Tomasz Nowakowski is a member of the physics.org community.
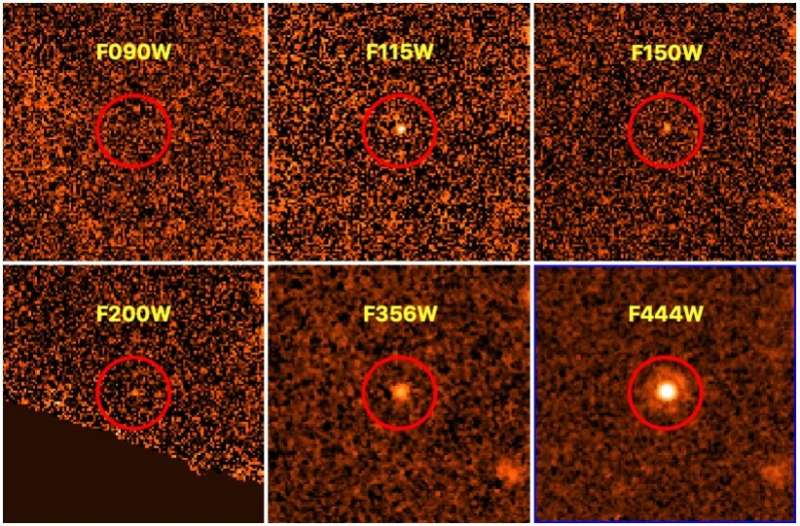
An international team ofAstronomers have detected a new faint, distant, and cold brown dwarf using the james wbb space telescope The object is 31 times larger than Jupiter. A paper detailing the discovery was published on arXiv.org.
There are brown dwarfs between planets. The mass range for substellar objects is between 13 and 80 Jupiter mass. T dwarfs are brown dwarfs that have an effective temperature between 500 and 1,500 K.
Studies of T dwarfs could help astronomy understand objects near the disputed planet/star boundary. Although many brown dwarfs have been found to date, T dwarfs are not as common as they could be.
A group of astronomer led by Mario Nonino of the observatory in Italy have found a brown dwarf that is most likely T dwarf subclass. The discovery was made as part of the ERS program of the Through the Looking GLASS project.
The discovery of a late T-type brown dwarf candidate is presented. The researchers wrote in the paper that the discovery was made because of the 4 m wavelength and panchromatic coverage of the energy distribution.
The age of this brown dwarf was estimated to be five billion years.
Theory suggests that GLASS-JWST-BD1 is a late type T dwarf. It was measured to be between 1,750 and 2,350 light years away from the Earth. The results show that this object is part of the halo population.
Further observations of GLASS-JWST-BD1 are needed to confirm its nature. More insight into the properties of this object can be obtained by using chemical abundance data.
The authors of the paper highlighted how their discovery demonstrates the ability of JWST to investigate distant low-mass stars.
The large estimated distance of GLASS-JWST-BD1 confirms the power of JWST to probe the very low-mass end of the stellar and substellar mass function in the Galactic thick disk and halo.
More information: M. Nonino et al, Early results from GLASS-JWST. XIII. A faint, distant, and cold brown dwarf. arXiv:2207.14802v1 [astro-ph.SR], arxiv.org/abs/2207.14802There is a science network.