Ours is the only world in the Universe that we know is hospitable to life.
Earth is often used as a template for other planets in other planetary systems.
A new study has shown that Earth is not as nice as it could be. If Jupiter moved a bit, it could be even better.
It's important because it's difficult to figure out which parts of the Solar System contribute to Earth's habitability.
It could help us understand what makes a planet hospitable.
"If Jupiter's position remained the same, but its shape changed, it could increase this planet's habitability," says planetary scientist Pam Vervoort.
A lot of people think that any change in Jupiter's position could be bad for Earth. Both assumptions are incorrect.
The new set of parameters provided by the results have implications for the search for planets outside the Solar System.
Although we don't currently have any tools that can measure the habitability of an exoplanet, scientists have been collecting a population of worlds at which we should take a closer look.
In relation to its host star, the exoplanet needs to be at a distance not so close that any surface liquid water would evaporate or that the water would freeze.
Is the size and mass of the exoplanet similar to Earth, Venus, or Mars? Do you mean gassy, like Jupiter, Saturn, or the other planets?
It has been suggested that a Jupiter-like gas giant in the same system could be a good indicator of habitability. There are some things that appear to be different.
The international team of researchers published a study in which they showed that changing the Jupiter's position could cause the Solar System to be unstable.
More simulations have shown that the opposite can be true, which will help narrow down the range of gas giant circles.
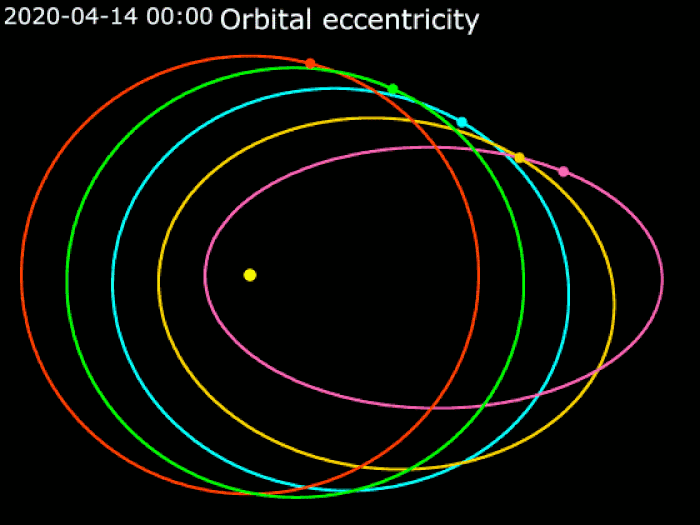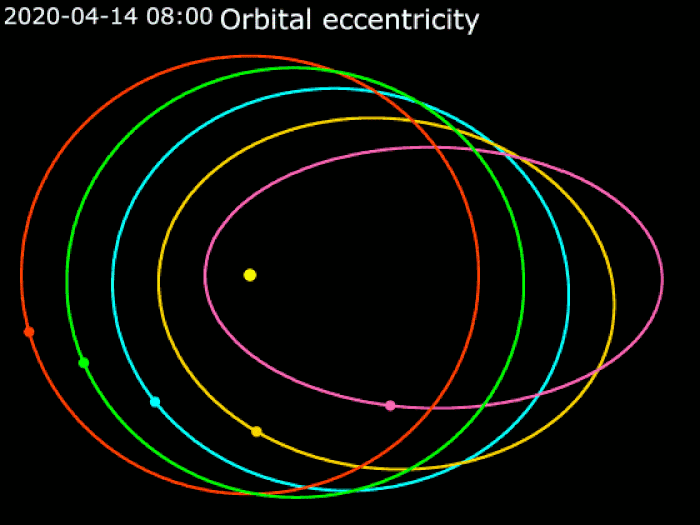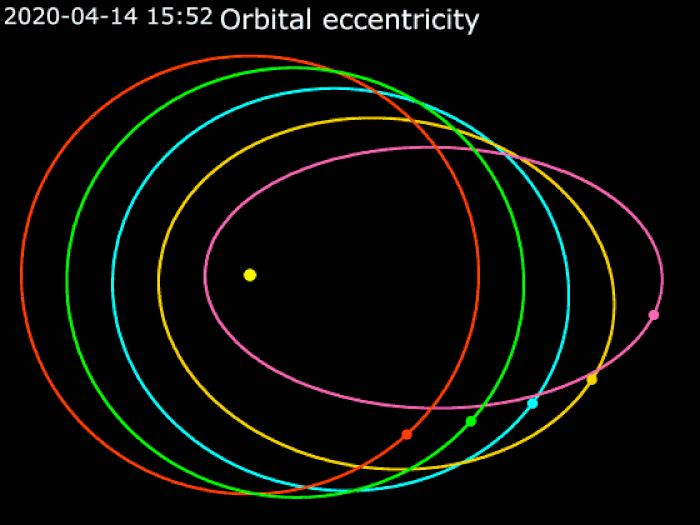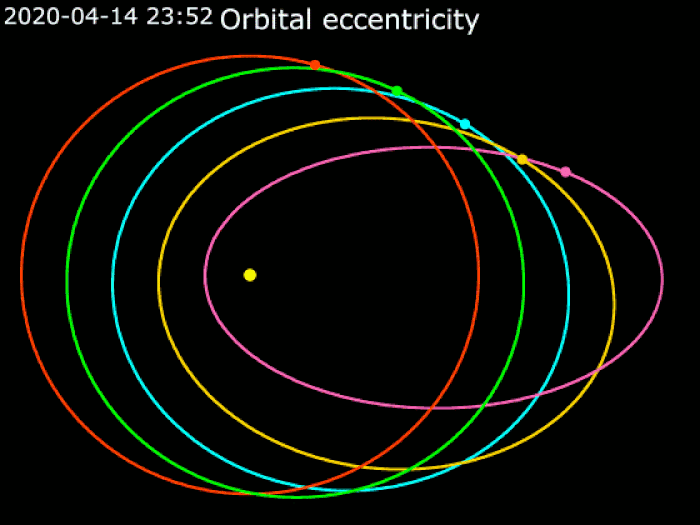
The study was done using the degree to which Jupiter's orbit is elliptical and long.
Jupiter is almost circular in shape.
It has a noticeable effect on the rest of the Solar System. Jupiter is 2.5 times the mass of all the other planets combined.
The effects of Jupiter's eccentricity on the other planets are real.
Earth will see an increase in eccentricity. The researchers found that some parts of the planet would warm up into a warm and hospitable range.
Jupiter is closer to the Sun than Earth is. It will cause our home planet to tilt more sharply on its axis and give us seasonal variations.
A sharper tilt would cause a lot of the planet to freeze. The area covered by winter sea ice would be four times larger.
The results can be applied to any multi-planet system we find.
They show how many factors may have affected our presence here on our pale blue dot. What would happen to the Solar System if it were to change?
Water on a planet's surface is a very simple first metric, but it doesn't account for the shape of a planet or seasonal variations a planet might experience.
Understanding the impact that Jupiter has had on Earth's climate through time, how it has changed us in the past, and how it might change us again in the future is important.
The research has appeared in a journal.