
The most precise measurement to date of two properties of a hypernucleus has been released by the ALICE collaboration.
Atomic nuclei and their antimatter counterparts, known as antinuclei, are produced in high-energy collisions. Hypernuclei are formed on a regular basis. Hypernuclei are unstable particles containing quarks of the strange type and are made up of hyperons.
Hypernuclei are fascinating to physicists because they are rare in the natural world and, although they are traditionally made and studied in low-energy nuclear-physics experiments, it's difficult to measure their properties.
The lightest hypernucleus has been observed at the collider, which is composed of a protons, a neutron and a Lambda.
The ALICE team looked at a sample of about one thousand hypertriton produced in the second run of the LHC. The hypertritons fly for a few centimeters inside the ALICE experiment before decaying into a charged pion and a helium 3 nucleus, which the ALICE detectors can catch and identify. The daughter particles were looked at by the ALICE team.
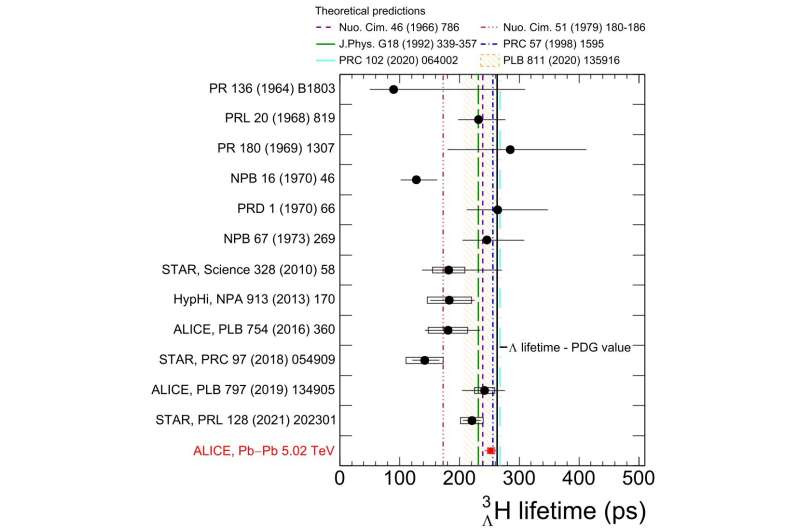
The most precise measurement of two of the hypertriton's properties were obtained by analyzing this sample of hypertriton, one of the largest available for these "strange" nuclei.
The internal structure of this hypernucleus and the nature of the strong force binding it together are fundamental to understanding. The study of this force can offer valuable insight into the particle interactions that may take place in the inner core of a neutron star. The creation of hyperons is predicted to benefit from the dense core.
The ALICE measurement shows that the interaction between the hypertriton's hyperon and its two nucleons is very weak.
The ALICE collaboration was able to study antihypertriton and determine their lifetime due to the fact that matter and antimatter are produced in almost equal amounts. Antihypertriton and hypertriton have the same lifetime according to the team. It is possible to find a slight difference between the two lifetimes.
ALICE will continue to investigate the properties of the hypetriton with the data from the third run of the LHC.
More information: ALICE Collaboration, Measurement of the lifetime and Λ separation energy of 3ΛH. arXiv:2209.07360v1 [nucl-ex], arxiv.org/abs/2209.07360 Citation: New insight into the particle interactions that may take place at the hearts of neutron stars (2022, September 21) retrieved 21 September 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-09-insight-particle-interactions-hearts-neutron.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.