It is over.
Some of the first images and data from the James Webb Space Telescope were released by NASA. Three images and a spectrum are included in the four targets. The fourth image, a sharply focused ultradeep field view, was unveiled on Monday by President Joe Biden during a live broadcast. The data and images show the huge potential of the telescope to contribute to scientific research.
I'm most excited about something. After the images were revealed, Thomas Zurbuchen said during the event. There are tens of thousands of scientists who are benefiting from this amazing telescope because it will be with us for a long time.
Gallery: James Webb Space Telescope's 1st photos
Live updates: NASA's James Webb Space Telescope mission
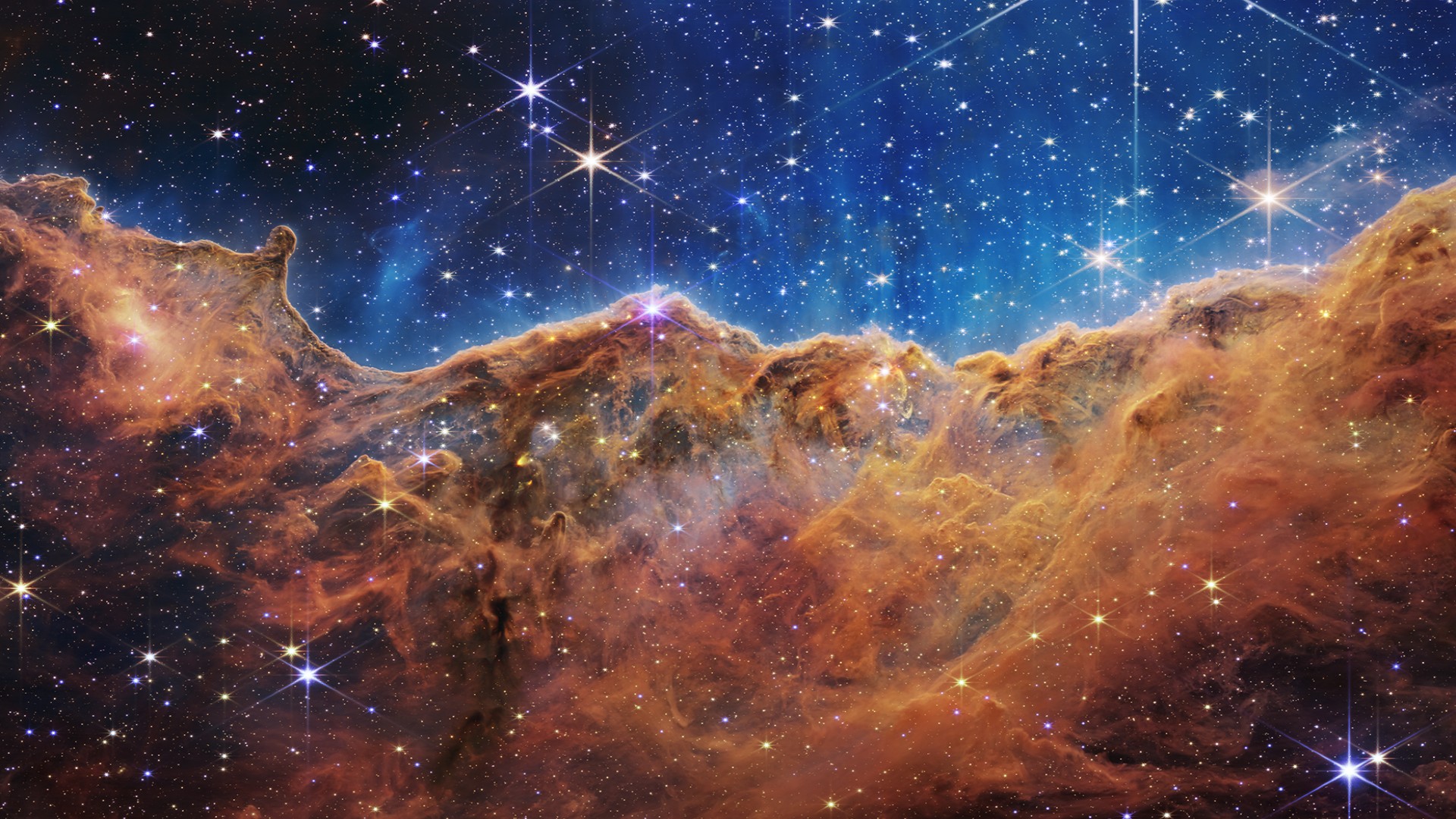

There are three images released during today's event that show the Carina and Southern Ring Nebulas. WASP-96 b is a gas giant exoplanet.
The Carina Nebula is 7,600 light-years away from Earth. One of the youngest known clusters of star formation is called Trumper 14 and it is located over 300 light-years across. A stellar nursery and a violent one are what Carina is.
"It's so beautiful, there's so much going on here, it's so exciting," she said. New details about the massive stellar nursery can be found in this stunning vista of the cliff. For the first time, we are seeing brand new stars that were previously hidden.
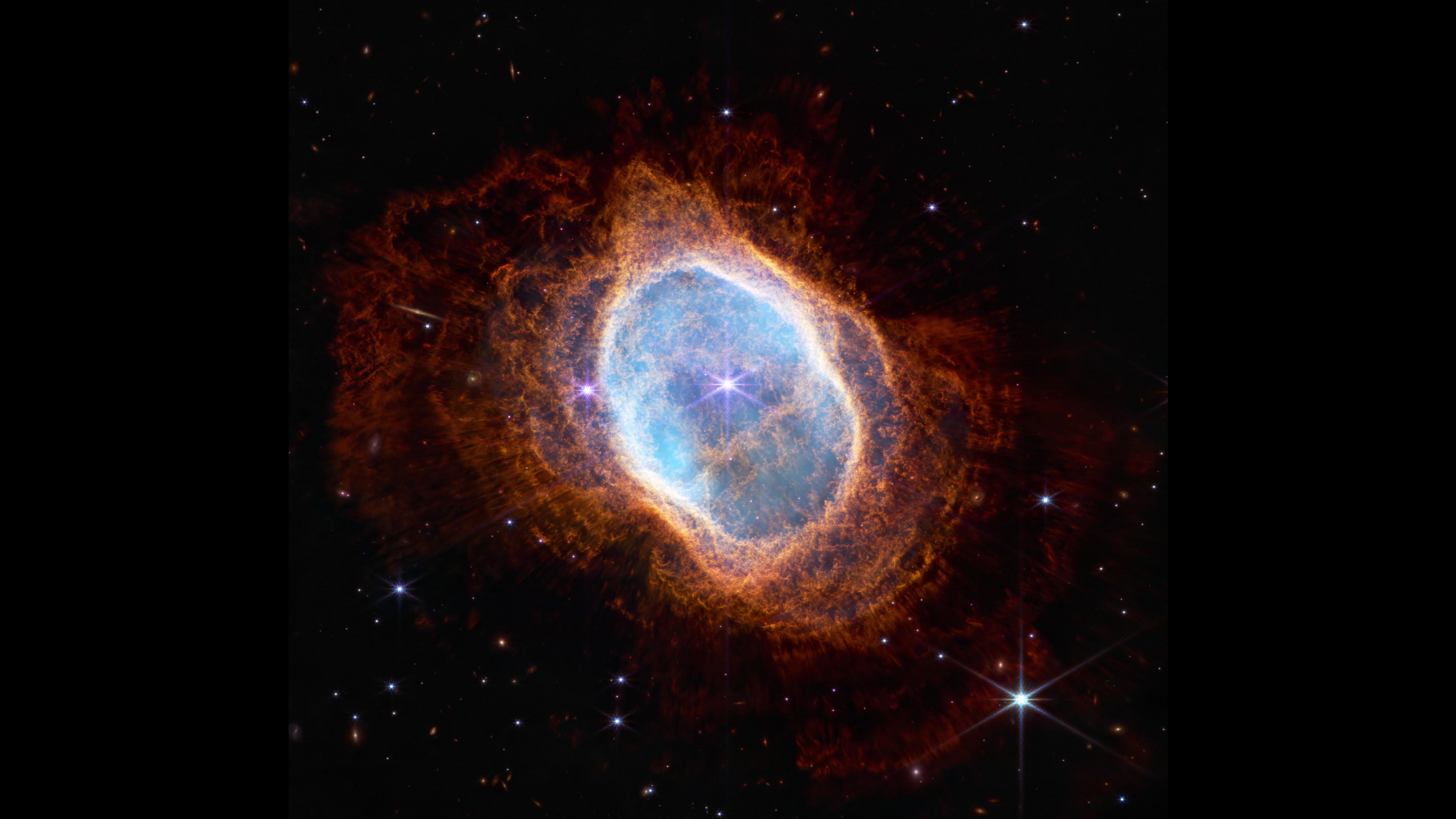

The Southern Ring Nebula is close to Earth. There is a cloud of gas around a dying star. After blowing off all its outer layers, the dying white dwarf star at the nebula's heart is extremely hot and releasing intense ultraviolet radiation, which causes the gas around it to light up.
During the event, Karl Gordon, an astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute, said that the new images show the shells formed by that gas.
The star in the center glows red because we didn't see much of the actual star that made the nebula.
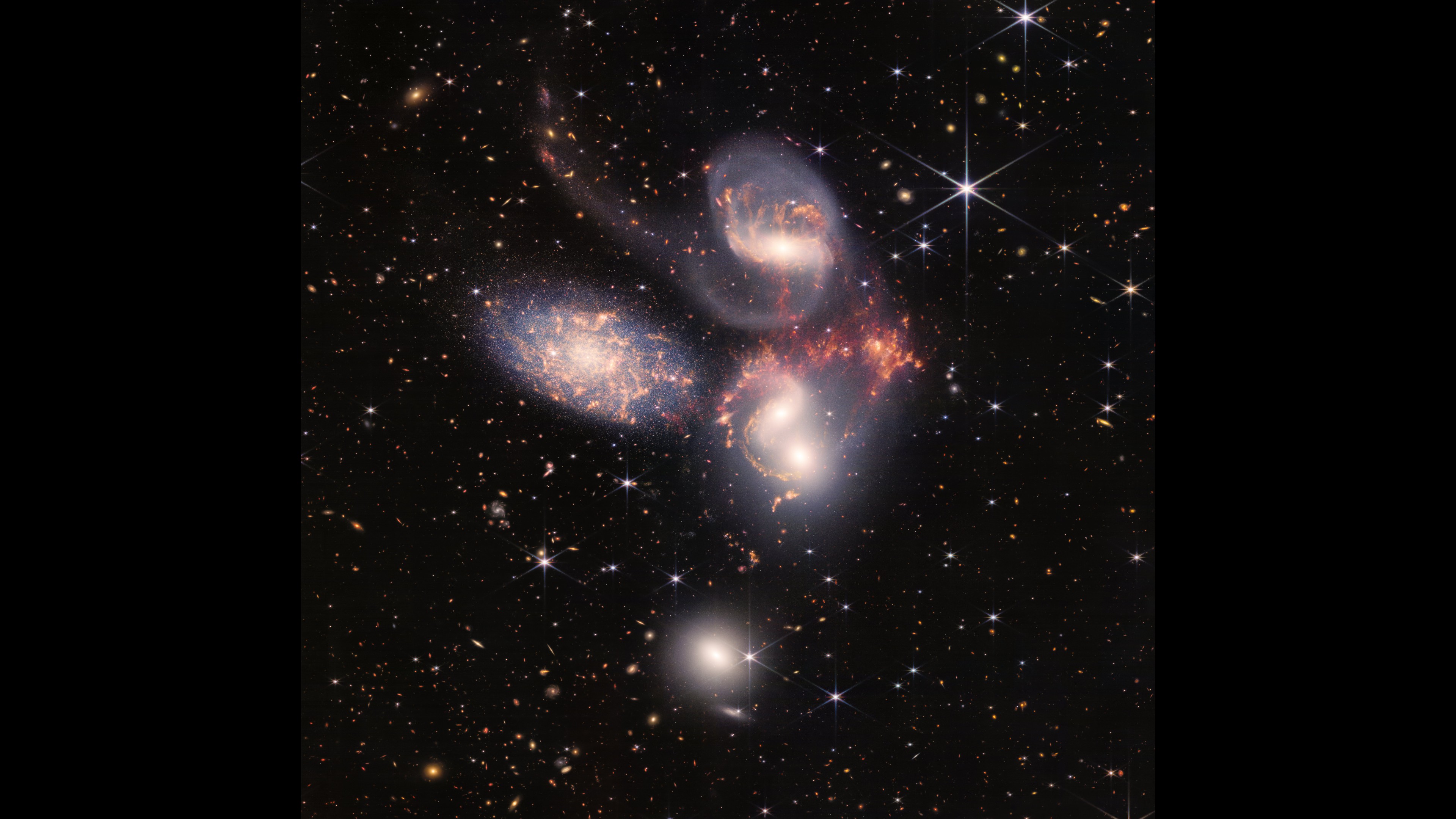
Stephan's Quintet is a group of five galaxies that are so close together that you can't tell them apart. Four of the galaxies are locked in a kind of dance that will one day cause them to collide, and three of them are shaped like spirals. The stars in the quintet ranged from newborn to ancient.
Giovanna Giardino, an astronomer at the European Space Agency, said that this is a very important image and area to study.
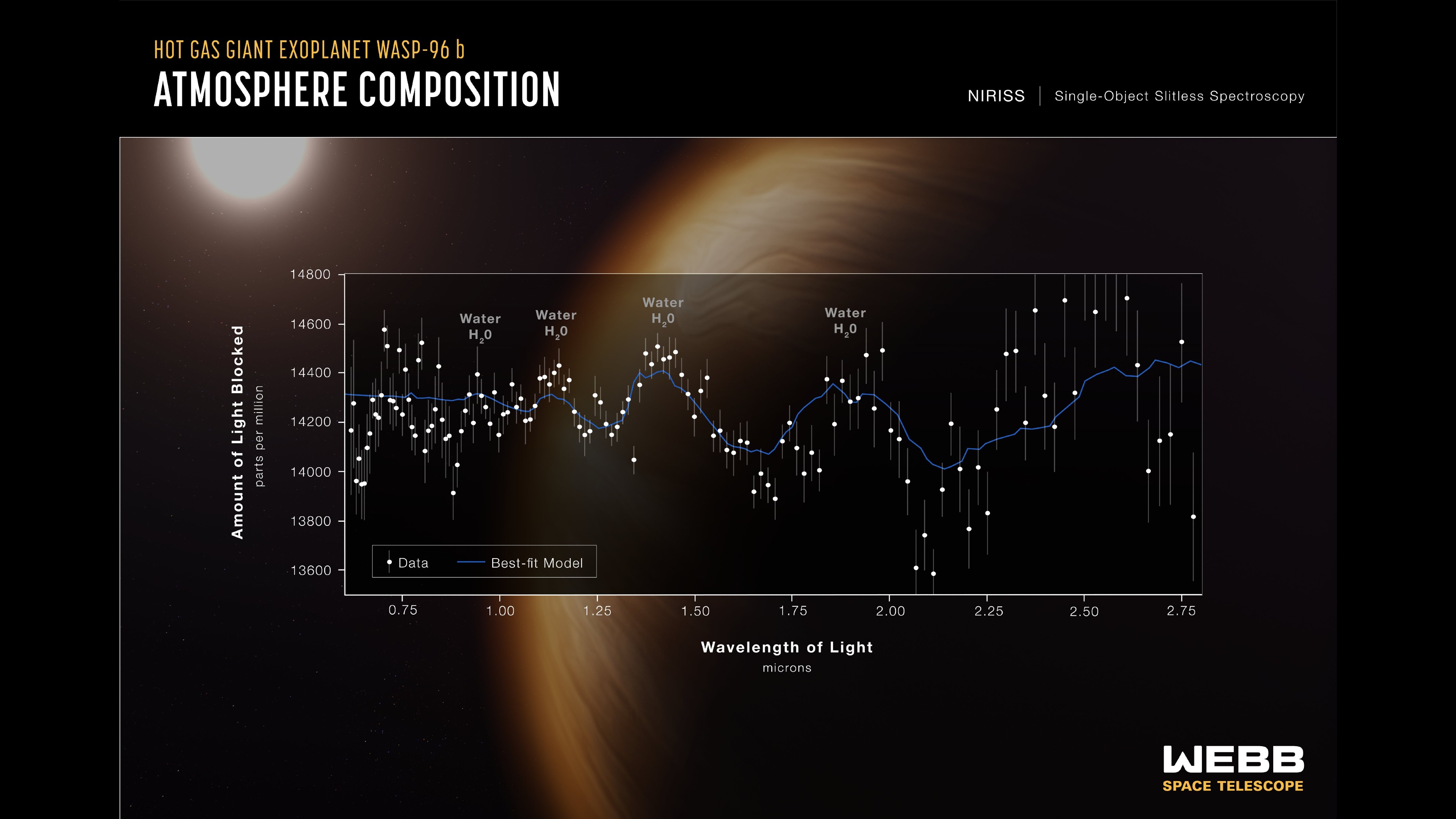
A spectrum is a representation of the amount of different wavelength light emitted by an exoplanet. The gas giant world is about half the size of Jupiter. It has a cloudless atmosphere due to the fact that it's a star and it's been around for 3.4 days.
WASP-96 b is the only cloudless planet that has been studied. Scientists now have more data about that strange atmosphere thanks to the new data from WEBB.
"We've been able to use other telescopes, but not to this level of detail," Knicole Coln said. The NIRISS instrument is being used to provide this data.
Coln said that it was full of information and that it looked like bumps and wiggles to some people. There are bumps and wiggles in the atmosphere that show the presence of water.

Seven months have passed since the launch of the telescope. Over two decades of development began in 1996 and culminated in the launch. At one point, Webb was in danger of being canceled due to soaring costs, and at other times, it was severely strapped for funds.
Despite the rocky road, scientists say that the now functional telescope, which is performing better than expected, should be able to operate for the next 20 years.
John Mather is a senior project scientist for the project and he said he was thrilled. There's always a chance that it won't work when you start something large. The thing did work. We are so happy.
The development of the telescope was a collaborative effort between NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency with scientists working together across agencies and divisions.
Throughout the telescope's tenure, Canada's Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph will allow it to make key observations of distant galaxies and exoplanets.

People often think of only one mission control room for a space mission, but there are several teams that manage it from different locations, and representatives from each agency helped choose the first image.
During the Apollo moon missions in the 1960s, James Webb was the NASA administrator. The mission was named in the early 2000s but people don't like it anymore. The "Lavender Scare" was a widespread discrimination against the LGBTQ+ government employees at the time.
Astronomers are excited about the new data and dislike the name, but at the same time they are also mixed about it. The name of the observatory has not been discussed by NASA officials since the spring.
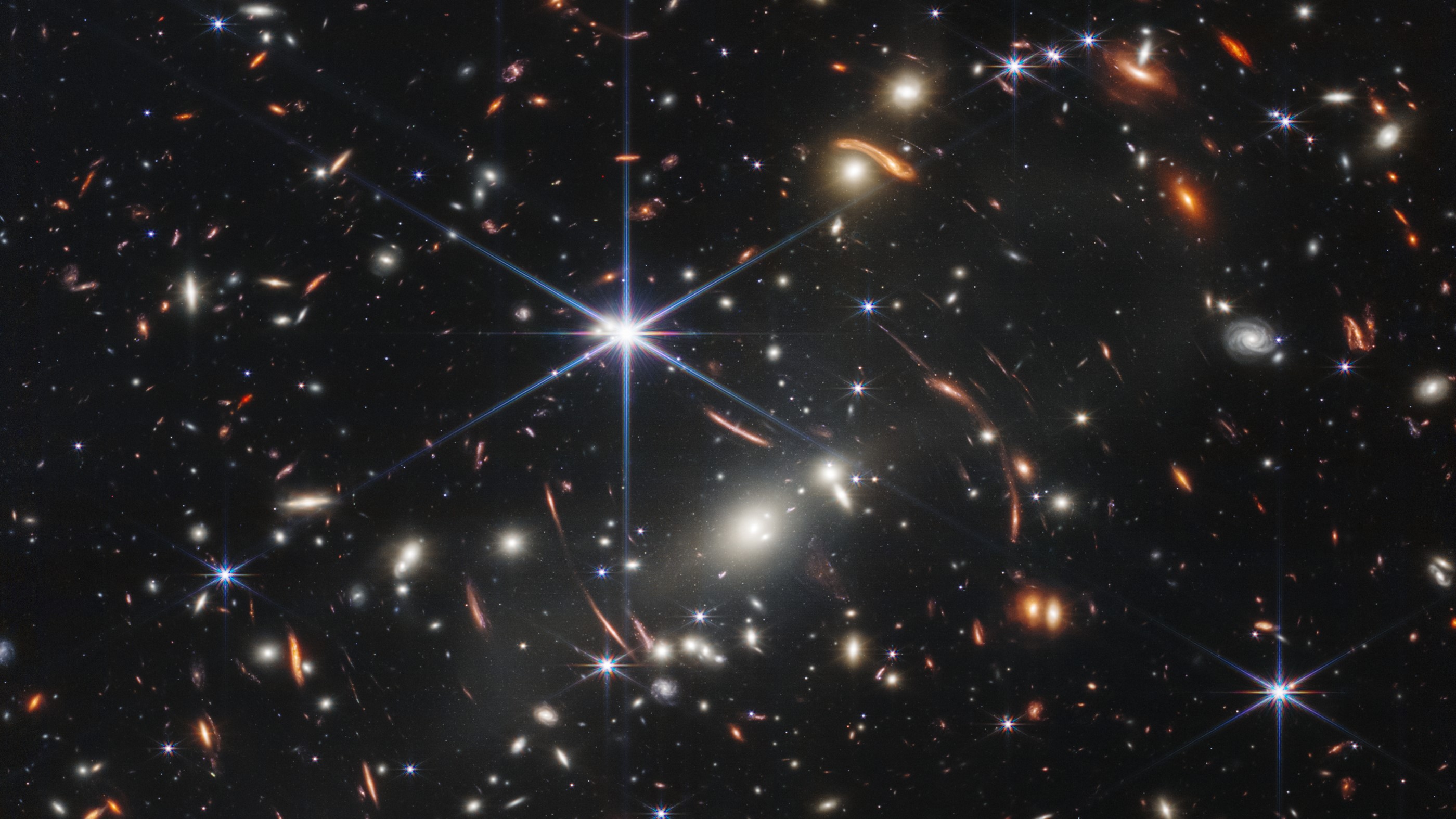
The telescope is going to make history. Hours before Biden unveiled the ultra deep field, its final instrument was cleared for science. The beginning of the observatory's tenure has made it possible for scientists to analyze data from the first targets.
As research begins on every conceivable scale in our universe, from our solar system to the very first galaxies, new insights could begin to stream in quickly. Regardless of what we find, the start of a new era will be defined by what we know about our universe and how we think about it.
"Our sun is like every dot of light we see here," he said. Our sun and our planets were formed out of the same things that we see here.
We encourage you to follow us on social networking sites.