There are some signs that you are in love. Is it possible to get someone out of your mind? Are you thinking about them when you should be doing something? Are you imagining your futures? There are a number of telltale signs that you are in love.
Scientists have come up with a definition of "fall in love." The brain of a person in love is very different from the brain of a person in a long-term relationship, according to researchers. Helen Fisher is an anthropologist at Rutgers University and one of the leading experts on the biological basis of love. There are a number of signs that you're in love.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN MEDICALLY REVIEWED BY
You begin to believe your beloved is unique when you're in love. It's not possible to feel romantic passion for anyone else. This monogamy results from elevated levels of dopamine in the brain, according to an article in the journal Archives of Sexual Behavior.

People who are in love tend to focus on the positives of their loved one, while ignoring the negatives. When partners are idealized, relationships are more successful.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
The people who are in love focus on trivial events and objects that remind them of their loved one. Being in love prevents people from focusing on other things.
This focused attention is thought to be caused by elevated levels of central dopamine and a spike in central norepinephrine.

Falling in love can lead to emotional and physical instability. You bounce between euphoria, euphoria, increased energy, sleeplessness, loss of appetite, trembling, a racing heart and accelerated breathing, as well as anxiety, panic and feelings of despair when your relationship suffers the smallest setbacks.
According to an article in the journal Philosophy, Psychiatry and Psychology, mood swings are related to drug use. When people are shown pictures of their loved ones, the same regions of the brain that are activated by drugs are activated. Being in love is a form of addiction that can lead to withdrawal and relapse.

According to Fisher, going through some sort of adversity with another person heightens romantic attraction. When a reward is delayed, dopamine-production in the mid-brain region becomes more productive.

According to Fisher, people who are in love spend more than 85% of their waking hours thinking about their love object. This form of obsessive behavior is called intrusive thinking and may be caused by a condition that has been associated with obsessive behavior in the past.
Men who are in love have lower levels of a brain chemical than men who are not in love, according to a study. Sixty five percent of the time the men and women were awake, they were thinking about their partner.
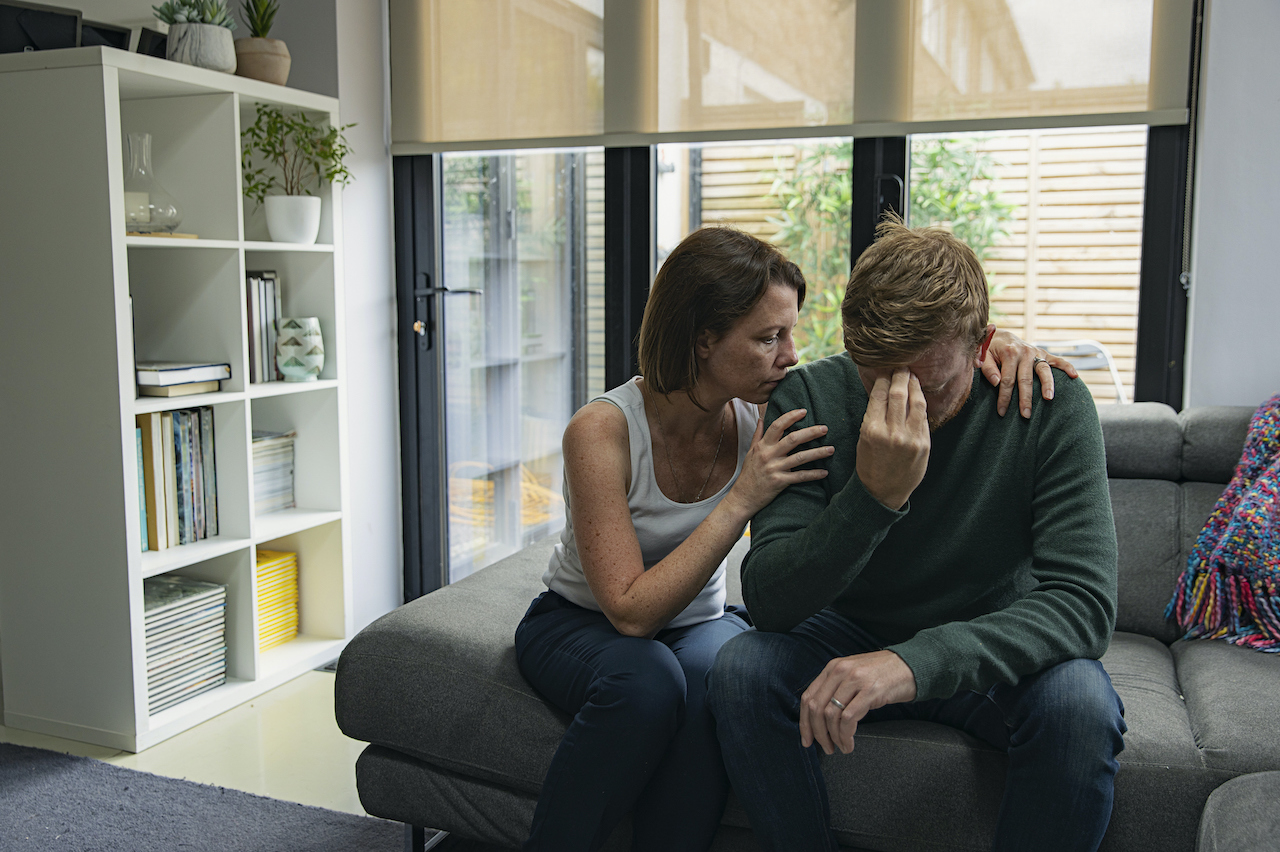

People in love often show signs of dependency on their relationship, such as possessiveness, jealousy, fear of rejection, and separation anxiety. Fisher and her colleagues looked at the brains of people who were still in love with someone even though they had been rejected.
The forebrain areas like the cingulate gyrus have been shown to be involved in cocaine cravings. The obsessive behaviors associated with rejection in love could be explained by theActivation of areas involved in cocaine addiction.

Longing for emotional union with a beloved, seeking out ways to get closer and day dreaming about a future together are all signs of love. According to an article by Harvard University, when Serotonin levels start to return to normal levels, the hormone O2 starts to increase in the body. More serious relationships are created by this neurotransmitter.
Lucy Brown is a neuroscience professor at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Magnetic resonance studies show that primitive neural systems underlying drive, reward recognition and euphoria are active in almost everyone when they look at their thoughts. Brown said that this puts romantic love in the company of survival systems.
The human reproductive strategy includes romantic love. Pair-bonds help us survive. We were built to experience love and be driven away from it.

People who are in love feel a strong sense of sympathy for their partner, as well as being willing to sacrifice their own life for that partner.
Scientists discovered patterns in the brain activity of people who were in love. People who were in a long-term loving relationship were more active in their mirror neurones.

Falling in love can cause a person to change their priorities. A study presented at the " Being Human" conference found that people are attracted to their opposites at least their "brain-chemical" opposites.
She found that people with so-called testosterone -dominant personality were more likely to be attracted to mates with similar personality types.

Those who are deeply in love often experience sexual desire for their beloved, but there are strong emotional strings attached: The desire for sex is coupled with a desire for sexual exclusiveness and extreme jealousy when the partner is suspected of infidelity. O2 is released during sex. Social bonds are created by this hormone and trust is developed by it.
The attachment is thought to have evolved so that an in-love person will compel his or her partner to spurn other suitors in order to ensure that the couple's courting is not interrupted until conception has occurred. This evolved as a biological need, allowing people in romantic relationships to focus their energy on one person.

The craving for emotional union is more important than the desire for sexual union. 64 percent of people in love disagreed with the statement, "Sex is the most important part of my relationship with my partner."

People who say they are in love often say their passion is uncontrollable.
400 men and women in Connecticut were asked to respond to 200 statements about romantic love in a 1979 book. Participants said their obsession was irrational and uncontrollable.
According to Fisher, a business executive in his early 50s wrote about an office crush that was not under voluntary or logical control. I am directed by it. I try to argue with it, to channel it into sex, to deny it, to enjoy it, and to make her respond! Fisher reported in 2016 that the thought of Emily is an obsession even though they have no chance of making a life together.

Being in love doesn't always last forever and psychologists say that the early euphoric stage lasts no longer than 3 years. It can either evolve into a long-term relationship that psychologists call "attachment" or it can disappear and the relationship can't be saved. The "in love" phase lasts longer if there are physical or social barriers that prevent partners from seeing each other frequently.
If you want to learn more about Helen Fisher's research on the brain in love, you can watch her talk. The science of love and attraction is explored in the book The Science of Love and Attraction.
"Romantic love: an fMRI study of a neural mechanism for mate choice" was published in the Journal of Comparative Neurology.
There are differences in Neural Response to Romantic Stimuli in monogamous and non- monogamous men. There is an Archives of Sexual Behavior article.
Positive illusions have benefits in terms of idealization and satisfaction. The journal of personality and social psychology was published in 1996
Cognitive control in lovers is reduced. The release is at: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013-11-131111091355.htm
"Love addiction and when should it be treated?" The article is titled "Philosophy, Psychiatry and Psychology"
There are reward, addiction, and emotion regulation systems associated with rejection in love.
"Defining the brain systems of attraction and attachment." The archives of sexual behavior was published in 2002.