Earth is as friendly to life as any planet can possibly be. A new study shows that Earth could be more hospitable in the future.
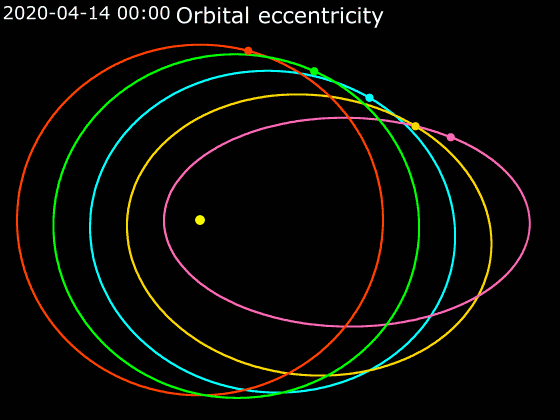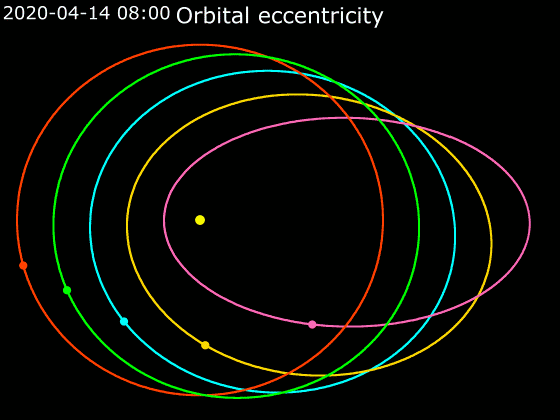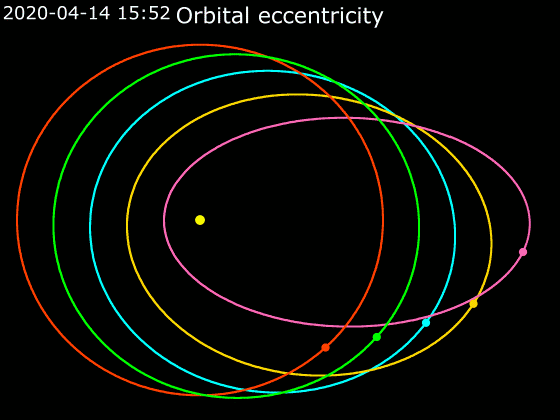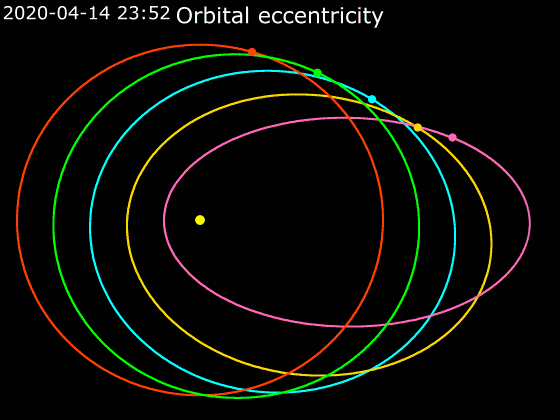
The distance between the star and the planet doesn't change when the planet is perfectly circular. Most planets have an elliptical shape around their stars. The climate is affected by the planet getting closer to its star.
An alternative solar system was created using models from the solar system. They found that if Jupiter became more eccentric, it would cause a change in the shape of Earth's orbit.
"If Jupiter's position remained the same, but the shape of its orbit changed, it could increase this planet's habitability," said Pam Vervoort, the lead study author.
The Earth's surface is able to support multiple life forms. Some parts of the Earth would get closer to the sun if Jupiter pushed the Earth's elliptical path. Parts of the Earth's surface that are currently sub- freezing would get warmer.
Two long-held assumptions about our solar system have been upended by this result.
Vervoort said that many people are convinced that any change in Jupiter's position could be bad for Earth. Both assumptions are incorrect.
The researchers want to apply this finding to the search for exoplanets.
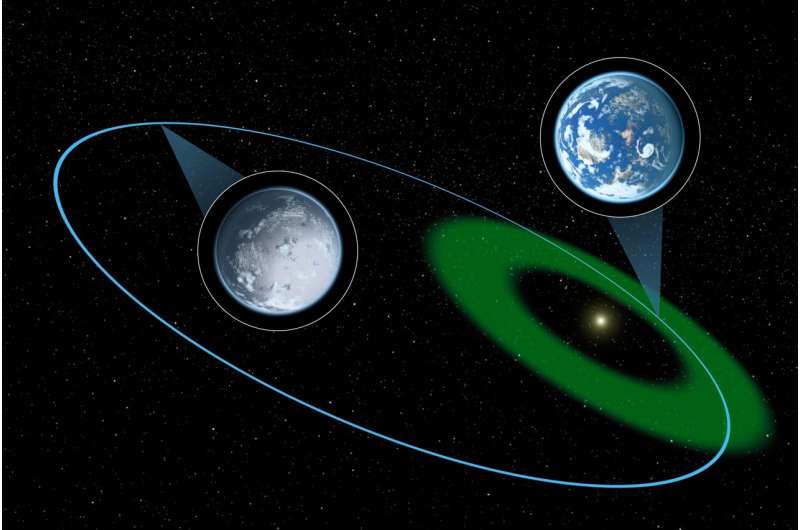
The habitable zone is the distance between a star and a planet to determine if there's enough energy for liquid water on the planet's surface.
The planet has seasons due to the fact that different parts of the planet get more or less direct rays. During one season, some parts of the planet may be pleasant, while others may be very hot or cold.
Kane said that having water on its surface is a very simple first metric.
The telescopes are able to measure a planet's position. Habitability can be affected by the degree to which a planet is tilted towards or away from a star. The part of the planet that is tilted away from the star is cold.
If Jupiter were positioned closer to the sun, it would cause large sections of the Earth's surface to freeze.
It is more difficult to measure tilt than it is to estimate the mass of a planet.
The movement of a giant planet is important in the quest to make predictions about the habitability of planets in other systems and to understand its influence in this solar system.
Kane said it's important to understand the impact Jupiter has had on Earth's climate through time, how it has changed us in the past, and how it might change us again in the future.
More information: Pam Vervoort et al, System Architecture and Planetary Obliquity: Implications for Long-term Habitability, The Astronomical Journal (2022). DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ac87fd Journal information: Astronomical Journal