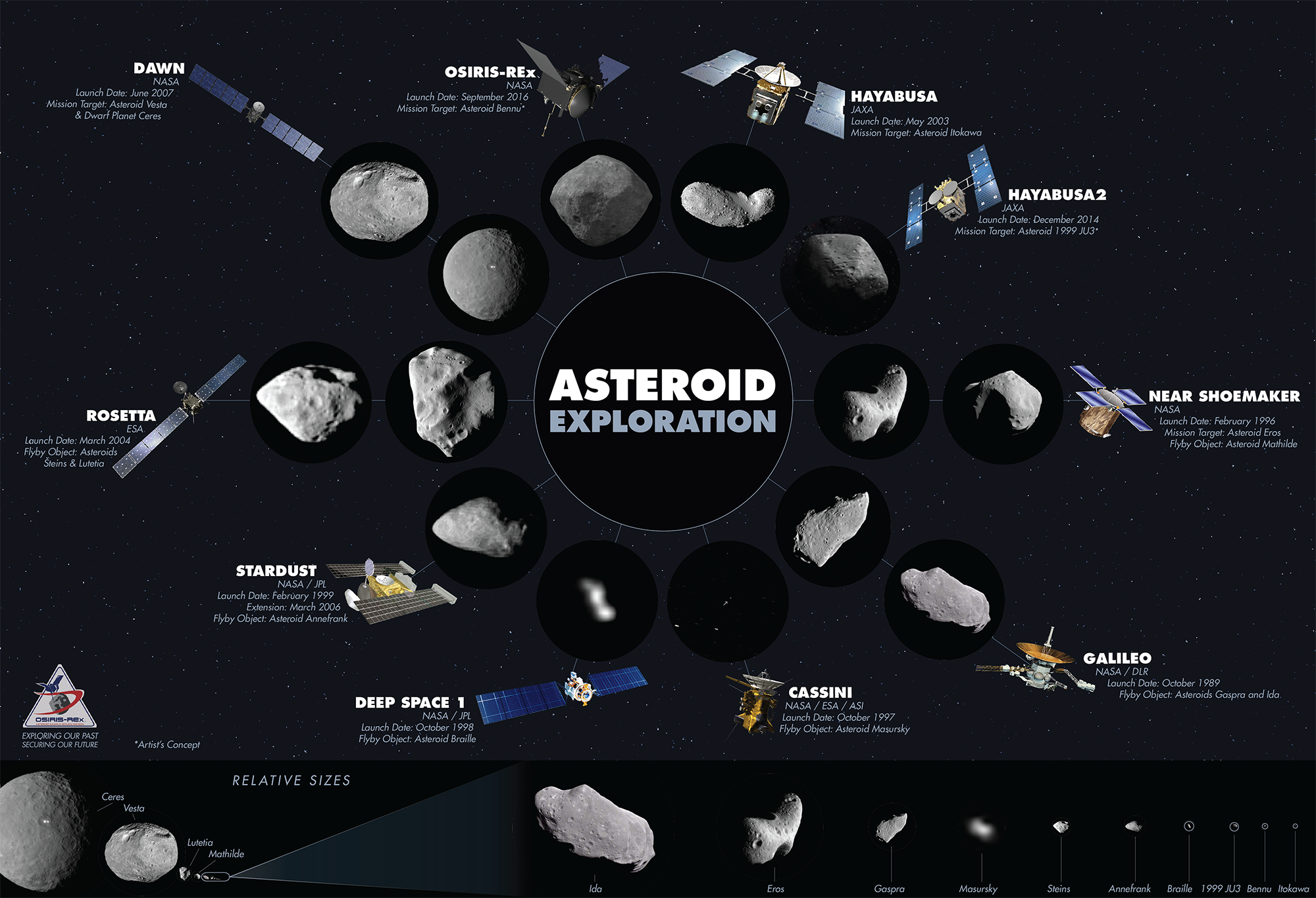
NASA's OSIRIS-REx is an ongoing mission that visited and collected a sample from asteroid 101955 Bennu with the aim of returning the sample to Earth in three years.
The OSIRIS-Rex arrived at the asteroid Bennu in December. The rock was carbon-rich on New Year's Eve. Bennu picked up a sample from the surface before beginning the long journey home.
OSIRIS-REx's sample return capsule will return a sample of Bennu to Earth in September of 2023, but that won't be the end of the mission. In 2029, it will be asked to swing by the asteroid Apophis.
There are many ways to stop an asteroid.

The OSIRIS-REx mission was named a finalist for NASA's New Frontiers mission class in 2009. OSIRIS-REx was the winner in 2011.
Medium-class missions are intended to help us understand the solar system. The third mission chosen was OSIRIS-REx, which flew by the dwarf planet Pluto in 2015 and by an object called 2014MU69 in 2019.
The OSIRIS-REx was launched in September of 2016 The flyby took place in September of last year. The probe arrived at Bennu on December 3rd. OSIRIS-REx took a detailed measurement of Bennu in the month after it arrived.
Bennu is the smallest body a spaceship has ever flown over, and OSIRIS-REx was the closest to a small body.
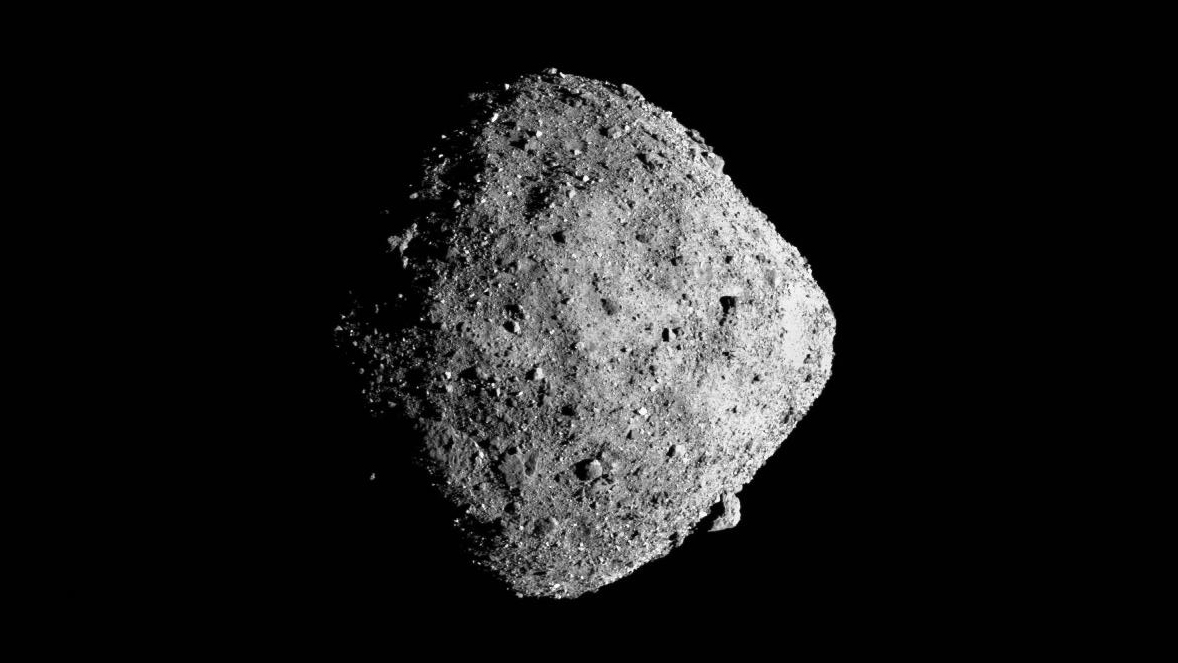

The five instruments onboard the spaceship studied, mapped and analyzed the asteroid.

The craft made a couple of deep-space maneuvers. The first took place in December of 2016 and was the start of the mission.
It took OSIRIS-REx almost a year to fly by our home planet. OSIRIS-REx's speed was increased by about 8,500 mph. On its way to Bennu, the spaceship continued.
The OSIRIS-REx took pictures of Earth and its moon from a distance of more than 3 million miles.
After aced its second and final major deep-space maneuver on June 28, the craft made a series of successful asteroid-approach operations to put it close to Bennu.
Scientists were able to identify a rocky zone with the nickname of Nightingale after studying the asteroid. The touchdown on October 21, 2020, lasted just six seconds and brought the Touch-And-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism into play.
TAG SAM blasted a sample of pure nitrogen gas at the asteroid as OSIRIS-REx drew closer. Dust and broken rock was pushed into the chamber. OSIRIS-REx was required to collect at least 2 ounces (60 g) of asteroid material, with a preference for 5 ounces (150 g) to account for any measurement errors. NASA said the goal was 2 ounces or 60 grams.
OSIRIS-REx carried three bottles of nitrogen gas so it could attempt multiple collection attempts. It could carry as much as 70 ounces. Before and after the sample is collected, scientists measured the angular acceleration of the spaceship.
The last flyover of Bennu took place on April 7, 2021. There is a plan for the sample capsule to return to Earth in September of 2023.

The rock OSIRIS-Rex visited was renamed Bennu by 9-year-old Mike Puzio after winning a contest. Bennu is an Egyptian god. Puzio thought the solar panels looked like the bird god's neck and wings.
Bennu is one of thousands of objects that are close to Earth. Bennu was one of less than 200 objects that was well known and similar to Earth's path. Every six years, this asteroid comes very close to Earth as it travels around the sun.
Bennu is about 1, 650 feet wide. Smaller rocks spin too fast for a spaceship to land on them. There were only a few large asteroids that could allow a visit.
Bennu's composition is more attractive. The asteroids that may have brought water and organic material to Earth and helped kick off life would look similar to Bennu.
The asteroid's total impact probability through 2300 is just 1 in 1,750, making it a potentially hazardous object. The impact of the asteroid won't destroy the planet but it will cause a lot of damage. An asteroid of this size wouldn't cause mass extinctions according to experts.
Scientists could use the advanced warning provided by OSIRIS-REx. NASA's recent DART mission demonstrated the use of the "kinetic impactor" technique, which could be used to divert the asteroid completely. DART hit a small asteroid called Dimorphos in a bid to change it's position. The mission was a roaring success and on Oct. 11, 2022, NASA officially announced that DART shortened Dimorphos' nearly 12-hour flight time by 32 minutes.

The Sentry Impact Risk Table keeps a record of asteroids that can't be ruled out for an Earth impact.
According to NASA, Apophis won't be a problem in the next 100 years because of improved simulations of its movements through space. On Friday, April 13, 2029, Earth will have a close encounter with the asteroid that will see it come just 19,000 miles from the planet.
Apophis had a very small chance of hitting Earth during a flyby in 2068, but a new assessment shows there is no threat anymore. NASA was presented with a unique moment when the asteroid came so close.
The OSIRIS-REx will be renamed after dropping off Bennu samples at Earth. In 2029, the mission will be known as OSIRIS-APEX.
There will be another $200 million added to the cost of the mission, which will bring the total cost to $1 billion. One of the riskiest phases of a new mission, which is blasting off the planet on a rocket, is probably not worth the cost.
The new OSIRIS-APEX mission will be able to do its job because the instruments on the spaceship are healthy. The goal of the mission is to get close enough to look at the asteroid in detail. The surface will be blasted away by a special maneuver.
Even though Apophis and Bennu are the same size, they are completely different types of asteroids. The S-type family of meteorites is similar to the B-type family of meteorites that may have delivered water to Earth.

The bits and pieces left over from the formation of the planets are called asteroids and are used as rudimentary blueprints of the early solar system. Scientists can see what the early solar system was like by studying them.
While OSIRIS-REx is the first to return samples to the US, Japan has already returned two similar missions. Hayabusa was the first craft to bring an asteroid back to earth. The Hayabusa2 mission did the same thing in 2020.
NASA's Dawn mission visited an asteroid before going on to a dwarf planet. OSIRIS-REx wants to bring home a piece of Bennu for in-depth laboratory studies that aren't possible from space. The OSIRIS-REx team wants to collect at least 2 ounces of material.
OSIRIS-REx's research is meant to give further insight into asteroid movements. Despite decades of searching the skies, there isn't anything to worry about. The designation of Bennu and Apophis as potentially hazardous asteroids is a statistical description.
How many threats are there? It is complex.
Astronomers will use OSIRIS-REx to study asteroids. The movement of an asteroid or other object is altered when heat from the sun pushes it. The push can help to change the path of a space rock. The effect varies based on the shape of the asteroid.
You can read NASA's overview of the OSIRIS-REx mission. You can learn more about the OSIRIS-REx mission from the company. There is a collection of photos from the University of Arizona.
The board of regents in Arizona. There will be a new year in2022. The OSIRIS-Rex sample return mission is in the galleries. There is a new tab on the Asteroid Mission website.
The company is called, "Lockheed Martin." There will be a new year in2022. The origin of the solar system is discovered in OSIRIS-REx. osiris-rex.html can be found from https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/ products/osiris-rex.html.
There is a space agency called NASA. Oct. 23. NASA collects a lot of asteroids. NASA's osiris rex spacecraft collects a significant amount of asteroid
NASA science OSIRIS REx. In-depth from: https://solar system.nasa.gov/missions/osiris-rex/.