Skywatchers will be able to see a mountain range on the moon.
The great Imbrium Basin is a vast lava plain on the lunar surface that was created by a massive impact from space.
The largest basin on the side of the moon is called the Mare Imbrium. The South-Pole-Aitken Basin on the moon's far side is the largest crater in the solar system.
There is a guide to what to look for on the moon.
The Montes Alpes is a group of mountains stretching 173 miles. Mount Blanc is 2.2 miles above the moon.
The Alpine Valley was formed when the moon's crust dropped between parallel fault lines. The area can be seen with binoculars or a telescope.
The Caucasus Mountains are a mountain range that sinks beneath a lava-flooded plain and connects Mare Imbrium with Mare Serenitatis.
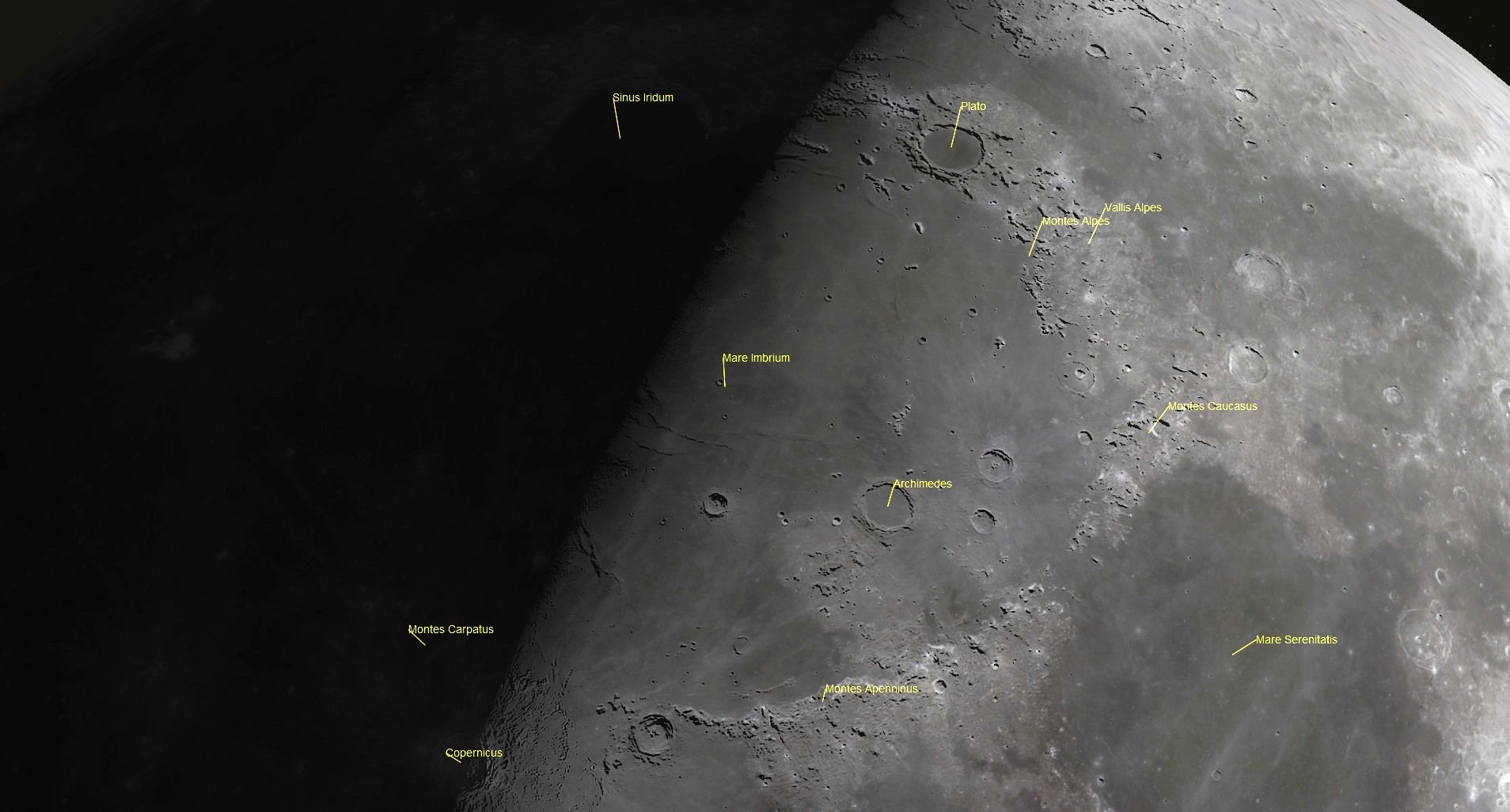

The Apennine Mountains are located to the southeast of the Mare Imbrium. The Apennine Mountains, which were named for the Apennine Mountains in Italy, rise up from the nearby Eratosthenes and rise to meet the Mare Imbrium at the Promontorium Fresnel.
The mountain range is located on the south side of the crater. The Bay of Rainbows is a plain of basaltic lava located to the northwest of the crater.
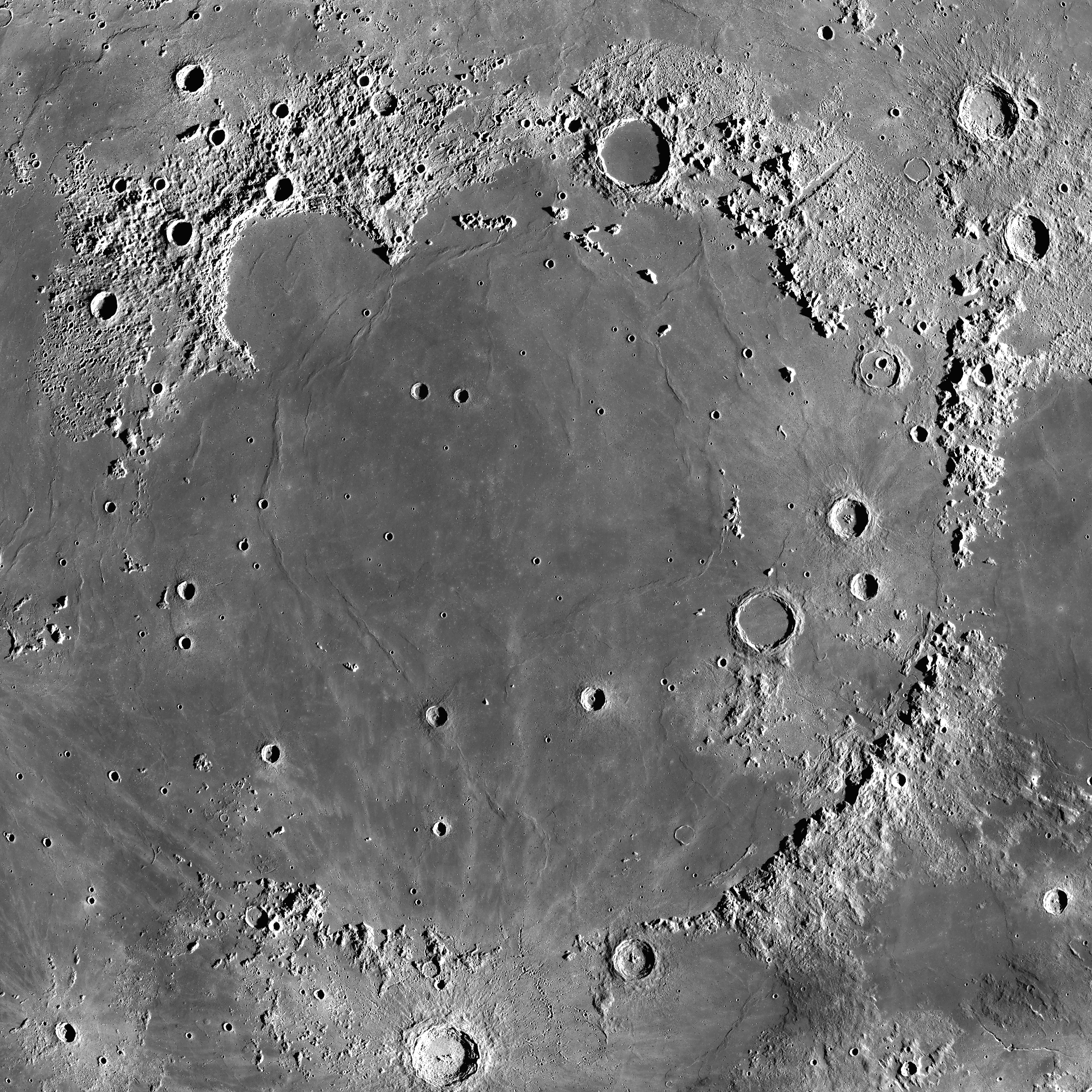
The Mare Imbrium is thought to have formed 3.85 billion years ago when a planet collided with the moon.
The late heavy bombardment is also known as the lunar cataclysm.
During a time when the Earth system and other inner planets experienced a large increase in space rock impactors, the LHB occurred.
Some planetary scientists think that the increased bombardment may have been caused by the giant planets of the solar system changing their orbits as a result of interactions with loose material.
The asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter and comets of the Kuiper belt at the outer edge of the solar system may have been disturbed due to this.
Smaller and younger craters can be found inside the Mare Imbrium basin following further space rock impacts. The area was flooded with lava over the next several hundred million years.
A fascinating insight into the moon's geological past can be found in the region of Mare Imbrium. On Sunday, skywatchers have an exciting chance to see one.
Send your photo, comments, and your name and location to spacephotos@space.com if you want to share it with Space.com's readers.
We encourage you to follow us on social media: