For the first time in history, a spaceship from Earth crashed into an asteroid to see if it could save the planet.
The world's first planetary defense test took place tonight when the DART probe slammed into a small asteroid. The goal is to change the space rock's position around Didymos so that it won't hit us.
The dinosaurs couldn't do that 65 million years ago when the huge asteroid hit the peninsula.
The dinosaurs did not have a space program to help them, but we do, according to NASA's chief scientist and senior climate advisor. DART is an important progress in understanding potential hazard in the future and how to protect our planet from potential impacts.
Related: 8 ways to stop an asteroid: Nuclear weapons & Bruce Willis?
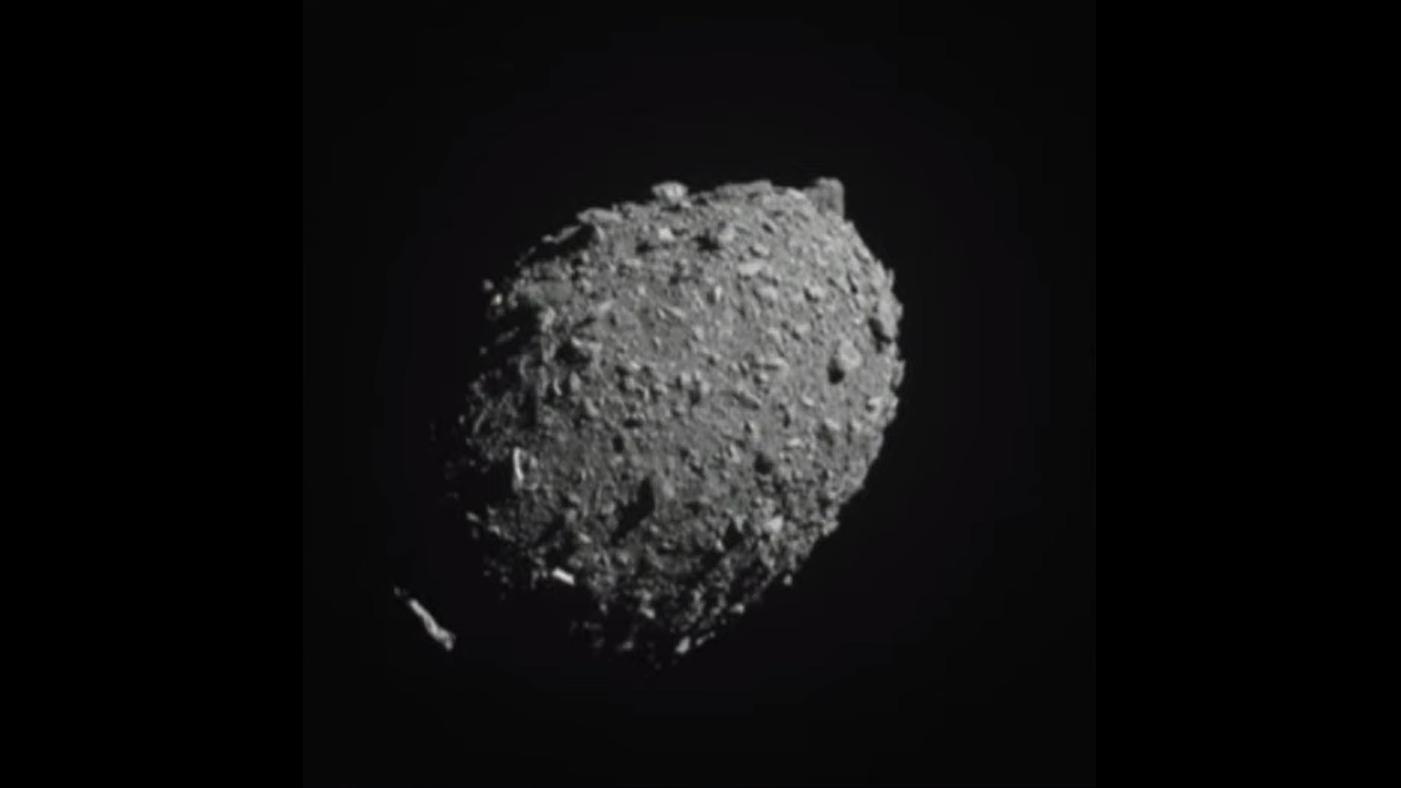

DART crashed into Dimorphos at 7:14 pm. The plane was flying at a speed of over 15,000 mph. The Dimorphos was not large as probes go, but NASA hoped that it could be moved a bit faster around its parent.
Nancy Chabot is the DART coordination lead for the mission for NASA. We sometimes call it a golf cart into the Great Pyramid.
Despite the on-target crash, tensions were running high at DART's mission control center. The navigation system of DART locked on to Dimorphos in the final hour of its approach. The main camera of DART beamed a picture to Earth every second until it crashed into the asteroid.
Andy Cheng came up with the DART mission's concept in 2011. The DART mission was launched in November of 2011.
The asteroid became a detailed landscape of boulders, crags and shadowed terrain as DART closed in. Flight controllers inside DART's mission operations center jumped for joy and exchanged hugs and high fives after the live feed from DART went black. DART hit the bull's eye.

NASA says the DART mission is the first demonstration of a "kinetic impactor" for planetary defense. If an asteroid were to be spotted five or 10 years before a potential impact, it would be a basic method to protect the Earth.
The motion of a body in space is being changed. Tom Statler is a DART program scientist. It's stuff of science fiction books and episodes of 'Star Trek' from when I was a kid, and now it's real.
NASA scientists say that the risk of a catastrophic asteroid impact is real. Roughly 40% of the large asteroids as wide as 500 feet are found by NASA and are regularly scanned for threats to the Earth. A new space telescope is being developed by NASA to find hazardous asteroids. The mission could be launched by the end of the century.
If a hazardous asteroid is detected, humanity needs to have a way to stop it. It's also called DART. Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA's associate administrator for science, told Space.com this morning that they're really excited about protecting life on Earth.
For a few reasons, NASA chose Dimorphos for the DART impact.
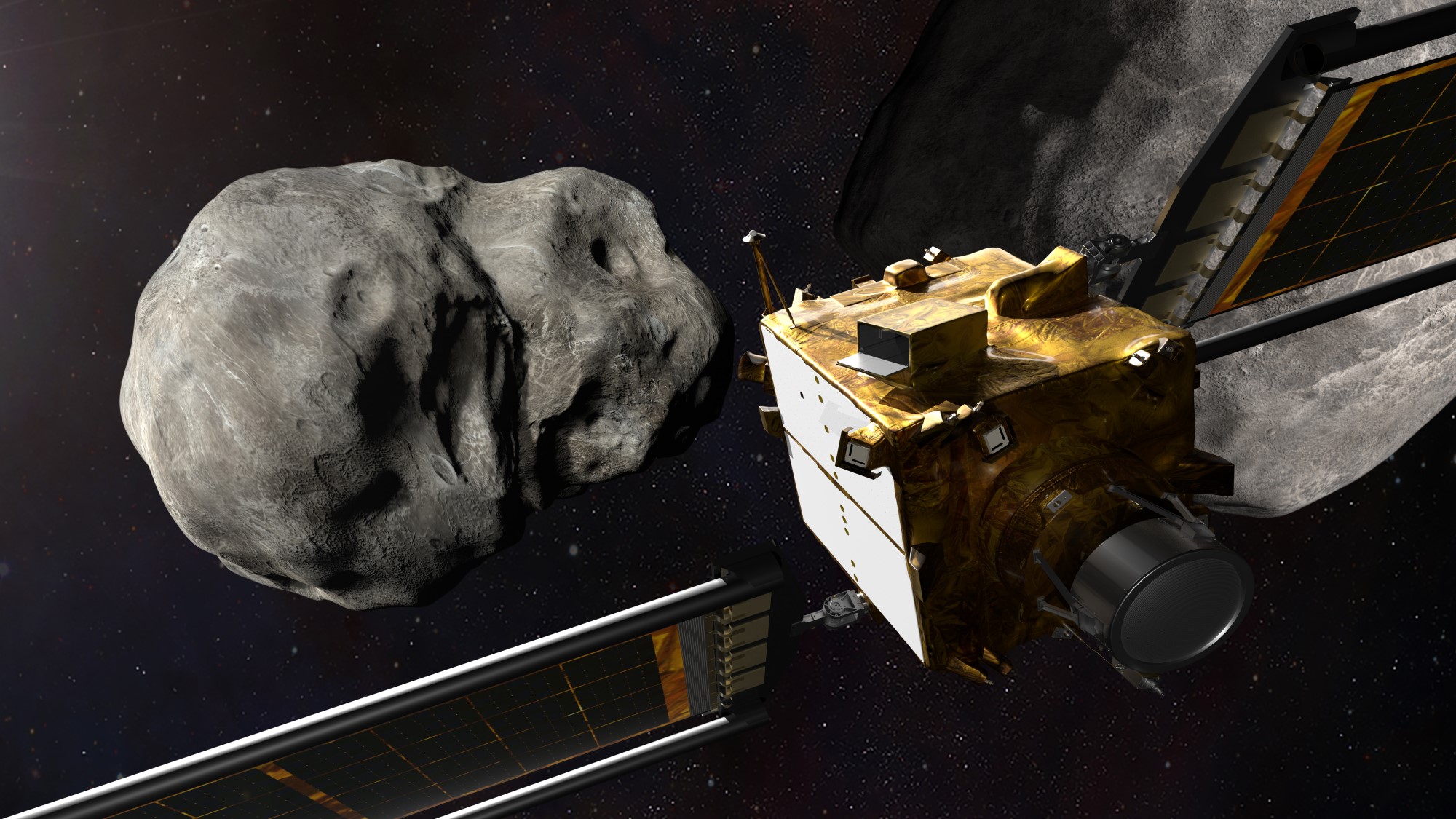

In 1996 and 2003 Didymos and Dimorpos were discovered, they are the first to be studied in detail. Cheng said that using a pair of asteroids meant that NASA could use a single telescope to measure the asteroid's impact.
Didymos and Dimorphos does not pose a threat of impacting Earth in the foreseeable future. It was expected that DART would accelerate Dimorphos just about 10 minutes faster around Didymos, so there was no risk of changing the system's flight path.
Didymos and Dimorphos will be at their closest to Earth in 40 years. The one-way trip from the DART to the Earth can be made in 38 seconds.
It's the right asteroid at the right time.
Astronomers like the fact that Dimorphos is similar to those asteroids that NASA is most worried about. One of the most common asteroid types in our solar system is called an S-type asteroid.
A planetary scientist told reporters in the hours before impact that DART could divert a Dimorphos-sized asteroid.
DART is a first-of-its-kind mission and mission scientists didn't know what to expect at Dimorphos Is the asteroid a large rock or a pile of sand? What was it like? Variables like those can help determine how effective DART will be.
According to the leader of DART's impact working group, the team's simulations and models show a crater up to 20 m wide.
When DART hits its target, Stickle expects it to fragment. There is a chance that DART could be left on Dimorphos.
The DART asteroid- impact mission is explained in pictures.
NASA said that hitting Dimorphos was a feat of engineering, with DART sending a photo every second as it closed in.
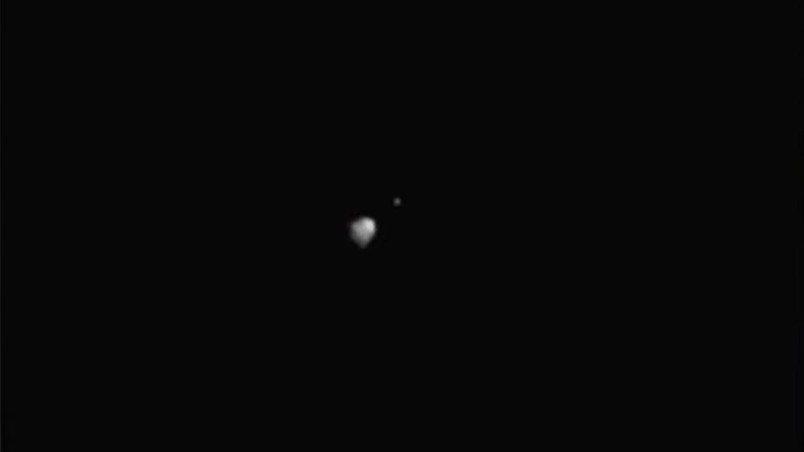
There were people who witnessed its demise. DART released a small cubesat to follow in the wake of the asteroid crash. Closeup images of the impact and the ejected particles from Dimorphos will be revealed in the photos from that cubeat.
The crash was watched by other spaceships.
The crash was tracked by NASA's new James Webb Space Telescope, the Hubble Space Telescope, and the Lucy mission. On Earth, a vast network of ground-based telescopes were trained on the event and will be following the Didymos-Dimorphos system over time.
"Our requirements are for 73 seconds, but we think we'll change by 10 minutes," Statler said.
It will be awhile before we know if the DART impact was a success.
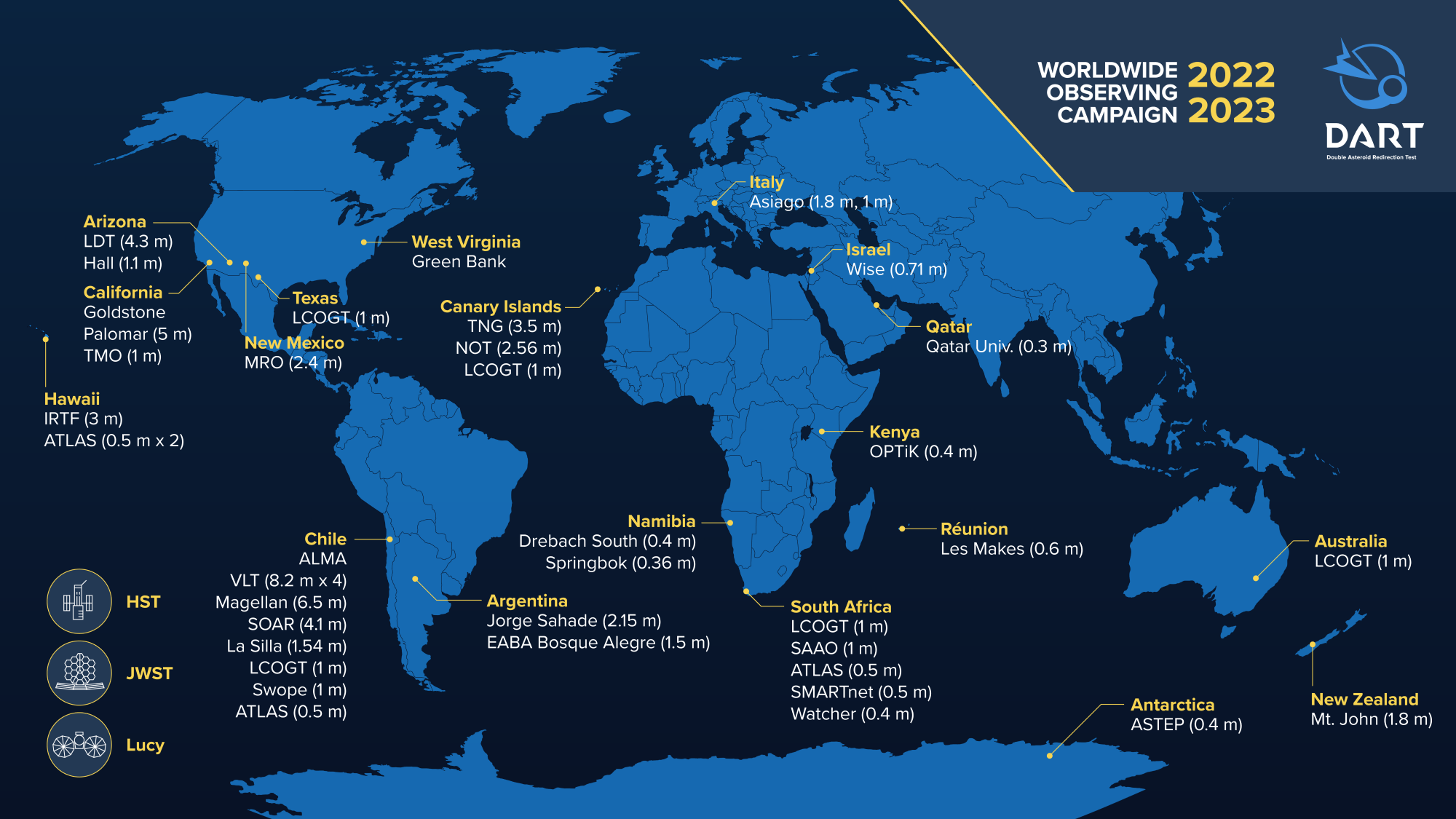
The Didymos-Dimorphos asteroid system will be tracked by more than 30 telescopes around the world over the next six months. The first radar observations of the impact could come as early as Tuesday, according to a planetary scientist.
Thomas said that they would be observing Didymos until it was no longer observable.
The DART effort has brought in volunteer student and university groups around the world.
There are a lot of ground-based telescopes. Having lost count is very exciting.
The Didymos-Dimorphos asteroid system will be followed up by the European Space Agency. To study the space rocks and the crater on Dimorphos created by DART, Hera is going to launch a spaceship to the asteroid in 2024.
The technology of hitting the asteroid is difficult. There is more to come after that.
If you want to follow Tariqjmalik, email him at tmalik@space.com We encourage you to follow us on social media.