Alzheimer's disease is linked to the development of the tau protein. There is still a lot we don't know. The work of an international team includes co-authors from the Faculty of Science of Charles University in Prague and graduate student Tereza Humhalov. The study was published in a journal. It shows that the cell can have a coating or envelope on its microtubule structures. These change the properties of the coated microtubules and prevent the passage of certain molecular motors.
Microtubule are thin tubes inside cells that are used to move cargo from one place to another. Transport over long distances must be provided in cells that are large or long in one direction. Nerve cells with their extensions are examples of cells that provide transport of cargo over a long distance. Microtubule pathways can be damaged if the transport processes don't go according to plan.
The acronym for "MAPs" is derived from the word "microtubule-associated" As their binding influences microtubule stability,MAPs are very important players in the orchestra of the cell. The protective envelopes on the microtubule are formed by the twoMAP2 andtau proteins. The parts are protected by an envelope.
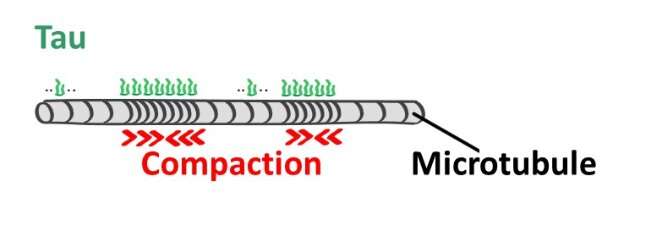
The work was led by Dr. Zdenk Lnsk from the Institute of Biotechnology of the CAS in the BIOCEV center. If they cover a part of the microtubule with their molecules as a coating, they also cause a change in the structure of the microtubule. The coated area will become more compact as the microtubule shortens.
The relationship between the envelope and the length of the microtubule is reversed if the microtubule is stretched by an external force. The sensitivity of the envelope-coated microtubule network to mechanical tension raises the question as to what purpose it might serve in nerve or muscle cells.
One of the interesting properties of the envelopes is that they affect the passage of the genes. The dynein motor can move towards the cell nucleus, but some kinesin motor can't move towards the nucleus because of the region. The binding of the studiedMAPs creates regions in which cargo transport can only be done in one direction or only certain types of motor can be used. The proper functioning of the nerve cell can be accomplished by certain sections of microtubules. Many more surprises seem to be in the works.
More information: Valerie Siahaan et al, Microtubule lattice spacing governs cohesive envelope formation of tau family proteins, Nature Chemical Biology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41589-022-01096-2 Journal information: Nature Chemical Biology