Oxygen can be found in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. Plants absorb carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water and produce sugars and starches for energy. If we can detect oxygen somewhere else, it will generate excitement.
Oxygen in an exoplanet's atmosphere is thought to indicate life. If we can't rule out other pathways, it's proof of life.
Scientists don't know if they are out.
Oxygen is present on Earth. The crust and mantle make up about the same percentage of the atmosphere.
About two billion years ago, the Great Oxygenation event took place. The ancient cyanobacteria absorbed sunlight and used it to make food. Life has had a couple of billion years to build oxygen up in the atmosphere and mantle.
If oxygen is found in an exoplanet's atmosphere, it's a sign of life. Simple life is taking in sunlight and releasing oxygen in the ocean.
There is a source of oxygen that doesn't depend on life.
Science Advances has a research article on abiotic molecular oxygen production. Mns Wallner is a PhD student at the University of Gothenburg.
A source of oxygen has been found. Terrestrial volcanic exoplanets may have oxygen in their atmospheres due to the fact that volcano produce sulphur and pump it into the atmosphere. Life isn't important.
High-energy radiation from a star can ionize the molecule. The molecule rearranges itself when it is ionized. The system becomes a double positively- charged system. It has two oxygen atoms next to each other and a sulphur at the other end. The oxygen atoms are free to move around in chaotic circles until they find a new home.
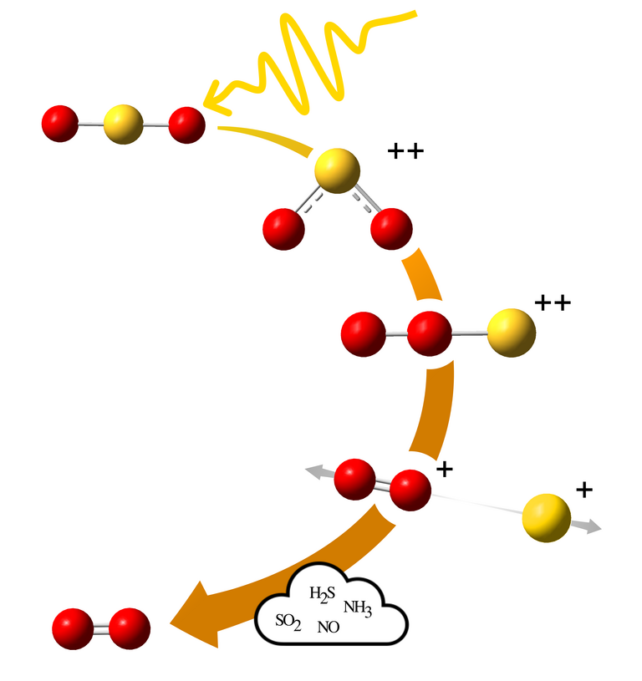
Two of the bound electrons in the molecule can be ejected and change the angle between the atoms in the molecule.
The molecule can take on a whole new shape if the atoms switch places.
The molecule might not reform into SO2 again. The oxygen molecule can remain if the sulphur breaks up. An electron can be attracted from another molecule. Oxygen is important to life on Earth.
Some of the oxygen we find is explained by the pathway to oxygen. Oxygen can be found in the atmospheres of Io, Ganymede, andEuropa.
Life is not possible in Io, the most volcanic world in the Solar System. Life could potentially be found in the oceans of the two planets. Life can't build an atmosphere similar to Earth's. Oxygen is found on these moons.
The oxygen pathway may happen on Earth as well.
Raimund said that they suggest in the article that this happens naturally on Earth.
The next step for the researchers is to see if this pathway works for other molecules. If carbon diselenide is subjected to double ionization, they want to know.
"We want to see if it also happens then, or if it was just a happy coincidence with sulphur dioxide," he stated.
Abiotic O 2 sources have been tackled by other researchers The paper presented evidence for the production of oxygen when exposed to high-energy UV light.
In a paper published in 2015, Japanese researchers showed that near-ultraviolet light can produce O 2 on exoplanets when interacting with water.
There was a small amount of oxygen in the atmosphere before the GOE. The pathways could be to blame since Oxygen is so reactive.
There is a backdrop for this research. One of the telescope's science objectives is to study the chemical makeup of exoplanet atmospheres.
It will be exciting if it finds oxygen. There is more to life than oxygen.
This article was published in the past. The original article is worth a read.