Many children dream of becoming astronauts and going to the moon.
In order to get that elusive job, would-be astronauts must make it through a competition. The space agency chose 10 candidates from more than 12,000 applicants.
US citizenship and a master's degree are included in NASA's basic requirements. In order to pass NASA's physical exams, astronauts need to be in top shape.
More than 350 people have become astronauts since NASA's first class in 1959 NASA wants future spacefarers to be trustworthy, tenacious, and detail oriented, according to Anne McClain, a NASA Astronaut.
Military men were the first to become astronauts during the space race between the US and the Soviet Union.
The 12 people who walked on the moon are all white. NASA aims to land the first woman and person of color on the Moon during its long-awaited Artemis mission, which will take place in the year 2024.
A two-year training course is required for astronauts to become fully qualified. Massive pools and hot deserts are some of the places where astronauts are trained to test their skills.
In order to prepare for travel beyond the confines of a spaceship, astronauts train underwater. They will experience microgravity while working in space.
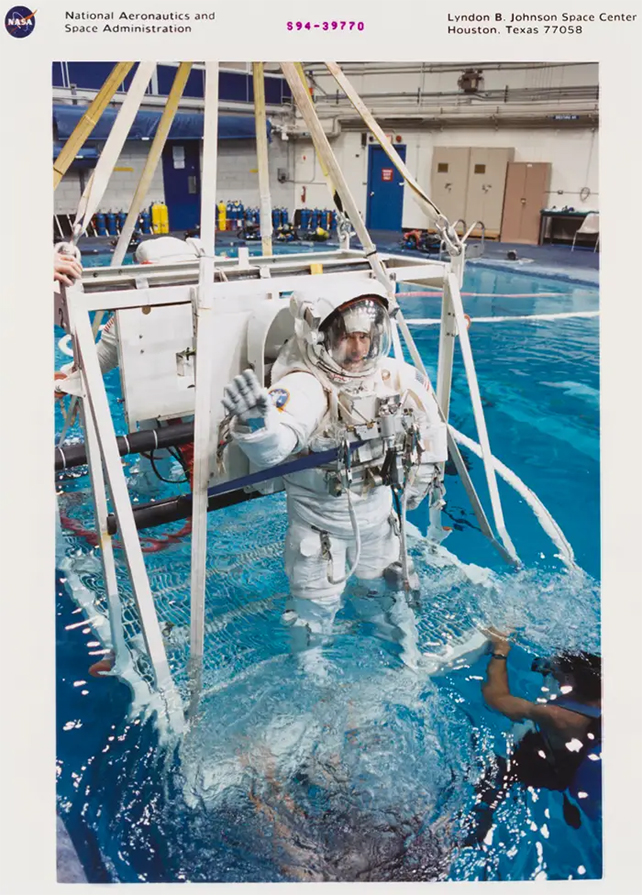

When astronauts leave the spaceship to work in the vacuum of space, they use a mock-up of it in the pool.
Most modern spacewalk training takes place at the neutral buoyancy laboratory at the Johnson Space Center.
There is a partial mock-up of the International Space Station that astronauts can use to practice using hardware in a weightless environment.
NASA's reduced gravity research began in 1959 A zero gravity airplane called the "vomit comet" is used as a training tool for astronauts.
The plane's passengers achieve about 25 seconds of zero gravity once they reach the top of the wave through a series of steep climbs and dives.
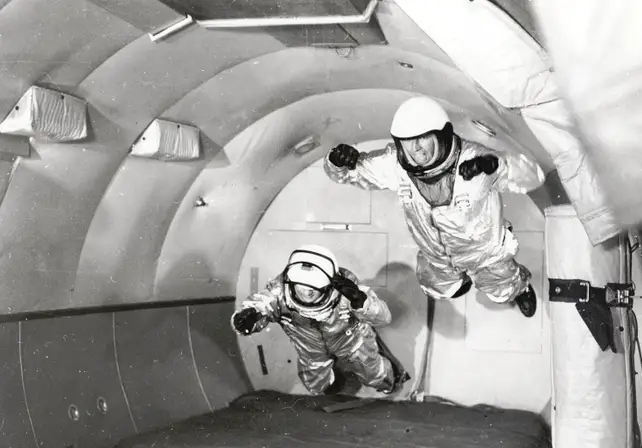

NASA's KC-135A aircraft was one of the aircraft involved in the program. Zero gravity flights were taken over by a private company in 2008.
A floating lab can be found on the plane. Medical studies and motion sickness experiments are performed on these flights because the plane's roller-coaster-like maneuvers make passengers feel unwell.
The plane has been used for film shoots. The zero gravity scenes in "Apollo 13" were filmed by actors Tom Hanks, Kevin Bacon, and Bill Paxton.
NASA astronauts have learned survival techniques in case they have to make an emergency landing.
Apollo 11 astronauts traveled to Nevada in 1964 to practice their survival skills in the desert. They are wearing clothes made from parachutes to stay cool in the heat.
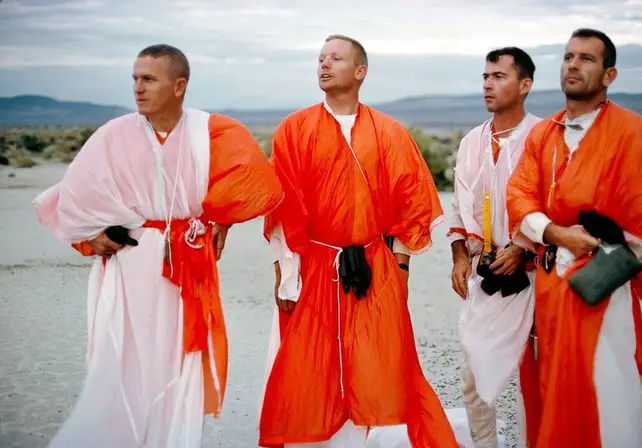

The environment of the desert is similar to an alien planet. The space agency will conduct two field trainings in the Arizona desert that are similar to the Moon as part of training for the Artemis Moon rocket missions.
During the space race, astronauts trained on a multi-axis trainer, which twirled them around in a wild combination of spins. The idea was to get astronauts used to the rides in a spaceship.
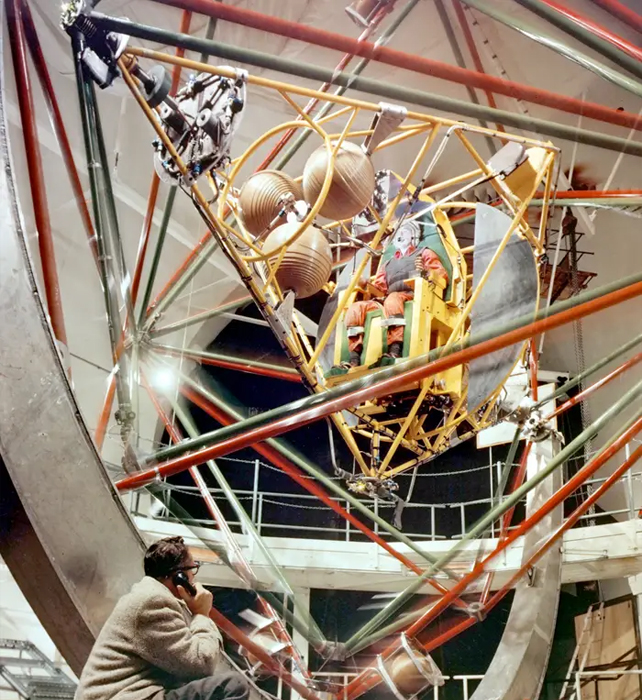

"That was one of the more demanding tests or training exercises we went through anywhere in the whole training floor for spaceflight," John Glenn said in a NASA Glenn Research Center video. We hated that rig.
In 1960, the seven original Project Mercury astronauts and 13 women of Mercury 13 were trained. The rig is in motion.
The spinning contraption is no longer used by NASA since they don't need spacefarers to control their spin.
NASA used a machine called a human Centrifuge to test the effect of gravity on astronauts training to go to the moon.
A human can be held at the end of a human Centrifuge with a capsule. The astronauts test their tolerance for the force of gravity.
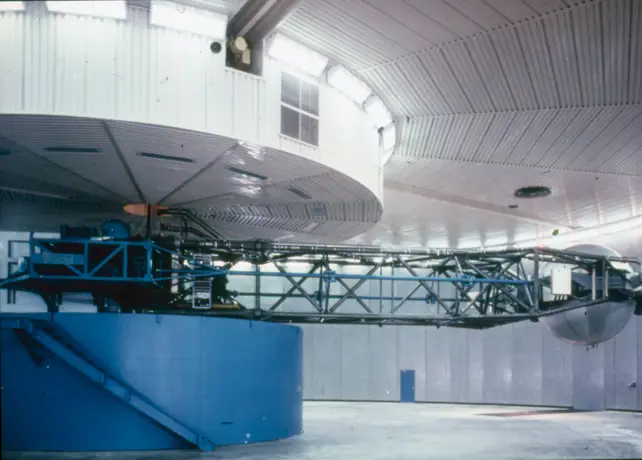

Glenn said in his 2000 memoir that he was acting as a "guinea pig" for what a human being might experience being launched into space or reentering the atmosphere.
People who aren't fit for space travel are screened for psychological and psychiatric problems.
The mental burden of space travel was understood by NASA as more humans ventured into space.
There was a person that became obsessed with the hatch. All I have to do is turn the handle and the hatch will open. In a 2001 interview, Henry Hartsfield said that one of his earlier missions was frightening. The hatch was locked.
Going to space is a lot of work. NASA's human research program found that crew members endure sleep changes, radiation exposure, and long bouts of isolation.
Crew members on the International Space Station talk with medical staff through private video conferences after they become astronauts.
NASA's goal of sending humans to the Moon and Mars in the not-so- distant future will pose a challenge to the mental well-being of astronauts.
The article was first published on Business Insider.
More from Business Insider: