We have evolved to thrive on this type of nutrition due to the fact that our ancestors were heavy on meat and low on carbohydrates.
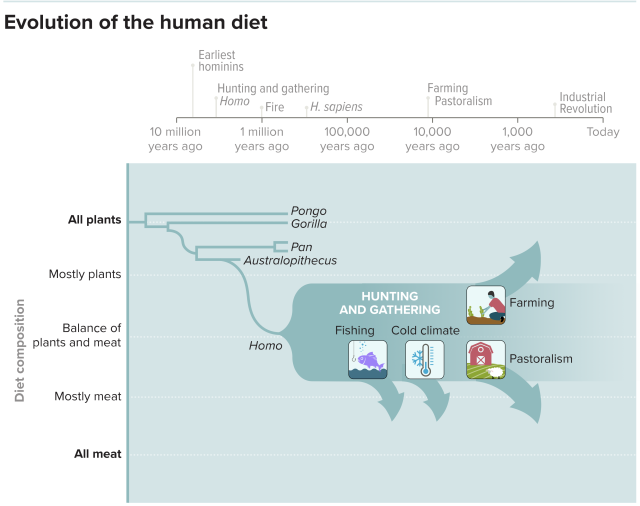
The diet is named after a time when humans were hunting and gathering rather than farming. Herman Pontzer is an evolutionary anthropologist and author of Burn, a book about the science of metabolism. Prehistoric people's eating habits were influenced by a number of factors, including climate, location and season, according to studies.
In the Annual Review of Nutrition, Pontzer and his colleague, Brian Wood, of the University of California, Los Angeles, talk about how we can learn about the eating habits of our ancestors by studying modern hunter-gatherer populations. Pontzer explains in an interview with Knowable Magazine what makes the Hadza's varied diet so different from popular notions of ancient meals.
The interview has been edited to make it clearer.
What is the current Paleo diet like? How do they get our ancestors to eat?
The original Paleo diet is a meat-laden one. Most of the Paleo diet today is very meat- and low-carb, and downplaying things like starchy vegetables and fruits that would only have been available during the season. It is said that humans used to be almost entirely meat-eating.
Our ancestors didn't have a consistent diet. We evolved as hunter-gatherers so we can hunt and gather food. Humans can only target the foods that are present in the area they are interested in. There was a lot of variation in what hunter-gatherers ate.
AdvertisementDue to variability, and also due to people's preferences, there's a lot ofCarbohydrate in most hunter-gatherer diet. Throughout history, honey was important. A lot of these small-scale societies are eating root vegetables that are very high in calories and low in fiber. It doesn't fit with the evidence that an ancient diet would be low in calories.
How did "Paleo" come to be a representation of meat- and low-carb eating?
There are at least two reasons for that. There is a romanticism to hunting and gathering. A lot of what I read on Paleo diet websites is based on a macho view of the past.
There are biases in a lot of the data. Many ethnographic reports were written by men who focused on men's work in the early 1900s. The way a lot of these small-scale societies divide their work is due to the fact that men hunt and women gather.
Since warm-weather cultures were the first to be pushed out by farmers, the available ethnographic data is skewed towards very northern cultures, such as theArctic cultures. Our ancestors had a varied diet. People living near the ocean and moving rivers ate a lot of fish. Populations that lived in forested areas were focused on eating plants.
In the archaeological record, there is a bias towards hunting. Stone tools and bones are evidence of hunting. Plants and wooden sticks don't.