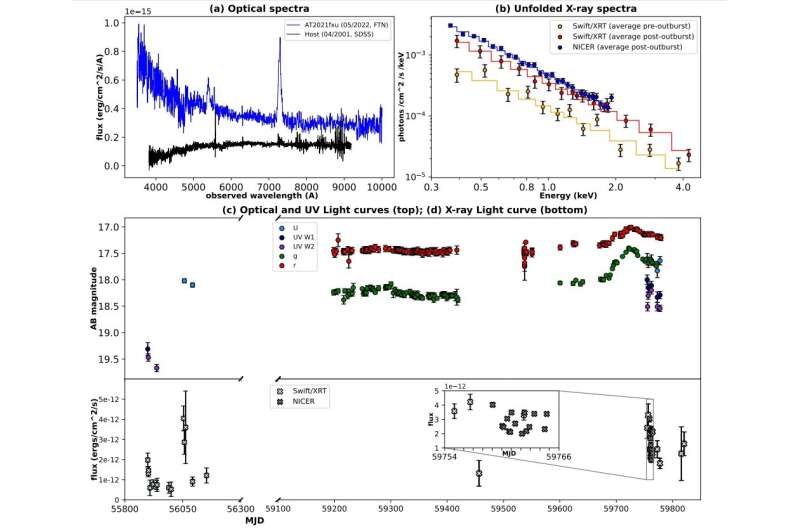
Astronomers used the data from NASA's Swift andNICER to investigate an active optical Transient known as AT2021fxu. The results of the study were published on December 14 on the arXiv preprint server.
The AGN is a compact region at the center of a galaxy. They are very energetic due to the presence of a black hole.
The emission line features are used to divide AGNs into two groups. Broad and narrow emission lines can be seen in type 1 AGNs, while only narrow emission lines can be seen in type 2 AGNs. Changing-look AGNs are AGNs that switch between different types.
At a redshift of 0.11, AT2021fxu is an optical Transient that was identified by the Zwicky Transient Facility. There are studies that suggest it may be a AGN.
A team of astronomer led by Yukta Ajay of the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) in Tirupati, India, took a closer look at AT 2021. They looked at the multi wavelength data from Swift.
The researchers wrote in the paper that they analyzed the multiwavelength data taken over two decades.
The optical spectrum of ZTF21aalxxzn shows the appearance of broad emission lines. The source may have undergone a transition from a Type 2 to a Type 1 AGN during which the individual photometric bands increased in brightness.
The optical g- and r- magnitudes of ZTF21aalxxzn have not changed since 2000.
There is little variation in the column density over the time studied. The results suggest that the transition is due to a variable accretion rate. The authors of the paper concluded that an accretion-drive CL transition resulted in strong broad Balmer lines that drove the change in classification.
The ongoing Changing-look AGN AT2021fxu, arXiv is being studied. There is a book titled "arxiv.2212.07272."
Journal information: arXiv
There is a science network.