DART is an ambitious project designed to test a method of redirecting an asteroid for the purpose of planetary defense.
DART mission facts are listed.
It was launched at 1:20 a.m. on November 24, 2011. The day begins at 0620GMT.
The space launch complex is located at the space force base in California.
The rocket is called the Falcon 9.
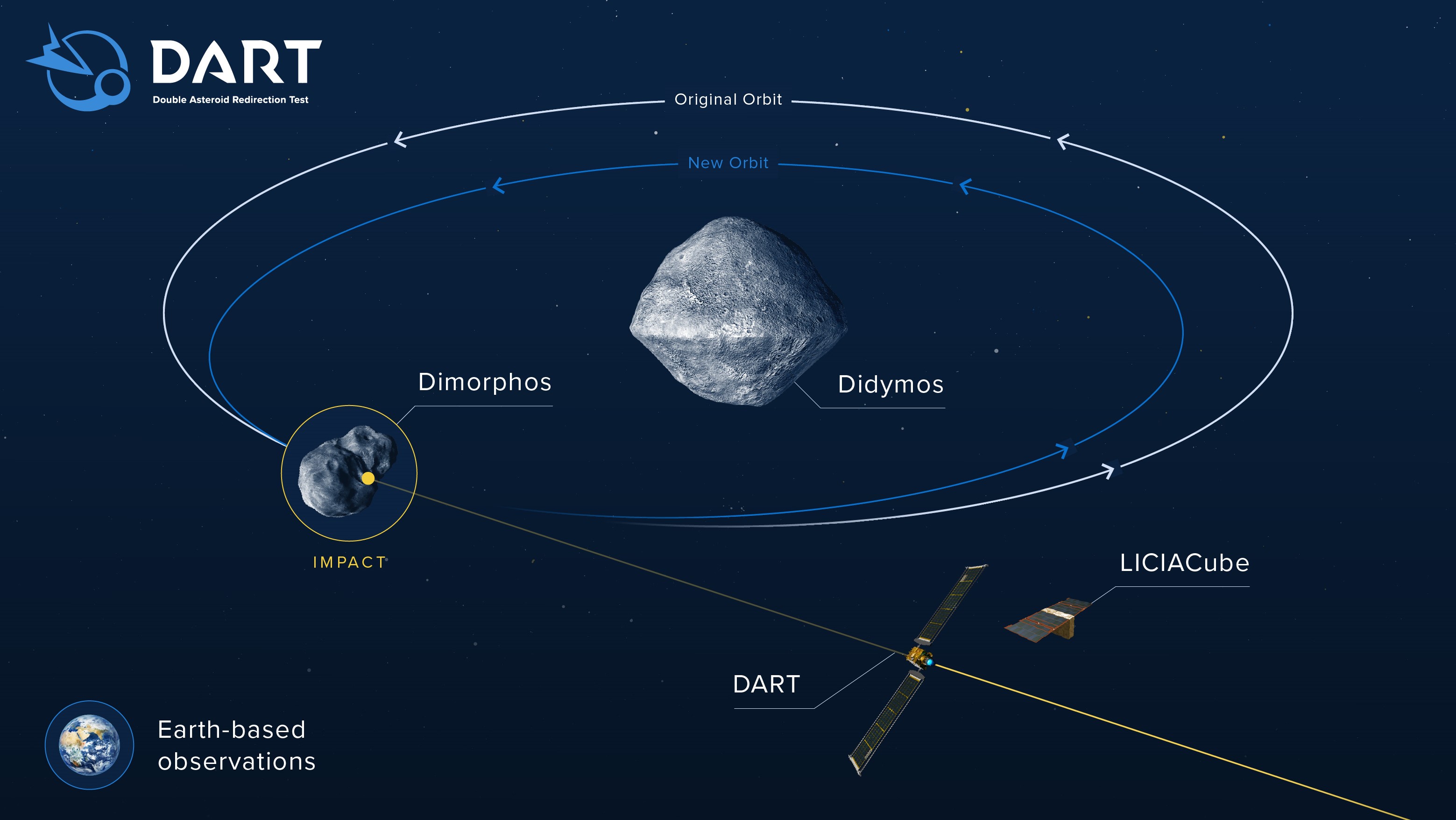
Didymos and Dimorphos are targets.
There is a target distance from Earth.
The estimated cost is $327 million.
The DART Impact window runs from September 26 to October 2, 2022.
The launch of the DART mission took place at 10:20 p.m. There is a rocket at the Space Launch Complex 4 in California. According to NASA officials, the spaceship is going to arrive at its target in September of 2022.
Didymos and its moonlet Dimorphos are the targets of DART. The DART mission is the first planetary defense mission to test how datememe datememe works.
We thought the asteroid could hit us.
DART will hit the moonlet Dimorphos at a speed of 4.1 miles per second. The speed is 14,760 mph. According to NASA, the impact should change the moonlet's speed by a fraction of a percent. It should be able to change its period by a few minutes. The change in Dimorphos' position around Didymos will be measured by telescopes on Earth to see if the mission has succeeded.
The threat from asteroid impacts is small and something we should be prepared for. The extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago was caused by an asteroid impact, so we need to look at past impact events like that to understand the consequences of an impact.
The first step in planetary defense is to detect asteroids early. There were more than 19,000 near-Earth asteroids discovered at the start of the year, according to NASA. DART is going to be the first mission to test a technique on asteroids.
There are great asteroid encounters of all time.
The DART mission is being led by the JohnHopkins University Applied physics Laboratory. The Didymos is the target of the mission. A near-Earth asteroid measuring 0.48 miles across and a moonlet measuring 525 feet across are part of the system.
Dimorphos is the same size as an asteroid that could pose the most likely threat to Earth if one were on a collision course with the planet. Ground-based telescopes can be used to observe and measure any differences after the collision.
Nancy Chabot spoke about the mission strategy with How It Works magazine.

One of the major technology challenges of the mission is targeting a small asteroid in space at very high speed.
"We know from other asteroids that have been explored that they have a variety of shapes, internal structures, surface properties and strengths, and these characteristics will influence how much the asteroid Dimorphos is diverted in its path around Didymos."
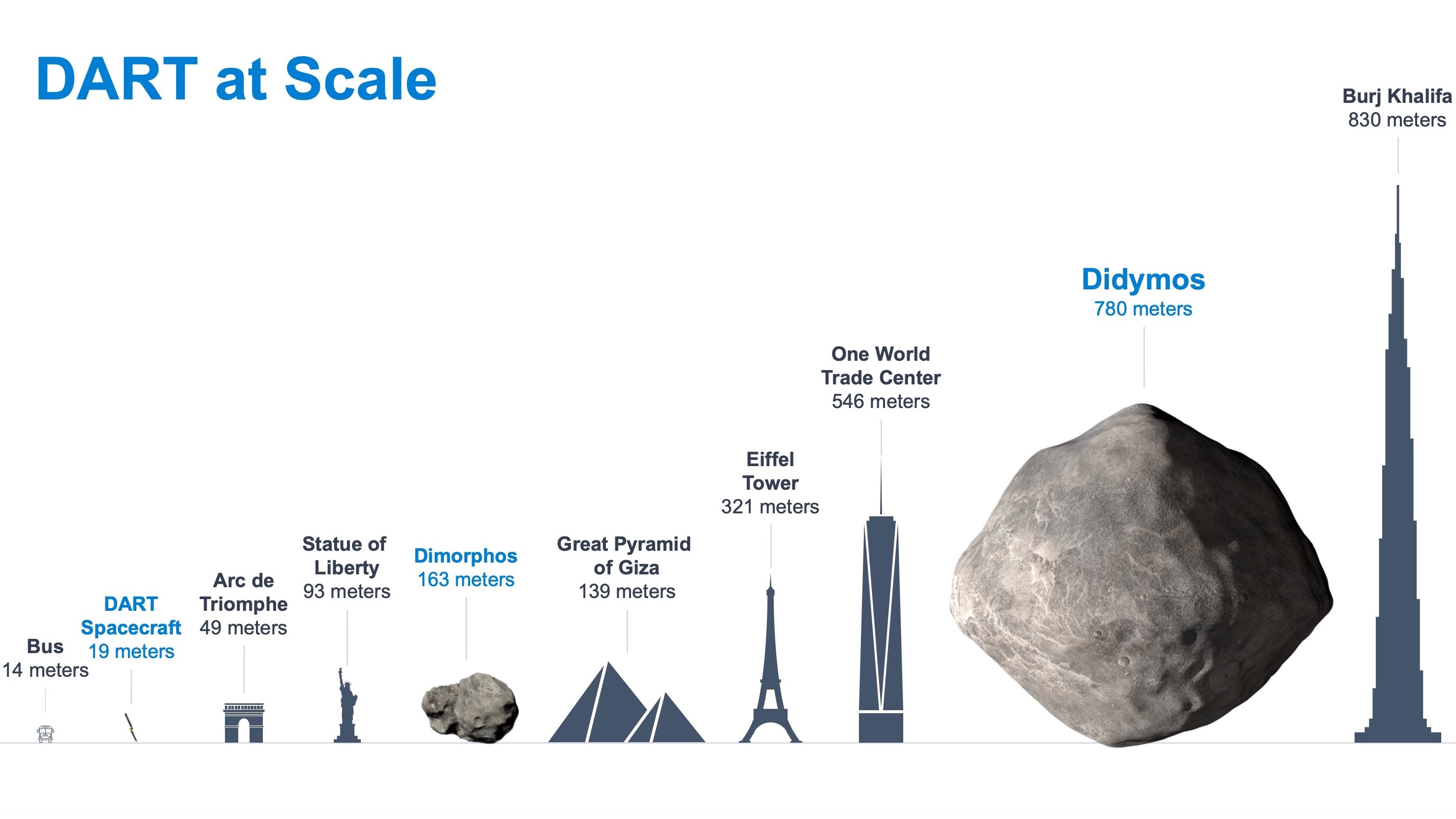
DART is a small craft. The box-shaped main vehicle is about the size of a fridge. When fully deployed, each of the two large solar array is more than 25 feet in length. Didymos is the only instrument in the DART spaceship. If you want to smash into an asteroid, you don't need to take much with you.
DART will power itself for the journey to Didymos with the help of its roll-out solar array. The power needed to support DART's electric propulsion system was found to be provided by the ROSA array on the International Space Station. The space station's own power grid has been updated with larger versions of the ROSA array. The DART will use the Next-C solar electric system as part of its in-space propulsion.
DART will be guided by sophisticated navigation software. It's difficult to find a target that is more than 10 million miles away from Earth. The navigation software is designed to distinguish between Didymos and Dimorphos so that the DART craft can be directed to the smaller body.
DART will use an onboard high-resolution camera to take pictures of the target asteroid and measure its size and shape. The LORRI camera from NASA's New Horizons was used to create DRACO.
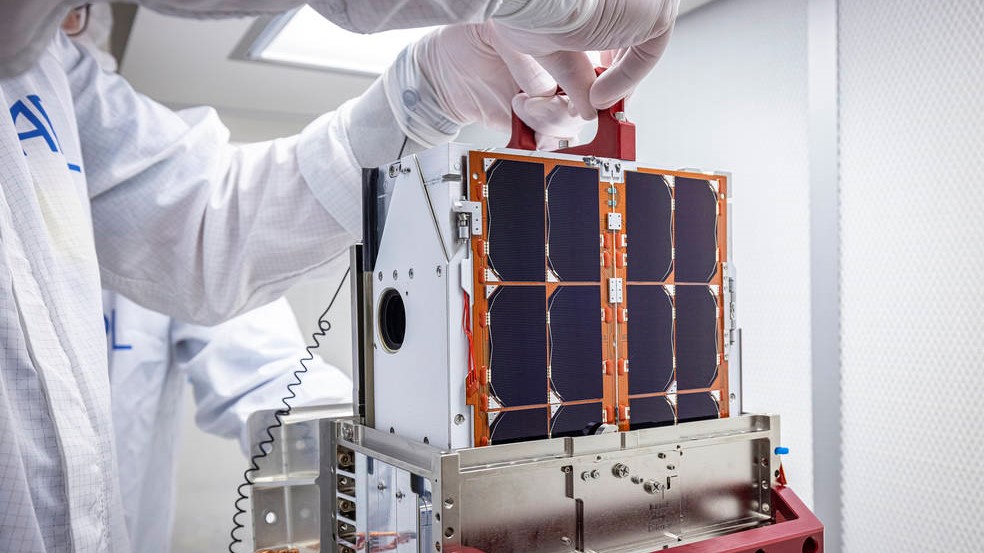

According to NASA, DART won't be making its journey to the asteroid alone, instead, it will be joined by LICIA. The Italian Space Agency contributed to the creation of LICIACube, which is a cubeSat.
The LICIRACube measures roughly the length of an adult's hand and forearm. The little cubeSat has a very important job and will be deployed by DART around 10 days before Dimosphos. LICIA will take pictures of the impact to help verify the effectiveness of the impact.
The Hera mission will investigate the impact of DART on Dimorphos. The Didymos system is expected to be reached in the year 2026.
Two CubeSats will join the Hera spaceship. They will look at the crater left by DART's collision with Dimorphos in order to conduct surveys of Didymos and Dimorphos. A precise mass of Dimosphos is one of the goals of the Hera mission.
DART and Hera are both designed and operated on their own. The team members from both missions are part of an international project. According to the European Space Agency, AIDA is a large international collaboration between them, as well as a number of other institutions.
NASA's planetary defence coordination office leads a larger planetary defence strategy that includes DART.
She said that DART's demonstration of this technology will be a major result.
DART is the first test of planetary defence efforts and finding, tracking and characterising the near-Earth object population is crucial to success.
You can view images from the mission at the mission image gallery or learn more about planetary defense with the European Space Agency.
DART was delayed as environmental testing began. The NASA spaceflight will take place in 2021.
NASA has a test to stop an asteroid from hitting Earth. The society was founded in 1992.
DART updates open in a new tab NASA will be up and running in 2020.
DART: Double Asteroid Redirection Test is open. DART is a laboratory at John Hopkins University.
The DART Impactor is open in a new tab. DART is a laboratory at John Hopkins University.