Daylight saving time began on March 13, 2022, at 2 a.m. Daylight saving time ends at 2 a.m. local time on Sunday, November 6th. Benjamin Franklin started a tradition of saving energy by changing the time of year.
Daylight saving time begins and ends during the year so you know when to change your clock and not miss an important meeting or an hour of sleep. You will learn about the history of daylight saving time, why we have it now, and some myths about the time change.
Daylight saving time is covered.
Daylight saving time usually begins in the summer and ends in the winter as the U.S. government has passed new laws.
The time changes. Daylight saving time begins in the US on the second Sunday in March. Daylight saving time ends on the first Sunday in November at 2 a.m.
When most Americans set the clock back an hour, the cycle will begin again, after the end of Daylight Saving Time in the U.S. Daylight saving time in the U.S. ended in November of 2022, according to timeanddate.com.
The author of " Seize the Daylight" says Benjamin Franklin came up with the idea to change the time in the summer to conserve energy. People could take advantage of the extra evening daylight if they moved the clocks forward. Franklin wrote a letter to the Journal of Paris in 1784, rejoicing over his discovery that the sun gives light as soon as it rises.
Daylight Saving Time didn't officially start until more than a century later. Daylight Saving Time was established by Germany in 1916 as a way to conserve fuel. Daylight saving time was adopted in the US in 1918.

Farmers objected to the idea of keeping daylight saving time because it would mean they wouldn't get an hour of morning light. It's a myth that Daylight Saving Time helped farmers. Daylight saving time was abolished until the next war came around. Daylight saving time was re-established in 1942 at the start of the war.
The free-for-all system in which U.S. states and towns were given the choice of whether or not to observe Daylight Saving Time resulted in chaos. The Uniform Time Act was enacted in 1966. Daylight saving time begins on the first Sunday of April and ends on the last Sunday of October in all but one state.
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 expanded daylight saving time to the current timing.
Daylight saving time is observed by less than half of the world's countries. Daylight saving time is observed by those who take advantage of the natural daylight in the summer. The longest day of the year on the summer solstice is when the days begin to get longer. Earth is tilted towards the sun during the summer season.
More about the science of summer
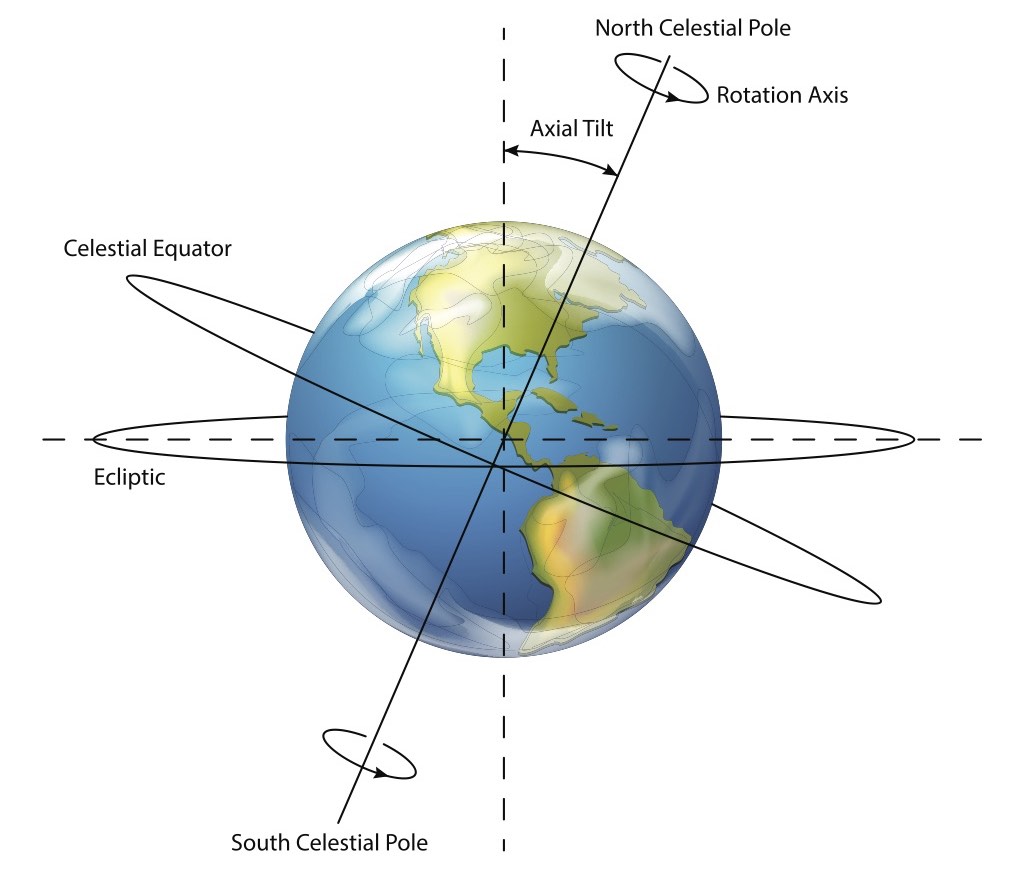
The DST clock change benefits regions farthest away from the equator and closer to the poles because there is a more dramatic change in sunlight.
There are fewer traffic accidents when there is more daylight in the evening, as there are fewer cars on the road. Full-time workers could benefit from more daylight.
Daylight saving time has always been about saving energy. The time change was instituted in the U.S. during World War I and again during World War II. Congress enacted a trial period of year-round daylight saving time after the Arab oil embargo because they wanted to save energy.
There is not much evidence for energy savings. A report to Congress on extended daylight saving time was prepared by a senior researcher at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The lighting is responsible for less of the energy consumption than it used to be. Some places may need air-conditioning during the hotter nights of summer daylight saving time.
The four weeks of extra daylight saving time that went into effect in the United States in 2007, saved about half of what would have been used on each of those days, according to a report to Congress. The effect of the entire months-long stretch of daylight saving could have a different effect.
There was a small increase in residential energy usage after daylight saving time was implemented in Indiana. Changes to Australia's daylight saving timing for the summer Olympics of 2000 didn't save any energy according to a study.
It's difficult to estimate the effect of daylight saving time on energy consumption because there aren't many changes to the policy. Before and after comparisons of only a few weeks' time were allowed by the extension of daylight saving time. Changes in Indiana and Australia were limited.
The real reason the US sticks with daylight saving time is not the energy question.
He said that the energy saving isn't the main driver. People want to take advantage of the light in the evening.
Most of the United States and Canada observe Daylight Saving Time on the same days. Daylight saving time is not observed in Hawaii and Arizona.
The sunshine protection act passed the senate but is stuck in the house The National Conference of State Legislatures says at least 450 bills have been considered to establish year-round daylight savings time. At least 30 states have introduced legislation to make standard time permanent, doing away with Daylight Saving Time. Florida's Senate and House passed legislation that asked the U.S. Congress to exempt the state from the Uniform Time Act. Florida would stay in Daylight Saving Time if approved. The Uniform Time Act needs to be amended in order for Florida to have year-round Daylight Saving Time. According to The New York Times, this allowance was authorized. The legislation hasn't been approved by Congress, according to the South Florida Sunentinel. Similar moves have been made by fifteen other states. Arkansas, Alabama, California, Delaware, Georgia, Idaho, Louisiana, Maine, Ohio, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming are included in the list.
In the fall of last year, Californians voted in favor of a proposal to repeal the clock changes. The result of the vote was that the legislature could change it with a two-thirds vote. The state legislature has been slow in pushing through changes on the federal level.
Daylight Saving Time is observed by nine of Canada's 10 provinces. In Canada, the provinces and territories that stay on standard time all year are: In British Columbia, Creston, Fort Nelson, and Fort St. John do not observe Daylight Saving Time.
Daylight saving time begins at 1 a.m. in most of Europe. When Europeans moved their clocks ahead one hour at 1 a.m. on March 27th, 2022, it was on the last Sunday in March. The time has changed. Daylight saving time ended in the early hours of the morning. The last Sunday in October was when the clock was moved back an hour.
According to timeanddate.com, the majority of European countries don't observe Daylight Saving Time. British Summer Time is also known as Daylight Saving Time in the UK.
In Austria, France, Germany, Italy, Hungary, Norway, Poland, Spain and Switzerland, there is Daylight Saving Time. Daylight saving begins at 2 a.m. for these countries. Daylight Saving Time (DST) Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) is followed by clock changes for many countries.
Irish Standard Time (IST) starts at 1 a.m. local time when the clock is moved ahead an hour. The Canary Islands, the Faroe Islands, and Portugal all have the same time zone. The Wall Street Journal reported that a recent poll found that a majority of people wanted clock changes to be abolished. According to the WSJ, the EU members could decide to keep the EU in winter or summer.
During September through November, Australia, New Zealand, South America and southern Africa set their clocks back an hour, so that they would be back to standard time in the spring.
New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, and the Australian Capital Territory don't follow daylight saving in the same way as the other states and territories. Daylight Saving Time began on the first Sunday in October and ends on the first Sunday in April.
The teacher planet has a lot of ideas to teach about daylight saving time. Daylight saving time is the subject of a one hour video on the History Channel. There was a time when the US had year-round Daylight Saving Time.
The article was changed on Nov. 2, 2022.