The seasonal flu shot protects against the flu and is given every year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that everyone over the age of six months receive a flu shot.
Young children, people with underlying health conditions, and pregnant women are all at risk of contracting the flu. The best way to prevent the flu is to get a flu shot.
Each year a new vaccine is made for the flu. Predicting which flu strains will be most common in the upcoming season is how scientists make the vaccine.
One of the reasons that people have to get a flu shot on an annual basis is because the vaccine needs to be reformulated due to the flu virus drifting in its genetic composition.

The CDC recommends that people get their flu shot by the end of October because the flu season can start and end differently. The peak of flu activity is in February.
"We want to make sure that as many people as possible are protected against the flu before it becomes a real problem," Schaffner said.
Although most flu vaccines are given before Thanksgiving, people can still get their vaccine in the winter. It's too late to get a flu vaccine if you're traveling to the Southern Hemisphere for the flu season, according to William Schaffner.
It takes about two weeks for a person to build up immunity after getting a vaccine.
The CDC has a website that people can use to find flu shot locations.
A flu shot can't be given to children younger than 6 months. Those who have had a severe allergic reaction to a flu vaccine in the past should not get that type of flu shot again, and they should speak with their health care provider about whether they can receive another type of flu shot.
The CDC says that people who have had a life-threatening reaction to flu-vaccine ingredients should not get flu vaccines with those ingredients, and they should speak with their health care provider about whether there is a flu vaccine that's right for them. Antibiotics are added to some flu shots to make them less likely to be contaminated withbacteria. Some flu shots have antibiotics in them.
Even if the flu shot is made with egg-based technology, it's still recommended for people with egg allergies to get it. People with egg allergies are not likely to have a severe reaction to the vaccine. The CDC says that people who have had a severe allergic reaction to eggs should get a flu shot. Several types of flu shots are egg free.
People with a history of Guillain-Barré syndrome should discuss with their doctor if they can get a flu vaccine. People with this condition can't get a flu shot. In rare cases, the condition has been linked with flu vaccine, but it's not known why.
You should talk to your doctor before you get a flu shot if you are not feeling well. If you have a high temperature, you shouldn't get the flu vaccine. You can still get a flu shot if you have a mild cold or headaches.
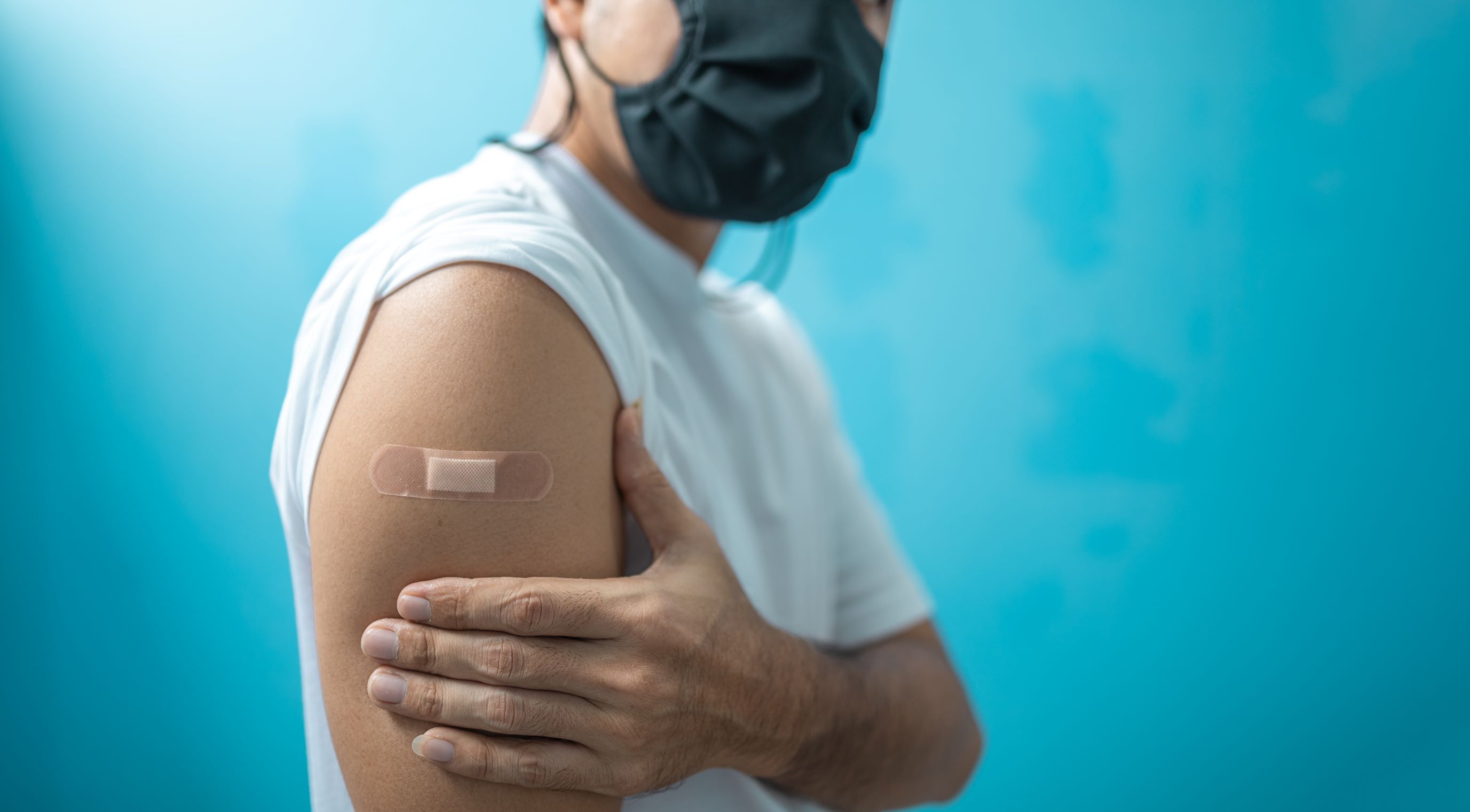
Mild side effects from the flu shot include redness or swelling at the injection site, low- grade fever, and aches. About 1% to 2% of people who get a flu shot will experience a side effect. Within a few days, these effects should go away.
Allergic reactions can be a rare but serious side effect. According to the CDC, symptoms of serious side effects include difficulty breathing, swelling around the eyes or lips, hives, racing heart, dizziness and high temperature. You should seek medical care if you have serious side effects. The CDC says it's important to ask your health care provider to file a Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System report.
Compared with other types of flu shots, the flu spray vaccine can cause a slightly different set of side effects. Side effects of the flu spray can be serious for children. Side effects from the spray can be experienced by adults. The CDC says that the side effects last a short time.
How well the flu strains in the vaccine match the strains in circulation is one of the factors that affects the vaccine's effectiveness. According to the CDC, when the vaccine strains are a good match with the ones that are circulating, people who aren'tvaccinated are 40% to 60% less likely to get the flu.
The effectiveness of the vaccine depends on the age and health status of the person receiving it. Older adults may have a weaker immune response to the H3N2 component of the flu vaccine.
There are many benefits to getting a flu vaccine. Several studies have shown that people who get the flu will have less severe symptoms if they arevaccinated. A study published in the journal Vaccine found that people who were hospitalized with the flu were less likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit if they werevaccinated. Vaccination patients spent four fewer days in the hospital, on average, than those who weren'tvaccinated, according to a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The flu shot doesn't work as well as other vaccines.
The flu vaccine protects against four strains of the flu. Two strains of H1N1 and H3N2 are included, as well as two strains of B/Yamagata and B/Victoria. The CDC says that all flu shots for the next two decades are quadrivalent.
In addition to the standard-dose flu vaccine given through a needle, flu shots are available in many other forms. There is a high-dose version for people ages 65 and older, an "adjuvanted" version that helps boost the immune response, and a "cell-based" version that's grown in animal cells.
The CDC says that there is a needle-free flu shot that uses a high pressure stream of fluid to inject the vaccine. It is approved for people over the age of 64.
The high-dose flu vaccine, called Fluzone High-Dose Quadrivalent vaccine, is recommended for people ages 65 and older by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. According to the CDC, recent studies suggest that these vaccines are more effective for older adults than other vaccines. The CDC doesn't recommend one vaccine over the other because it's linked with increased protection for older adults. Older adults should get a standard dose of the vaccine instead of waiting for the recommended shots to be available.
The composition of the flu shot is not the same as it was last year. Two components of the flu shot were updated for the upcoming season.
The CDC says that the flu shot contains strains of the flu.
There are two different types of flu vaccines that don't use eggs. Cells from mammals are used to grow the inactivated flu virus in cell-based flu vaccines. Scientists combine a lab-made antigen specific to the flu virus with a baculoviruses in order to create a synthetic flu vaccine.
The egg-based vaccine and the cell- or recombinant-based vaccine contain the same components as the H1N1 component.
Flu activity was low in most of the U.S. In Texas, New Mexico and Georgia, which are currently reporting moderate levels of flu activity, as well as the District of Columbia, which is reporting high flu activity, activity is already increasing.
You shouldn't wait to get your flu shot even if flu activity is low. It takes people about two weeks after getting a vaccine to develop an immunity against the flu.
According to some health experts, the flu season in the Southern Hemisphere could be bad this year.
"I think it's going to be a worse year for flu than we've seen in the last few years," Dr. Bessey Geevarghese said. The end of most COVID-19 restrictions has led to the return of flu. People are more likely to get the flu this year because they have had less exposure to it over the past two years.
I don't know how to tell if I have the flu.
If you have symptoms similar to the flu, your doctor can order a test to see if you have the disease. There are tests that look for both the flu and the COVID-19 at the same time.
Is it a good idea to get a flu shot during the flu season?
Flu shots are the best way to protect yourself from the flu. If you get a flu shot you can wear a mask and get a vaccine against the coronaviruses.
Is a flu vaccine safe against COVID-19?
Flu shots don't protect against the new disease. There are two vaccines against the disease that have been approved for use in the US. The risk of getting sick from the flu, as well as the risk of hospitalization and death from flu, can be reduced by getting a flu shot.
I would like to get a flu shot at the same time.
The CDC says that people can get a flu vaccine and a COVID-19 vaccine at the same time. According to the CDC, people get the same protection from diseases even if they are given a vaccine alone. If both shots are given at the same time, people are more likely to experience fatigue and muscle aches. The study found that people who got a flu shot and a COVID-19 booster shot at the same time were more likely to have side effects. The CDC said that the side effects were mild and resolved quickly.
You should aim to get a flu shot by the end of the year if you haven't received a vaccine against COVID-19.
Schaffner said that it is a myth that you can get the flu from the vaccine.
People can't get the flu from a flu vaccine. Some people may catch the flu if they are exposed to the flu during this time period because it takes about two weeks for people to build up immunity. Schaffner said that some people may wrongly attribute a cold to the vaccine.
The vaccine is weakened so that it can't cause the flu. The cold temperatures of the lungs and other parts of the body make it impossible for the viruses in the spray to replicate. The cold causes a small infections in the nose. Schaffner said that this infection doesn't cause symptoms in most people, but it does cause symptoms in some people. The CDC says that these symptoms are usually short lived.
The body will make an immune response against the flu. Better protection against the real flu is provided by that, a virus that can make you seriously ill.
Studies show that the flu vaccine is safe for pregnant women. It is important for pregnant women to get a flu shot.
Schaffner said pregnant women have a tendency to get a more severe disease when they get the flu.
During the first six months of the baby's life, when the baby is too young to get a flu shot, pregnant women should get a flu vaccine. Schaffner said that the mother gives protection to her baby.
There are 12 early signs of a baby being born.
The flu is caused by a Viruses and antibiotics only killbacteria. Antibiotics don't help people get better from the flu.
If you give the drugs within 48 hours of the start of symptoms, they'll work. Dennis Cunningham is the medical director of infection prevention at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
The drugs might help patients with severe flu. For most people who aren't hospitalized, these drugs can only cut down on the duration of the flu by a day or two.
Cunningham told Live Science that people should get the flu vaccine every year.
The strains of the flu virus vary from year to year. He said that there are more than one type of viruses that cause the flu. According to the CDC, the most likely strains of the flu to cause illness are identified each year.
The immunity you develop after you get the shot fades over time. "If you get your shot in August, you'll be safe through March, but your immune system won't be ready for the next flu season," Cunningham said.
Cunningham said that Thimerosal has never been shown to be dangerous. He said that there is a type of mercury linked with nervous system damage. Certain types of fish, such as swordfish, are not recommended for pregnant women to eat due to concerns over mercury levels.
There is an ethyl mercury compound that has anti-bacterial properties. Almost all U.S. vaccines were taken out of circulation in 2001 because of the controversy surrounding the preservative.
Health care providers can get the flu vaccine in bottles and small jars. Cunningham said that a small amount of thimerosal is added to multidose bottles to make sure there is nobacteria in the vaccine. There are individual-dose bottles.
He noted that the flu vaccine has no trace of the deadly substance.
Cunningham stated that the flu is a very serious disease.
Between 15 million and 60 million cases of the flu are reported in the United States every year. Between 3000 and 50,000 people in the US die of the flu each year. The CDC estimated that 38 million Americans were exposed to the flu and 22,000 died from it.
Cases of the "stomach flu" are mistaken for the flu and people don't think it's serious. Cunningham said that true flu is an illness of the lungs and respiratory Tract. He said that people with an infectious disease may develop a high temperature.
People with the stomach flu have a variety of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Influenza doesn't usually cause these symptoms.
The article is not meant to give medical advice.
The article was last updated in September of 2022. Nicoletta Lanese is a writer for Live Science.
It was originally published on Live Science