There is a solar eclipse when the moon passes between the sun and Earth. During the phase of the new moon, when the moon passes between the sun and Earth, a solar eclipse can only happen. The alignment can produce a total solar eclipse, a partial solar eclipse, or an annular solar eclipse.
It's not a coincidence that an eclipse can happen at all. The moon has been moving away from Earth since 4.5 billion years ago.
The moon is so close to the sun that it blocks out the sun's light. This is not always correct.
There is a guide to how to see the solar eclipse.
There are four different kinds of solar eclipses. Here are the reasons why each type is different.
Nature creates total solar eclipses. The sun's diameter is 400 times larger than the moon's. A total eclipse happens on average every 18 months.
The umbra is the part of the shadow where the sun can't see anything. The umbra is a cone-shaped object. It is surrounded by the penumbra, a shadow that partially obscures the sun's rays.
A third of the planet can be seen in a few hours during a solar eclipse. Those who are positioned in the direct path of the umbra will see the sun's disk diminish into a crescent as the moon's dark shadow moves towards them.
The corona is revealed when the sun is completely covered. Most total eclipses are shorter than 7 minutes.
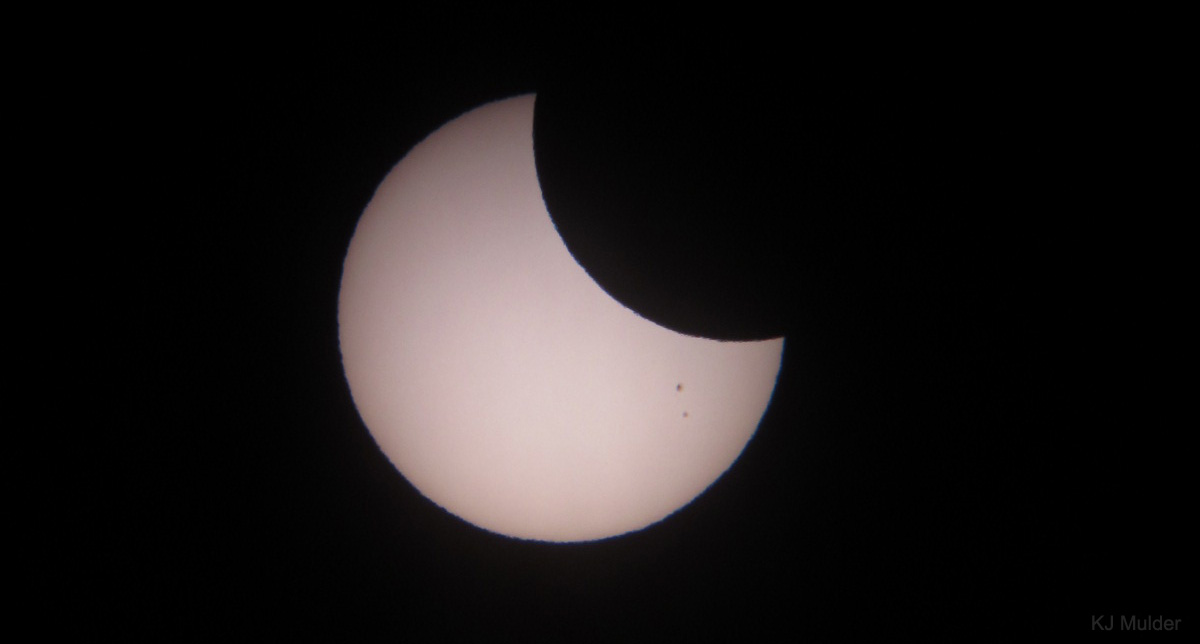
When the penumbra passes over you, there is a partial solar Eclipse. The part of the sun that is visible during the eclipse is always there. Depending on the situation, how much of the sun remains in view can be determined.
Those who are positioned close to the path of a total eclipse will be able to see a partial eclipse.
The solar obscuration is greater if you are close to the path of totality. If you are positioned outside of the path of the eclipse, you will be able to see the sun diminish to a narrow crescent as the shadow moves by.
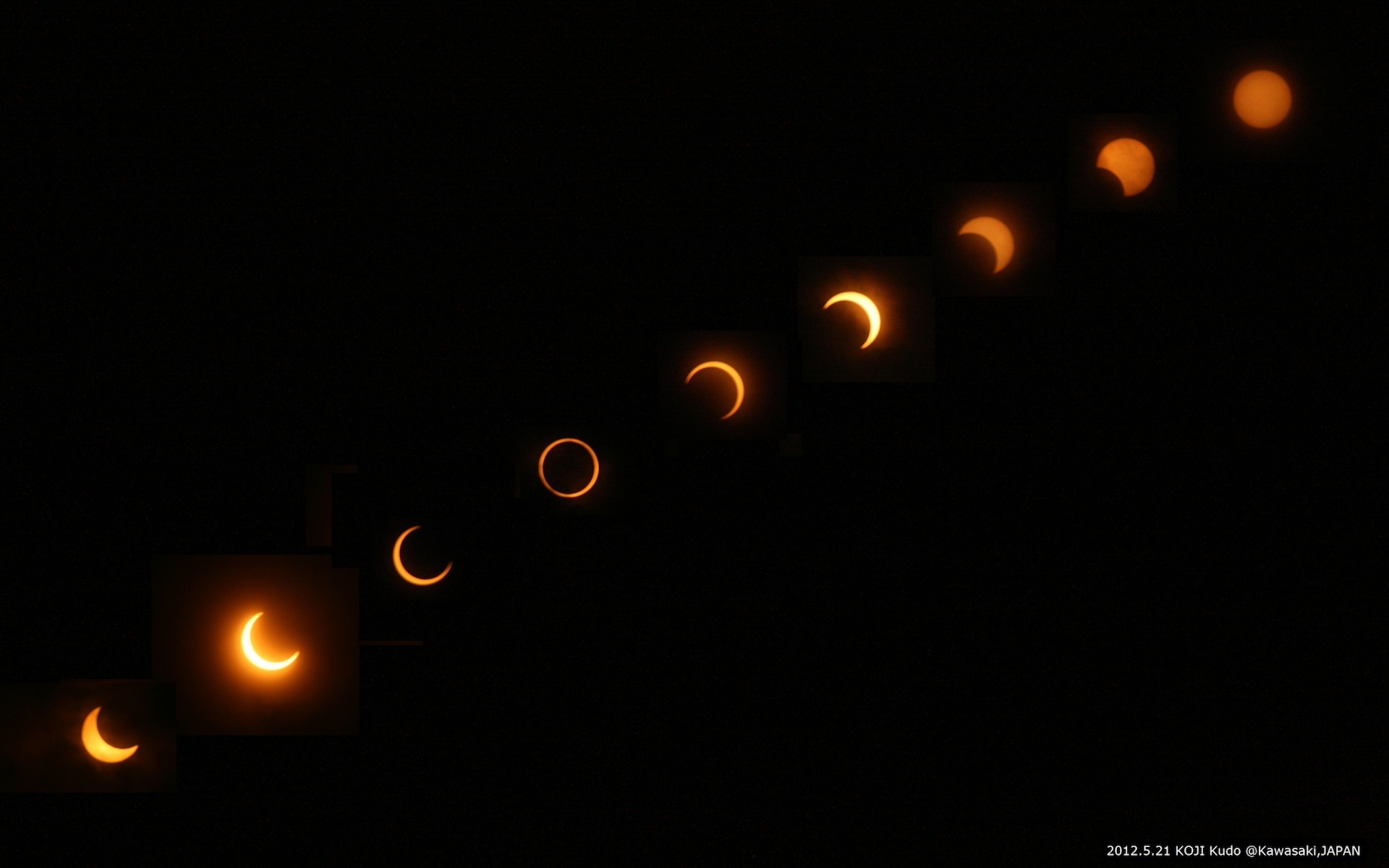

A total eclipse is not the same as an annular eclipse. It will be a sort of weird twilight since so much of the sun is still visible. A partial eclipse is not a full eclipse. There is a maximum duration for an eclipse.
An annular solar eclipse is similar to a total eclipse in that the moon passes in front of the sun. The moon is too small to fully cover the sun's disk. The moon's distance from Earth can be as little as 221,478 miles and as much as 258,712 miles. The shadow cone of the moon's umbra can be seen for less than the average distance from Earth.
The tip of the umbra doesn't reach Earth if the moon is at a higher distance. During an eclipse, the antumbra, a theoretical continuation of the umbra, reaches the ground, and anyone can look up past either side of the umbra and see a ring of fire. If you put a penny on a nickel it would be the moon and the nickel would be the sun.
There are eclipses called A-T. When the moon's distance is close to the umbra, there is a special type of eclipse.
Because the moon appears to pass in front of the sun, total, annular and hybrid eclipses are called "central" eclipses to distinguish them from eclipses that are only partial.
Only 5% of solar eclipses are hybrid.
Eclipses don't happen at all the time. The moon's tilt is related to Earth's tilt around the sun. The solar eclipse doesn't happen because the moon's shadow passes above or below Earth.
At least twice a year, a new moon will align itself with the sun in a way that will cause it to be completely obscured. The alignment point is referred to as a nodes. Depending on how close the new moon is to the earth, it can be either a central or partial eclipse. If the moon's distance from the Earth is taken into account, a central eclipse is a total one.
An eclipse will repeat itself or return after a certain interval of time. The Saros cycle was used as far back as the days of the early Chaldean astronomer. The word Saros means "repetition" and is equivalent to 18 years, 1113 days, or a day less or more depending on the number of leap years that have interceded. The relative positions of the sun and moon are almost the same as before. The path of each eclipse of a series is displaced in a third of the way around Earth to the west by that third of a day.
On March 29, 2006 a total eclipse swept across parts of western and northern Africa. The eclipse will track across northern Mexico, the central and eastern United States, and the Maritime provinces of Canada.
A partial solar eclipse will take place on October 25, 2022, It will be the last partial solar eclipse of the century.
There will be a partial solar eclipse on October 25.
As a solar eclipse approaches, the mainstream media often will provide warnings against looking at the sun with bare eyes. Most people think that eclipses are dangerous.
That's not true!
All the time, the sun is dangerous. Your eyes can be damaged by the sun's rays. We don't have a reason to look at the sun. We shouldn't get a reason from an eclipse.
There are ways to get around.
The safest way to view a solar eclipse is to build a hole. A screen with a small opening behind it is used to create an image of the sun. A magnified image of the sun can be projected onto a white card with a telescope or binoculars. The larger the image, the closer you can see it. You should look for sun spots. The sun is a bit darker around the edge. If you remember not to look through the binoculars or telescope when they are pointed toward the sun, this method is safe.
The "pinhole mirror" is a variation of the pinhole mirror. A piece of paper with a small hole in it can be used to cover a pocket mirror. If you want to see a disk of light onto the wall, place the covered mirror on the sunlit windowsill. There is a disk of light. The image will be one inch across for every nine feet or three centimeters from the mirror if it's farther away. The mirror can be held in place with the help of modeling clay. There are different sized holes in the paper. A large hole makes the picture bright, but fuzzy, and a small hole makes it dim. The room should be dark. To make sure the mirror is good enough to project a clean, round image, be sure to try this out before you buy it. Don't allow anyone to see the sun in the mirror.
You can see the shadow cast by the trees during the partial phases. Do you see anything? Do you think it's worth a photograph? The suns will be projected through a series of gaps between the leaves. The property of light causes this. The light rays don't shoot straight by the rim of the gaps, but bend around the edge according to Vince. Waves create a pattern of rings that look like a bull's eye. If you want to get all set up for it, we have guides to the best cameras for Astrophotography and the best lens for Astro, so you can be prepared when the time comes.
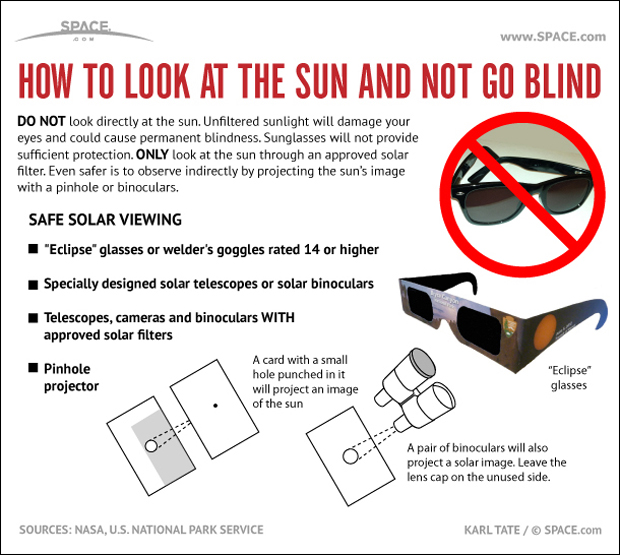
The aluminized Mylar is one of the acceptable filters. The Mylar filters are specially designed for solar observing. shade 14 arcs-welder's glass is just a few dollars and is acceptable. It's a good idea to test your observing techniques before the eclipse.
Old color film negatives, black-and-white film, and sunglasses are not acceptable filters. Although these materials have very low visible-light transmittance levels, they transmit an unacceptably high level of near-IR radiation that can cause a thermal burn. It's not a guarantee that your eyes are safe if the sun appears dim or you don't mind looking at it through a filter.
During a total eclipse, when the sun's disk is completely covered, you can see directly at the sun. During those few seconds or minutes, the corona shines in all its glory as it surrounds the sun. It is different from eclipse to eclipse. It is faint and delicate, with a sheen similar to an Aurora. It has different looks. Sometimes it has a soft continuous look, but at other times, long rays shoot out in multiple directions. It can be seen from the petals and streamers. You'll need to protect your eyes again when the sun comes back into view.
The earliest record of a solar eclipse happened over 4,000 years ago.
The account of Hsi and Ho, two court astronomer who were caught completely unaware of a solar eclipse, is in the ancient Chinese book of documents. Hsi and Ho were ordered to have their heads chopped off by the fourth emperor. In the year 2134 B.C., there was an eclipse.
Amos 8:9 in the Bible states, "I will cause the sun to go down at noon, and I will darkness the Earth in the evening." The eclipse that took place at Nineveh in ancient Assyria on June 15, 763 B.C. is believed to be a reference to this.
There was a solar eclipse.
The war between the Lydians and the Medes lasted for five years. The Ionians were told that the time was near when the day would turn to night. The sun faded away on May 17th. Herodotus wrote that without a strong bond, there is little security to be found in men's covenants.
A new meaning to the term "scared to death" has been given by the timid emperor Louis of Bavaria, who witnessed the longest total eclipse of the sun on May 5, A.D.
Astronomers have learned a lot by studying eclipses and by the 18th century, observations of solar eclipses were seen as a great source of information.
The total solar eclipse was observed by Samuel Williams, a professor at Harvard. During the Revolutionary War, Penobscot Bay was behind enemy lines. The British granted the safe passage due to the interest of science over politics.
It was all for nothing.
When the narrowing crescent of sunlight slid around the dark edge of the moon, it was likely that Williams made a crucial error in his computations and inadvertently positioned his men at Islesboro.
A few spots on the moon may appear to be red during a solar eclipse. The tongues of hydrogen gas rise above the sun. A new chemical element was discovered during the total eclipse of August 18, 1868. The name "Helios" came from the Greek helios (the sun). In 1895, the gas was identified.
Some stars and planets can be seen in the dark sky during a total eclipse. The general theory of relativity was tested under such conditions. Light from stars beyond the sun was predicted to bend as it passed the sun. The positions of stars photographed near the sun's edge during a total eclipse on May 29, 1919, were compared with photographs of the same region of the sky taken at night.
Astronomers used to have to wait for an eclipse before making most of the observations. A total eclipse of the sun is one of the most impressive natural phenomena and will be remembered for a long time. It should be on your bucket list.

Find information from the Eclipse Chasers, Mr. Eclipse.com, and NASA's Eclipse Website.
If you snap an amazing solar eclipse photo and would like to share it with Space.com's readers, send your photo, comments, and your name and location to space photos@space.com
We encourage you to follow us on social media: