Astronomers said that the impact looks to have been much greater than expected, as they revealed the first images of a spaceship deliberately smashing into an asteroid.
The world's telescopes turned their gaze towards the space rock Dimorphos earlier this week for a historic test of Earth's ability to defend itself against a potentially life threatening asteroid in the future.
NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test hit its target 11 million kilometers from Earth on Monday.
There was a huge cloud of dust after the spaceship hit Didymos.
Alan Fitzsimmons, an astronomer at Queen's University Belfast who is involved in observations with the ATLAS project, said that the James Webb and Hubble images are closer to the ground.

Fitzsimmons told Agence France-Presse that James and Hubble can offer a view of the asteroids from a few kilometers away.
He said it was quite spectacular.
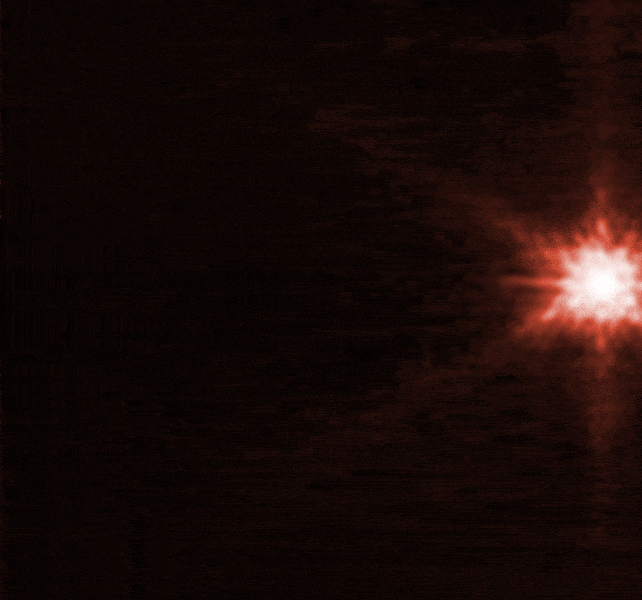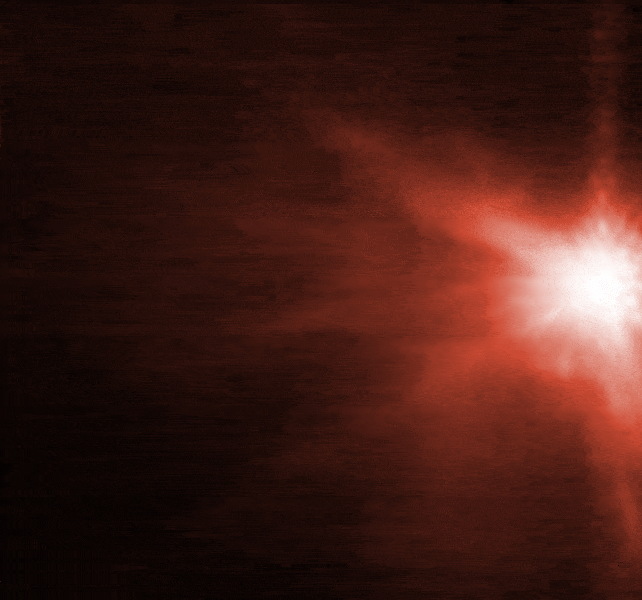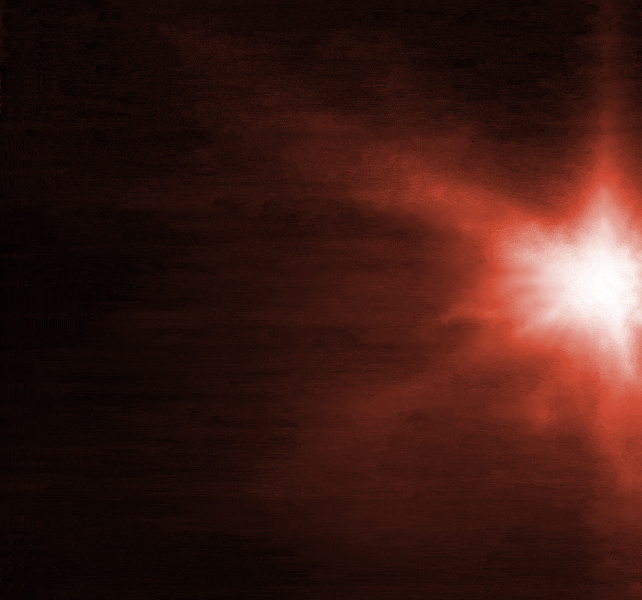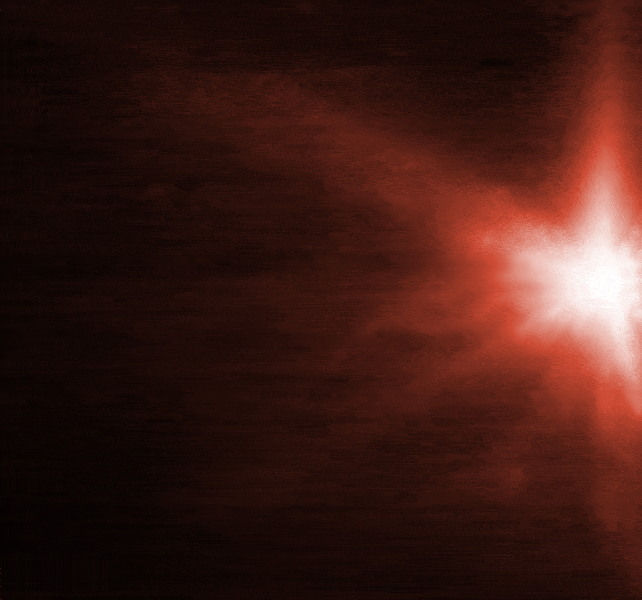
According to a joint statement from the European Space Agency, James Webb and Hubble, an image taken four hours after impact shows "plumes of material streaming away from the center of where the impact took place"
The spray of matter from where DART hit is shown in Hubble images.
The European Space Agency's Ian Carnelli said that the "really impressive" images taken by the two space probes were very similar to the ones taken by the small satellite LICIA.
The manager of the Hera mission said that the images depict an impact that looks a lot bigger than anticipated.
Carnelli told Agence France-Presse that he was worried that there was no left of Dimorphos.
The Hera mission was supposed to survey a crater that was around 33 feet in diameter.
"If there is a crater at all, maybe a piece of Dimorphos was just chunked off."
The true measure of DART's success will be how much it diverted the asteroid's path, so the world can start preparing to defend itself against larger asteroids that could head our way in the future.
It will probably take Earth-bound telescopes and radars at least a week for a first estimate of how much the asteroid has changed.
He said he was expecting a bigger deflection.
It means that this technique could be used for larger asteroids.
We used to think that the only way to get attention was to send a nuke.
Fitzsimmons said that even if there had been no material left over from Dimorphos, DART still would have had a slight affect on its trajectory.
He said that the more material and the faster it was moving, the more of a distraction there would have been.
The amount of matter sprayed from the asteroid, as well as the nature of its surface, will be revealed by the observations from the two telescopes.
It was the first time the two telescopes observed the same body.
Since launching in December and releasing its first images in July, it has been named the most powerful space telescope from Hubble.
The images were a demonstration of the extra science you can get by using more than one telescope at the same time.
Agence France- Presse.