Space is not as cold as we would think in a sci-fi movie. It doesn't have a temperature
The temperature and heat of particles are related. There would be no particles or radiation in the empty region space.
Space has particles and radiation that can produce heat and a temperature. Is there any region that is completely empty and the temperature drops to zero?
There is a place in the universe that is very cold.
The hottest regions of space are located around stars.
When a star's radiation reaches a spot in space, it warms up. The sun's radiation is something to act upon.
The region between our planet and its star is cooler than the one between Earth and its planet. The heat comes from the particles in the atmosphere vibrating with the sun's rays.
It's not a guarantee of warmth if you're close to our star and possess particles. Mercury is hot and cold at the same time. The temperature drops to a low of 95Kelvins.
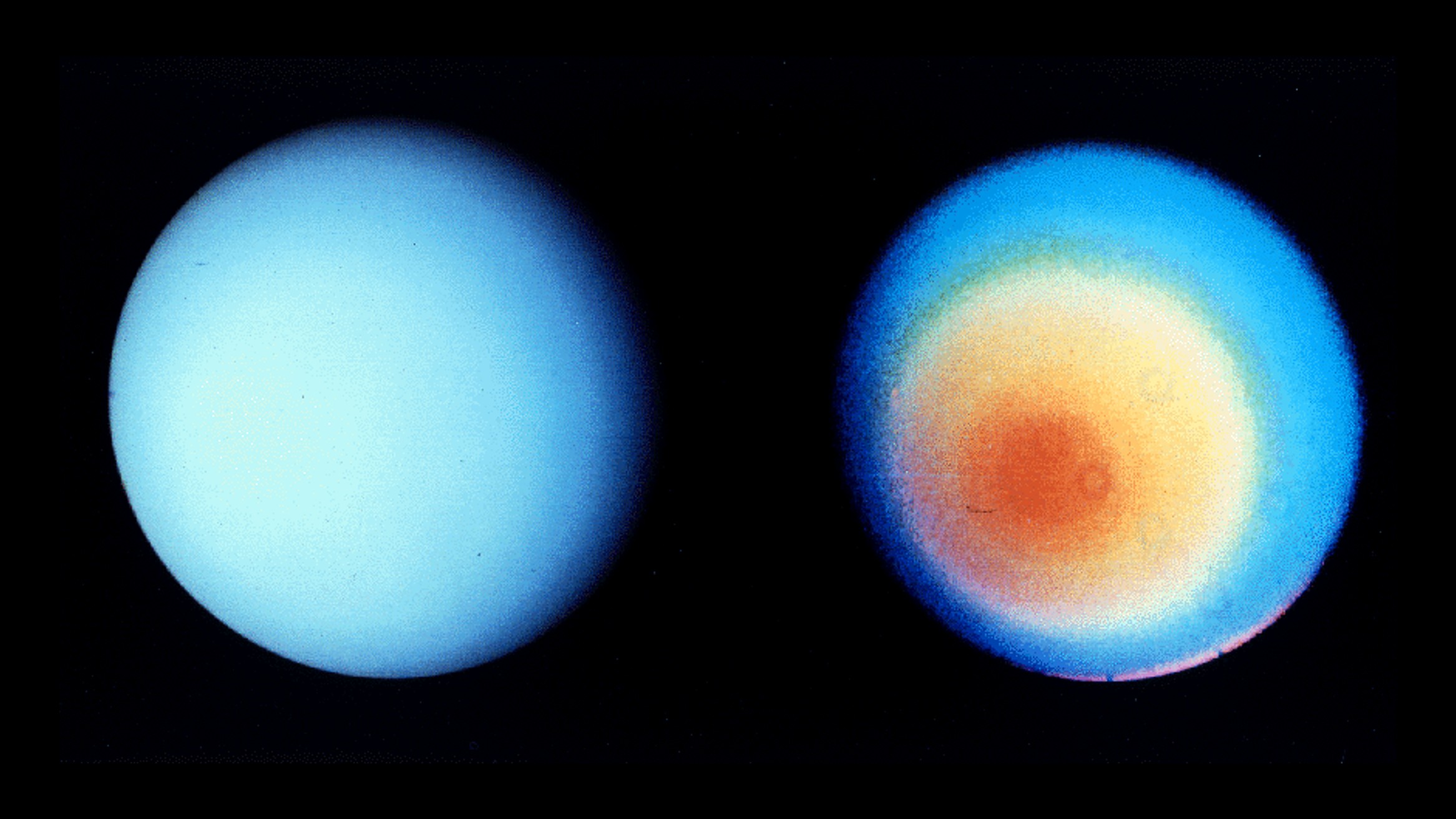
On the farthest planet from the sun, Neptune has a surface temperature of -353 0F, but on the smallest planet, Uranus, it has a temperature of -372 0F.
Due to a collision with an Earth-sized object early in its existence, Uranus was unable to hang on to it's interior heat.
The particles are so far away from the stars that radiation is not possible. The area is called the interstellar medium.
The densest cloud can have a temperature of 10 K, while the less dense cloud can have a temperature of 100 K.
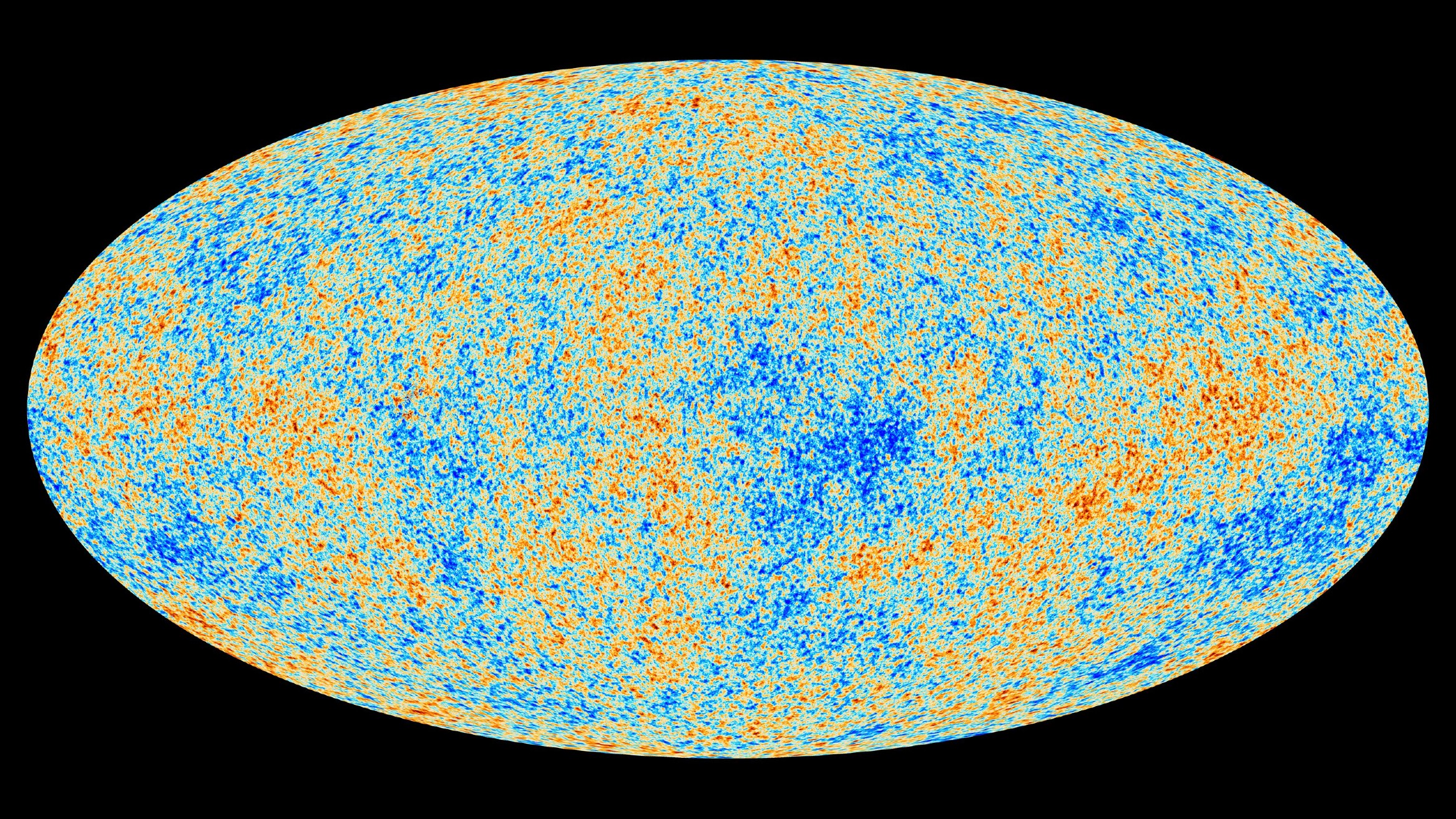
It shouldn't be possible to give space a single temperature because the universe is so large and filled with so many different objects.
Our universe has a temperature that is uniform to one part in 100,000. The difference between a hot spot and a cold spot is very small.
The Cosmic Microwave Background has a uniform temperature of 2.7 K. This is a temperature just above absolute zero.
There is a remnant leftover from an event that took place 400,000 years ago. After electrons bonding to protons forming hydrogen atoms, the universe ceased to be opaque.
The last point when matter and photons were aligned in terms of temperature was represented by this relic.
The expansion of the Universe has redshifted the photons that make up the Cosmic Microwave Background to a lower energy level.
The starting temperature of the radiation that makes up the CMB is thought to have been around 3000 K when the universe was much hotter than it is today.
Space is getting colder as the universe continues to grow.
Exposure to the near-vacuum of space wouldn't freeze an astronauts like it would in science fiction.
The three ways for heat to transfer are through touch, convection andradiation.
Due to the lack of matter, heat transfer can't happen in empty space. The heat doesn't transfer quickly in space
Exposure to radiative processes alone would cause an exposed Astronaut to die of decompression due to the lack of atmosphere much more rapidly than they freeze to death.
" Astrophysics for People in a Hurry" and "Origins of the Universe: The Cosmic Microwave Background and the Search for QuantumGravity" are available.