It was around 100 million years ago. Although the shark is already swimming in the prehistoric oceans, we still have dinosaurs roaming the land and odd looking birds. roses and flowering plants are making their debut, along with other conifers, and with them come bees and ants. It's warm, volcanically active and humid and there's no ice sheet in sight.
There were icy conditions in the region of the South Pole.
John Cottle said that it was probably multiple glaciers or a large ice sheet. He said there was evidence that polar ice existed at the height of global greenhouse conditions. The study was published in the journal.
There is a puzzle.
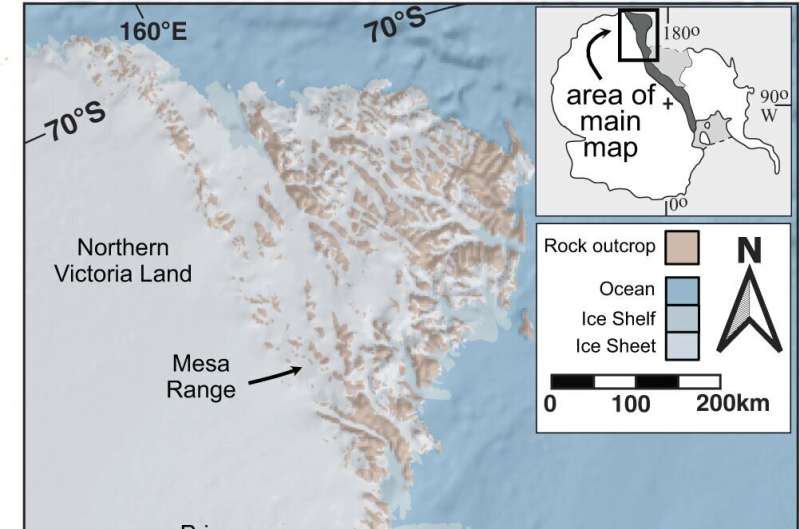
Today is fast-forward to yesterday. We're in the middle of the ocean. There is a large group of exposed glassy rock along the Transantarctic Mountains next to the Ross Ice Shelf.
When Cottle was a graduate student he heard about the rocks. The BRIC is unusual because the rocks' composition and formation are atypical of nearby rock formations with large amounts of glass and layers of altered minerals.
Cottle and his team encountered an "unusually large amount of water" as they analyzed how the BRIC was formed.
"You have a hot rock that interacts with water, and as it cools, you put it into the glass," he explained. You can tell where that water came from by looking at the composition. It's possible that it came from the magma or it's possible that it's external.
They were expecting the water in the magma to cause the rock to change. They found a record of a climate process that was thought to have never happened.
As the molten rock cooled into glass just beneath the Earth's surface, the researchers found that some of the water came from magma as it plumed upward from Earth's interior.
Cottle said that most of the water in the rocks is outside. The oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of the water is very similar to the composition of the snow and ice.
The rock and its alteration were dated by Cottle and team.
He said that the rocks are about 180 million years old. What you don't know is when the change happened. They were able to find a younger age of the rock. "When these rocks cooled and were altered, you can match the age of the alteration to the composition of the rock," he said.
There are volcanic rocks that are 700 km north of the BRIC that have the same age as the one that caused the last ice age. If we recover the same results that we've already found, we'd like to go to other places in the area to see if we can determine the scale of the ice age.
"If we were to find evidence of large sheets of ice from the past, we would have to think about the environment differently than we do now," Cottle said.
The research done in this study was done by four other people.
More information: Demian A. Nelson et al, Ultra-depleted hydrogen isotopes in hydrated glass record Late Cretaceous glaciation in Antarctica, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32736-9 Journal information: Nature Communications Citation: Research team confirms icy conditions existed in South Pole region during Late Cretaceous period (2022, September 7) retrieved 7 September 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-09-team-icy-conditions-south-pole.html This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.