Tomasz Nowakowski is a member of the physics.org community.
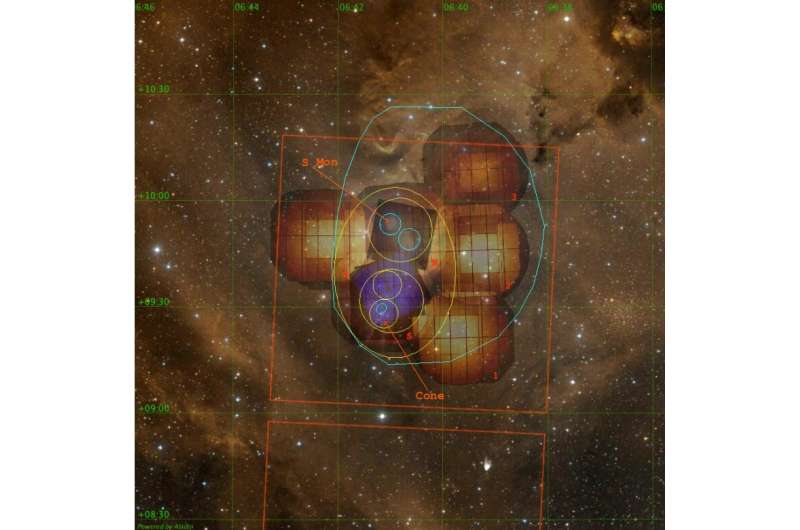
Astronomers used the data from the XMM-Newton and Gaia satellites to investigate a young star cluster. The results of the study, which was published on the arXiv pre-print repository, shed more light on the structure of this object and could help us understand stellar evolution.
A star cluster is a group of stars. They're seen as important laboratories for studying the evolution of stars. The structure of the Milky Way can be explored with the help of scs.
More than a thousand stellar-mass members can be found in a young stellar cluster located some 2,480 light years away. One of the most accessible star-forming regions in the Milky Way is due to its proximity and the fact that the cluster's activity is still going on.
A group of astronomer led by Ettore Flaccomio of the Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Italy studied the structure of the stars. They analyzed the new X-ray data obtained with the XMM-Newton. The study was complemented by a lot of data.
"We revisit the structure, dynamics, and star-forming history of NGC 2264 in order to advance our understanding of the processes that lead frommolecular clouds to Protostars, stellar associations, and the evolution of both," the researchers wrote in the paper.
The team was able to create a catalog ofPukiWikiPukiWikiPukiWikiPukiWikiPukiWiki candidates, which was almost twice as large as previousPukiWikiPukiWikiPukiWiki candidates. The astronomer analyzed the distribution of the objects and found new structures in the cluster.
The scientists were able to identify four new substructures based on the surface density map of candidate members. Almost 80% of the candidate members are contained in the extended halo. S Mon(C) may be older than the surrounding region or has a lower fraction of stars with disks.
According to the authors of the paper, the identification of a high number of candidate members in the extended halo greatly enlarges the known extent of NGC 2264.
The researchers said that a less contaminated membership is needed in order to get a better idea of the outer population.
The results show that the stars in the south are younger than the ones in the north. They think that star formation started four million years ago in the S Mon region and has continued ever since.
The findings of the study show that the present configuration of NGC 2264 is due to multiple processes. One of the best places to look at the formation mechanisms of stars and clusters is this site.
There is more information about the structure of the star forming region. There is a book titled "arxiv.2211.09000."
Journal information: arXiv
There is a science network.