Beer is one of the oldest and most popular beverages in the world, with some people loving and others hate the bitter taste of the hops used to flavor its many varieties. There are health benefits to an especially hoppy brew. The chemicals found in hop flowers can be used in lab dishes to fight Alzheimer's disease, according to a recent study.
Alzheimer's is a disease that can be marked by memory loss and personality changes. There is a time lag between the start of underlying biochemical processes and the start of symptoms that is difficult to treat. This means that damage to the nervous system can happen before someone knows they have the disease. There is increasing interest in preventative strategies and therapies that can be used before symptoms appear.
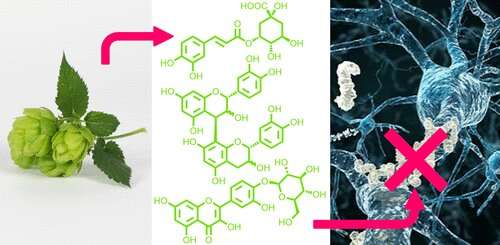
One of the strategies is called "nutraceuticals," which are foods that have a certain type of health benefit. The hop flowers used to flavor beers have been explored as one of these potential nutraceuticals, with previous studies suggesting that the plant could interfere with the build-up of amyloidbeta. They wanted to find out which chemical compounds had this effect.
In order to identify these compounds, the researchers created and characterized extracts of four common varieties of hops. In tests, they found that the extracts had anti-aging properties.
Many types of lagers and lighter beers contain the Tettnang hop. The extract that was separated into fractions contained the most potent antibiotic and aggregation-inhibiting activity. There are processes that allow the body to clear out toxic substances.
The Tettnang extract was found to protect the worms from AD-related paralysis, though it was not very noticeable. Although this work doesn't justify drinking more bitter beers, it shows that hop compounds can be used to fight AD.
There is more information about Alzheimer's Disease Prevention through Natural Compounds. The activity of multi targets in chemical neuroscience. The book is titled "acschemneuro.2c00444."