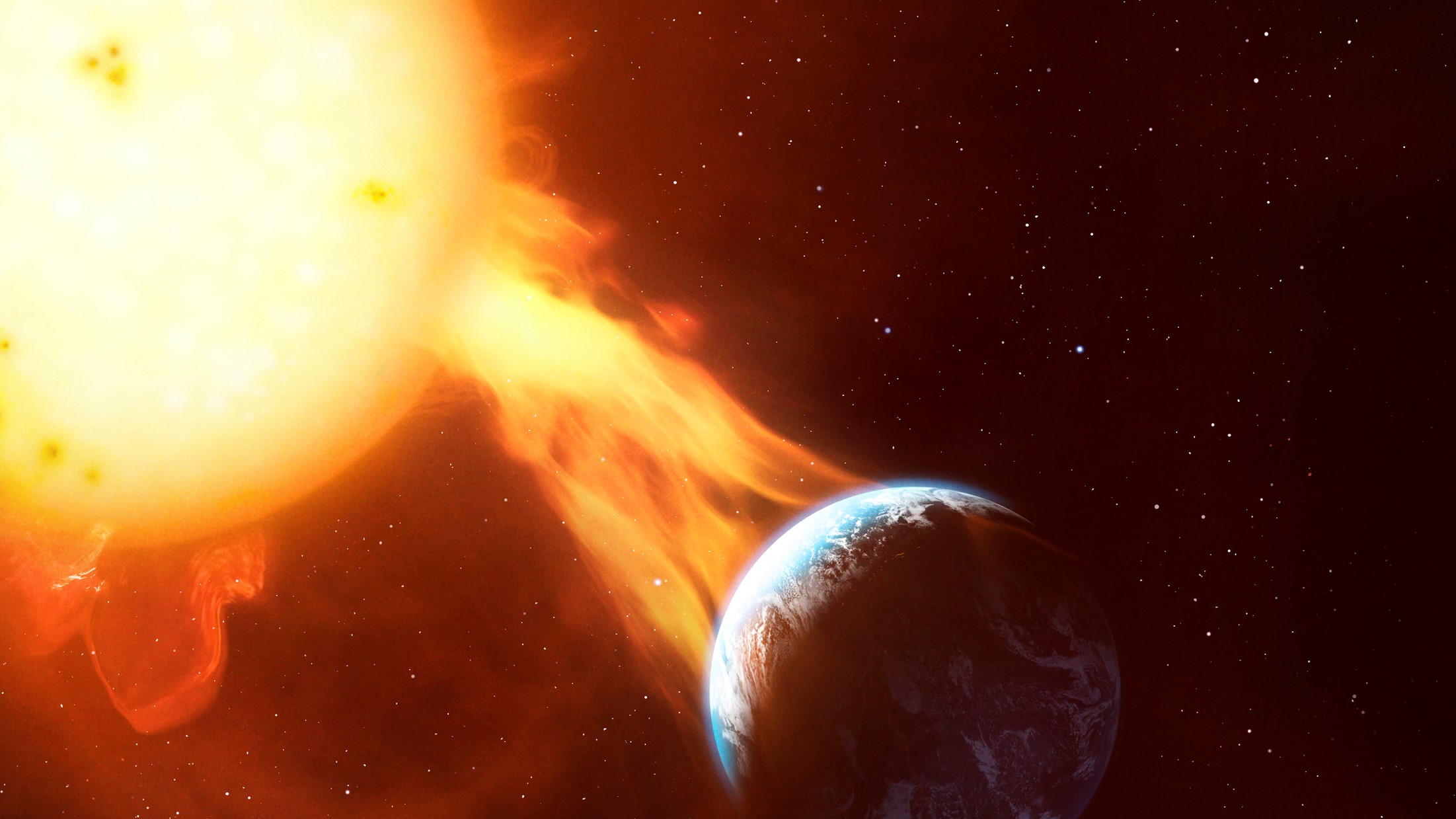

There is an increased likelihood of solar storms when we experience solar cycle 25 because of the large release of energy in form of solar flares or coronal mass ejections.
Increased radiation exposure from solar storms can affect technology on Earth. According to NASA, large storms of the sun's magnetic field can interfere with radio communications and global positioning systems.
We looked at some of the worst solar storms.
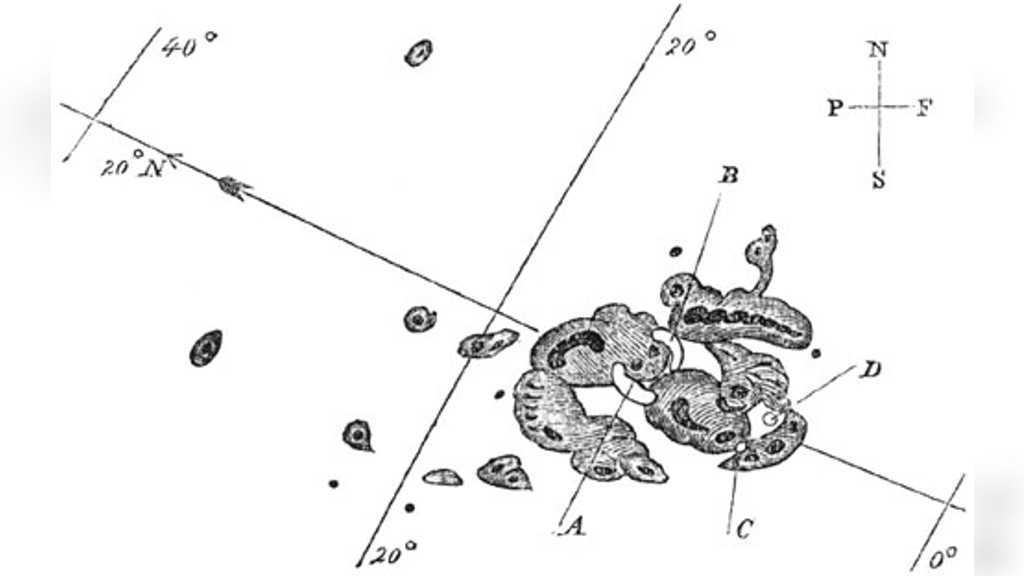
The first documented event of a solar flare was the Carrington event of 1859. At 11:18 a.m., the event took place. The solar astronomer who saw the event through his telescope and sketched the sun's sunspots was named after. NASA scientists said that the solar storm was the biggest in the last 500 years.
Major displays of the northern lights were visible as far south as the Caribbean. According to a NASA description, it caused severe disruptions in global telegraph communications, even shocking some telegraph operators and sparking fires when discharges from the lines ignite telegraph paper.
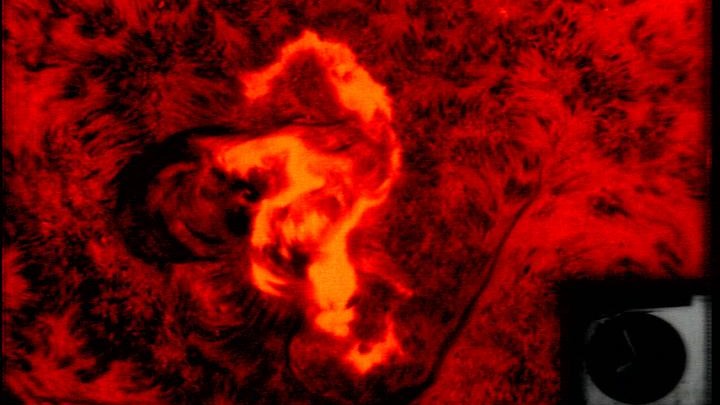
According to a NASA account, the solar flare knocked out long-distance phone communication in some states.
NASA said that the event caused AT&T to change its power system.
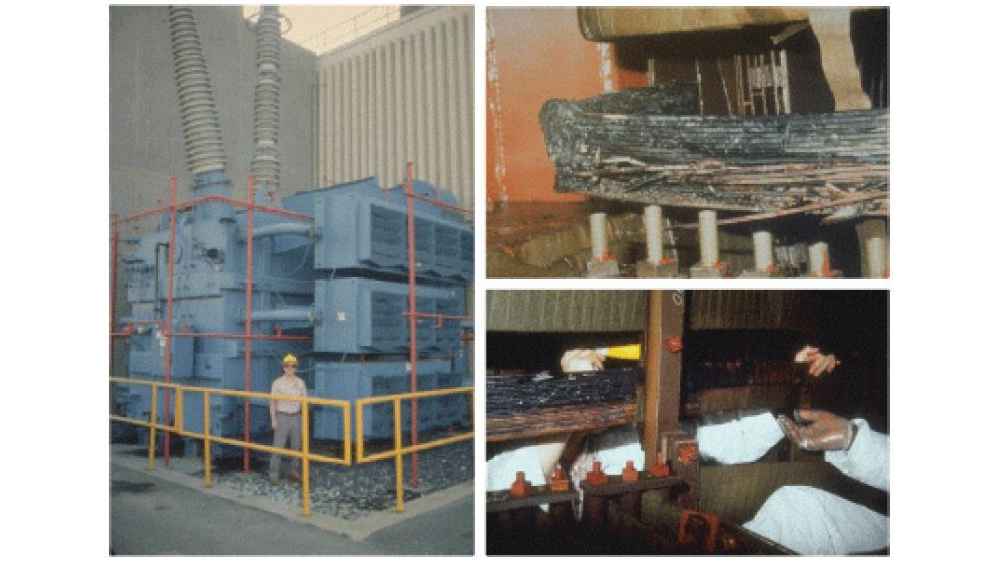

Six million people in Canada were without electricity for nine hours in March of 1989 after a powerful solar flare caused a geomagnetic storm.
The flare disrupted electric power transmission from the Hydro Québec generating station and even melted some power transformers in New Jersey. NASA scientists said that the solar flare was not close to the size of the event.
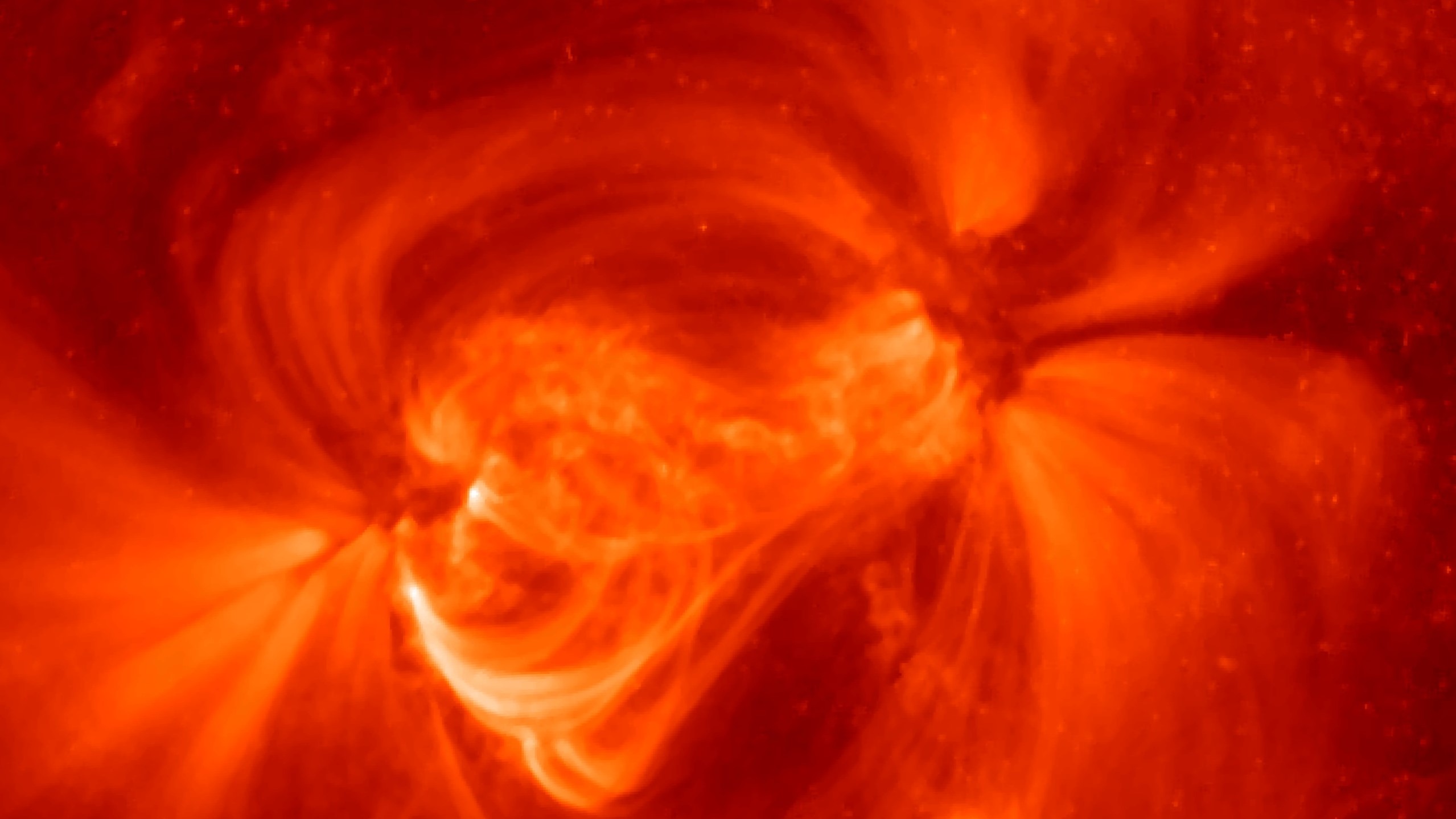
Bastille Day is named after the French national holiday of July 14, 2000. The solar eruption registered an X5 on the scale of solar flares.
Satellites were short-circuited by the Bastille Day event. It was the most powerful flare since 1989 and was one of the most highly observed solar storms.
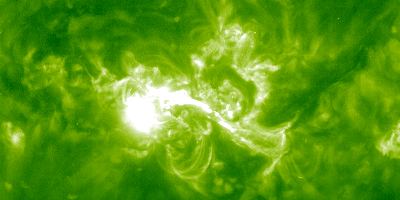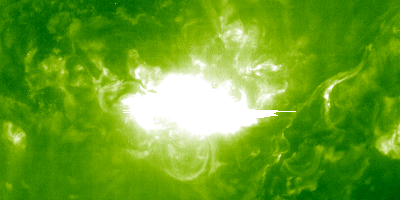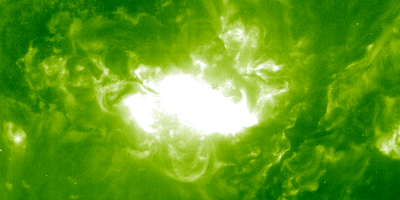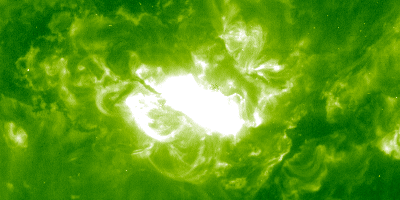
Solar flares and mass ejections slammed into Earth's atmosphere from October through November of 2003
The "Halloween Storms of 2003" were solar storms that caused aircraft to be re-routed, satellite systems to be affected, and power to be lost in Sweden. During the solar onslaught, theSO HO failed.
A solar flare occurred on October 28, 2003 The sensor that measured the flare was overwhelmed by it. NASA said that the flare reached a peak strength of about X45 after the sensor peaked at X28.
During a time in the solar cycle when solar activity should be relatively quiet, the Halloween storms were especially frightening. There were 17 major flares that erupted from the sun during this time.
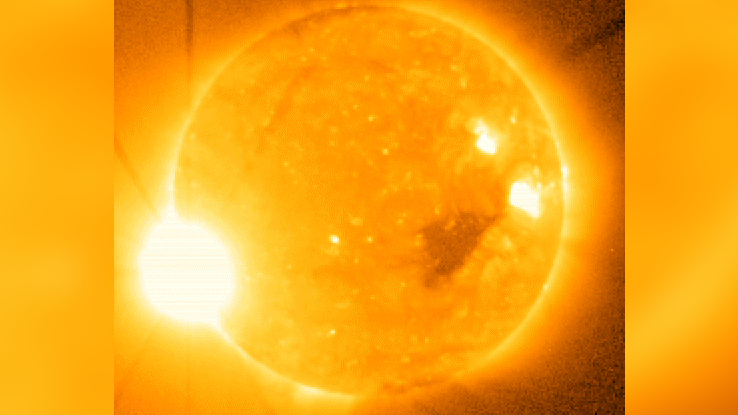
The X9 on the space weather scale was registered when a major solar flare erupted on the sun.
According to a NASA description, a storm from the sun disrupted satellite-to-ground communications for about 10 minutes.
The sun storm caused damage to the solar X-ray imager instrument on the GOES 13 satellite.
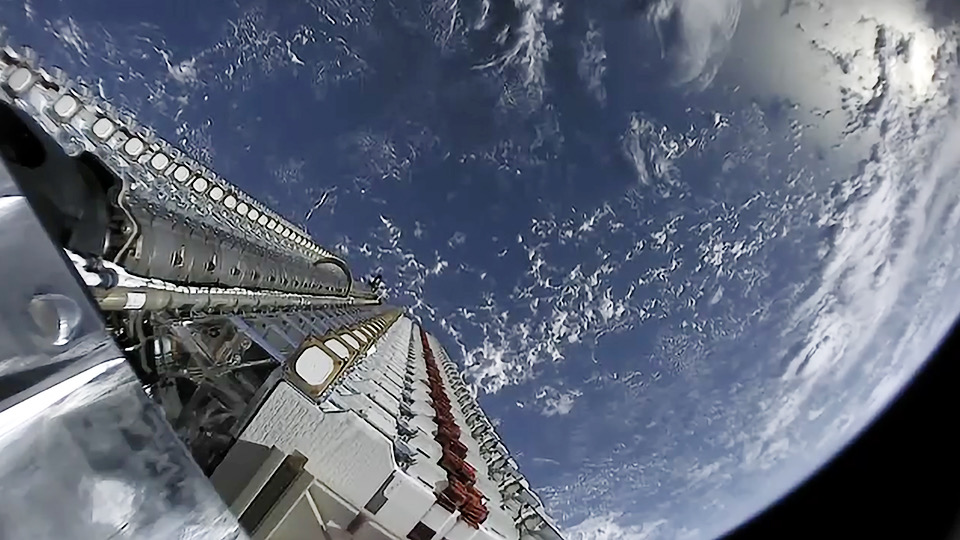

A storm destroyed up to 40 Starlink satellites worth over $50 million shortly after they were deployed.
The Starlink satellites are vulnerable to storms because they are released into very low-altitude orbits, and they rely on onboard engines to overcome the force of drag.
During a storm, the Earth's atmosphere absorbs energy from the storms, heats up and expands upwards, leading to a denser thermoosphere that extends from 50 miles to 1000 miles above the Earth's surface. Satellites can be affected by a denser thermoosphere.
The Starlink satellites fell back to Earth in February after they failed to overcome the increased drag caused by the storm.