Tomasz Nowakowski is a member of the physics.org community.
Astronomers from Switzerland and Austria have discovered a new alien world using the EchelleSPectrograph. The exoplanet is at least four times more massive than the Earth, and it's outside of our solar system. There is a paper on arXiv.org.
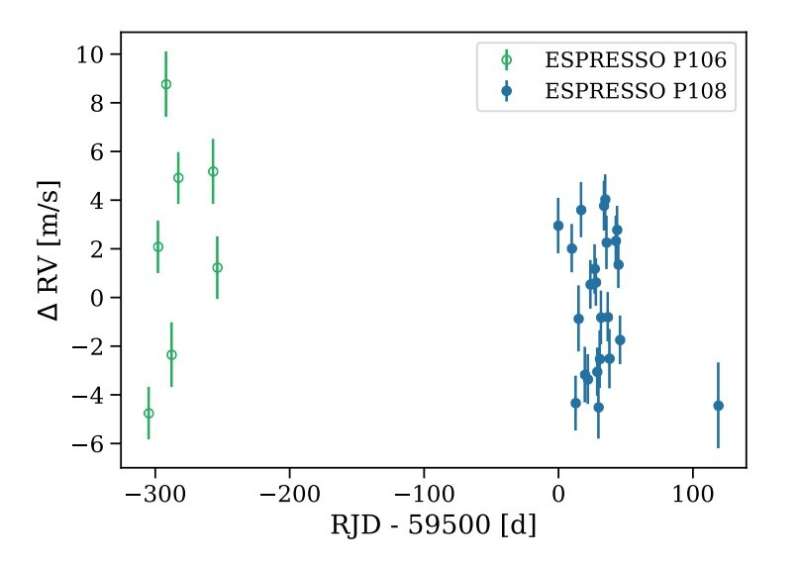
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile has a state-of-the-art ultra-stable high resolution spectrograph named Espresso. It is possible to detect Earth-like planets around sun-like stars thanks to the instrument.
Lia F. sartori is an astronomer at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zrich. An M dwarf was one of their targets. Between December 12, 2020 and February 08, 2022, they observed this star for 31 days and found a new planet.
The detection and characterization of a planet is reported in the following. The researchers wrote in the paper that this is one of the few discoveries of its kind.
The planet L 363-38 b has a minimum mass of about 4.57 Earth masses and a radius of between 1.5 and 2.5%. The host of the exoplanet is at a distance of 0.048AU from the planet. The equilibrium temperature was calculated to be around 330 K.
The star L 363-38 has a radius of 0.274 and a mass of 0.21 solar mass. The star's effective temperature was 3129K.
Some other planets may be in the vicinity of L 363-38, according to the astronomer. They say that planets around M dwarfs are likely to occur in multi-planet systems. In order to uncover the presence of other extrasolar worlds around L 363-38, follow-up observations of this planetary system are required.
The authors of the study show the potential of ESPRESSO to detect and investigate exoplanets around M dwarf stars.
The faintness of M stars makes them difficult to study with a 3.6-m telescope and a 8-m telescope.
L 363-38 b is a planet newly discovered with a dwarf star in the background. There is a book titled "arxiv.2210.12710."
Journal information: arXiv
There is a science network.