
The Conversation contributed the article to Space.com's expert voices.
Danny Price is a senior research fellow at the university.
"Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence."
— Carl Sagan ("Cosmos," 1980)
Astronomers will apply this phrase to a strange signal captured with China's "Sky Eye" telescope that may be a transmission from alien technology.
An article reporting the signal was posted on the website of China's state-backed science and technology daily newspaper, but was later removed. Is it being kept quiet?
We should be interested but not excited. An interesting signal has to go through a lot of tests to find out if it is a sign of extraterrestrial technology or if it is the result of an unexpected source of interference.
Media releases are usually timed for simultaneous release with peer-reviewed results, so it was probably just released a bit early by mistake.
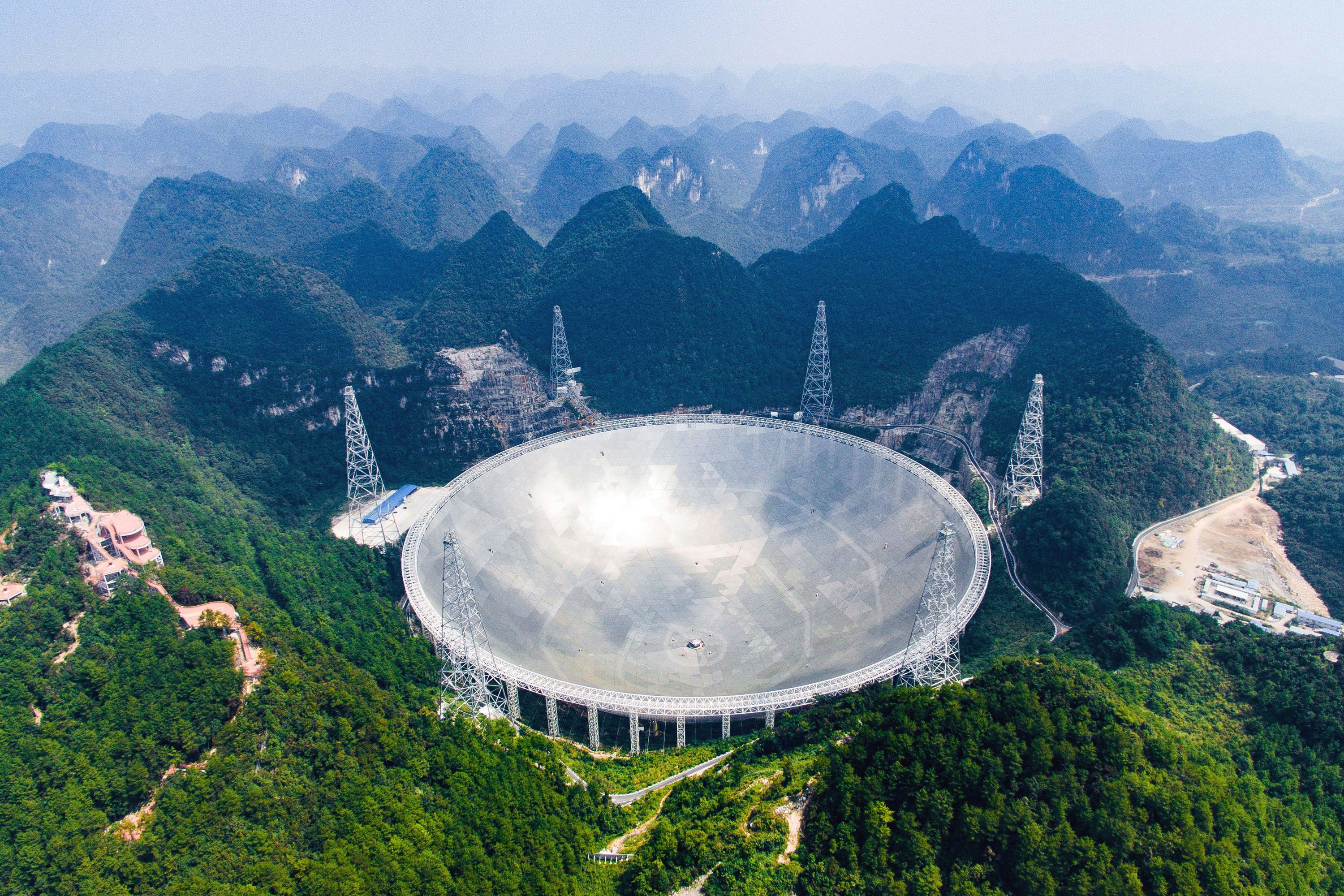
Sky Eye is the biggest and most sensitive single-dish radio telescope in the world. The structure is built inside a natural basin in the mountains of China.
The telescope is so large that it can't be tilted, but it can be pointed in a direction that makes it look less reflective. The location of the telescope's focal point can be changed by changing the surface.
FAST can be used for astronomy research in a variety of areas. The search for SETI is one of the areas.
While the telescope is also running its primary science programs, SETI observations are mostly done iniggy-back mode. Large swaths of the sky can be scanned for signs of alien technology without disrupting other science operations. Dedicated SETI observations are still being carried out.
Frank Drake, an American astronomer, pointed the Tatel telescope towards two nearby sun-like stars and scanned them for signs of technology in the 1960's.
The searches have become more sensitive over the years. The systems in place at FAST can process billions of times more radio spectrum than Drake could.
We haven't found any evidence of life outside of Earth.
Fast is able to sift through a lot of data. A telescope feeds 38 billion samples a second into a cluster of high- performance computers, which then produce exquisitely detailed charts of incoming radio signals. There are signals that look like technosignatures.
FAST is able to pick up faint signals. The Parkes Radio Observatory's telescope is less sensitive than it is. The output power of a transmitter on a nearby exoplanet could easily be detected by FAST.

The problem with being so sensitive is that you can find interference that is too faint to detect. The SETI researchers have had this before.
The signal we called BLC1 was detected last year.
It turned out to be weird interference. A new verification framework was developed to uncover its true nature.
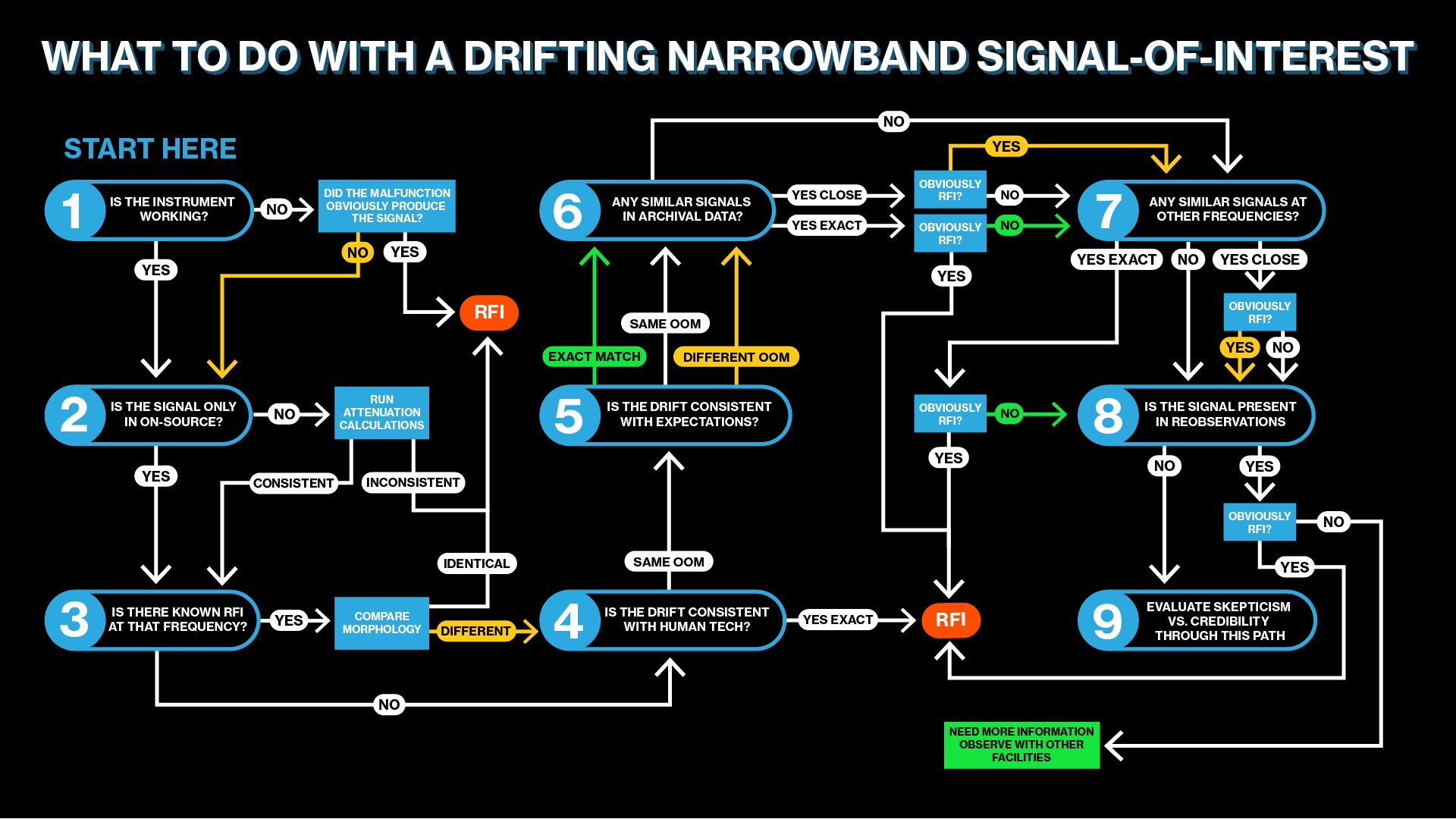
It took about a year for peer-reviewed analysis to be published. We might need to wait a bit for the FAST signal to be analysed.
The chief scientist for the China Extraterrestrial Civilization Research Group acknowledged this.
There is a very high chance that the signal is radio interference and needs to be ruled out. It might be a long process.
We might need to get used to a gap between finding signals and getting them verified. Many more signals are likely to be found byFAST and other telescopes.
Some of these may be new astrophysical phenomena and some may be technosignatures.
The burden of extraordinary evidence will be met by FAST's extraordinary signals. It's too early to say, but it's encouraging that their SETI searches are finding strange signals.
There is a lot of interest and activity in the SETI field between the two initiatives. It's not just radio waves that are being searched with optical and IR light.
Stay interested but don't get too excited.
Under a Creative Commons license, this article is re-posted. The article is open in a new tab.
Become a part of the discussion and follow all of the Expert Voices issues and debates on social media. The author's views do not represent those of the publisher.