The sun's corona is the source of the solar wind.
The charged particles breeze through the solar system at speeds ranging from around 250 miles ( 400 kilometers) per second to 500 miles (800 km) per second.
The solar wind creates a flurry of charged particles in the magnetosphere and along Earth's magnetic field lines. Aurora displays can be seen above the polar regions.
There is a question about how hot the sun is.
The existence of the solar wind was first proposed by an astronomer named EugeneParker.
The University of Chicago says that in 1957, when he was an assistant professor, he realized the sun should emit charged particles at high speed. Solar physicists don't fully understand why the sun's atmosphere is hotter than it is on the surface.
The sun's corona has a temperature of 3.5 million degrees Fahrenheit, which is two million degrees Celsius. The solar wind drags the sun's magnetic field along with it as the sun's gravity can no longer hold it down.
He had a theory that was criticized at the time. The first reviewer on the paper said that the author should read up on the subject before writing a paper about it.
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar became the namesake of the Chandra X-ray Observatory due to his support for the theory. The University of Chicago said that Chandrasekhar accepted the theory because he could not find any problems with it.
The presence of solar wind particles was detected by NASA's Mariner 2 in 1962.
In addition to the constant streams of solar wind, the sun sometimes expulses huge quantities of charged particles. Power grids, telecommunication networks and satellites can be affected by these events, known as coronal mass ejections, which can cause storms in the environment around Earth.
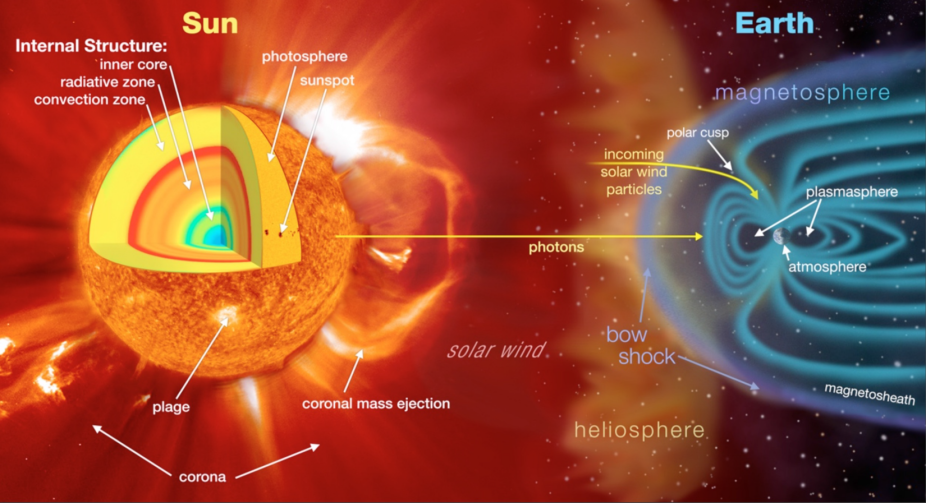
The solar wind sweeps through the solar system and forms a bubble called the heliosphere. The heliosphere is shaped like a long wind sock as it moves with the sun.
According to the statement, the closest boundary to the sun is 100AU. The average distance from Earth to the sun is equivalent to over 100 million miles.
Cosmic rays that can damage living cells are protected by the heliosphere. Comic rays are created outside of our solar system and travel at a high rate of light. The high-energy atom fragments were bombarding Earth without our bubble. Life would have evolved differently if it weren't for the heliosphere, according to heliophysicist Richard Marsden.
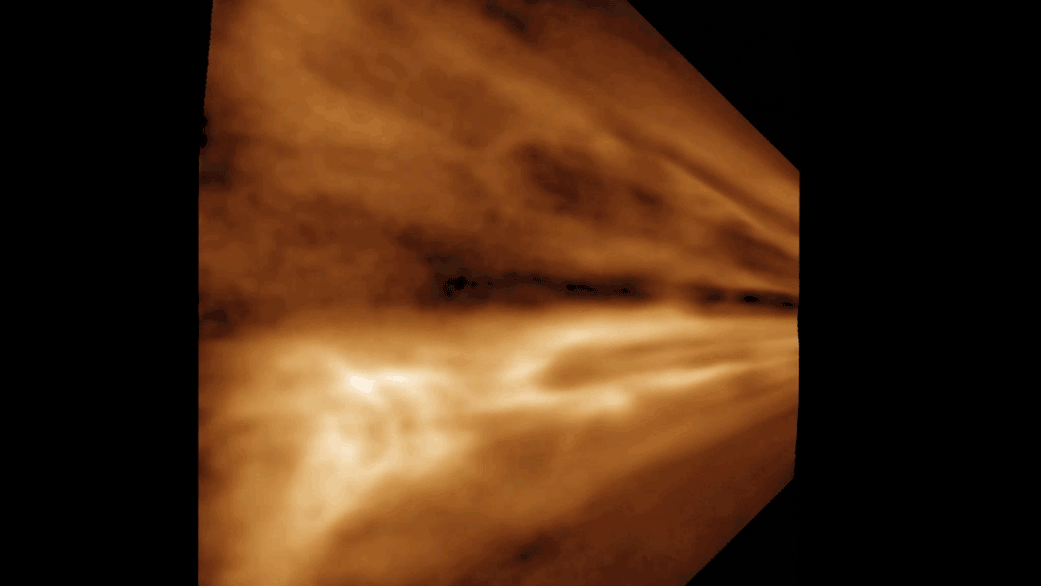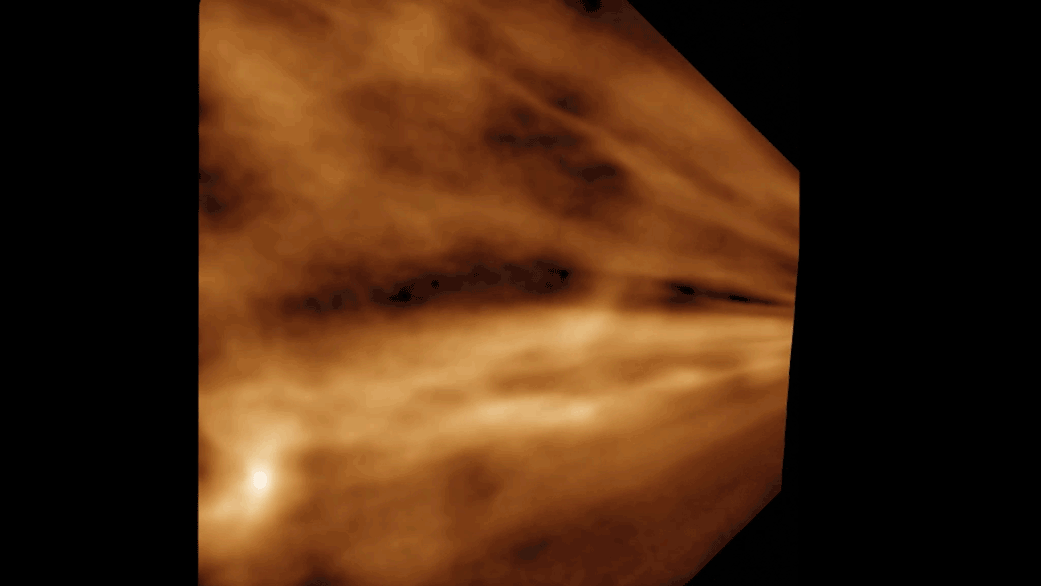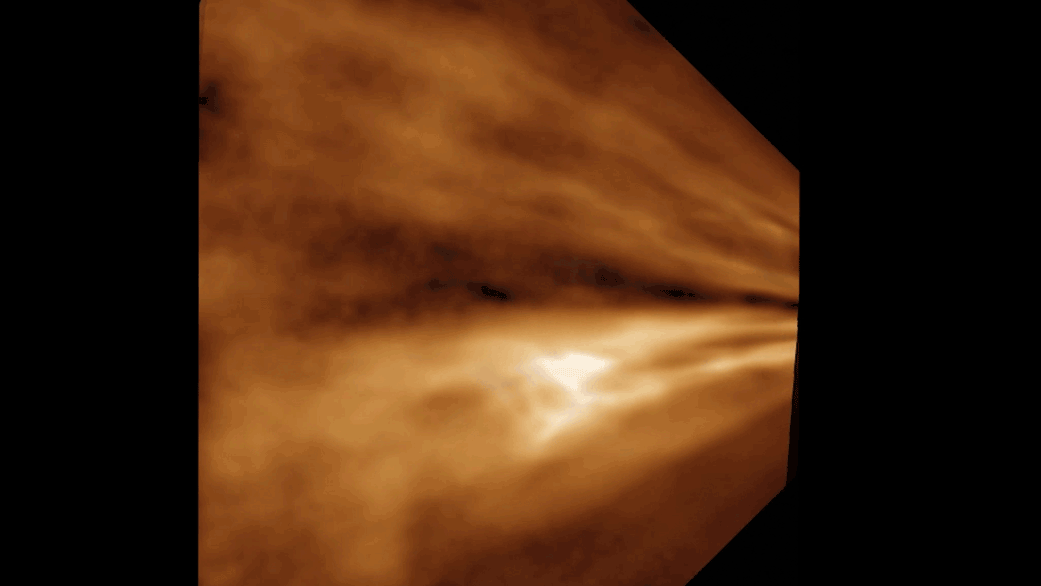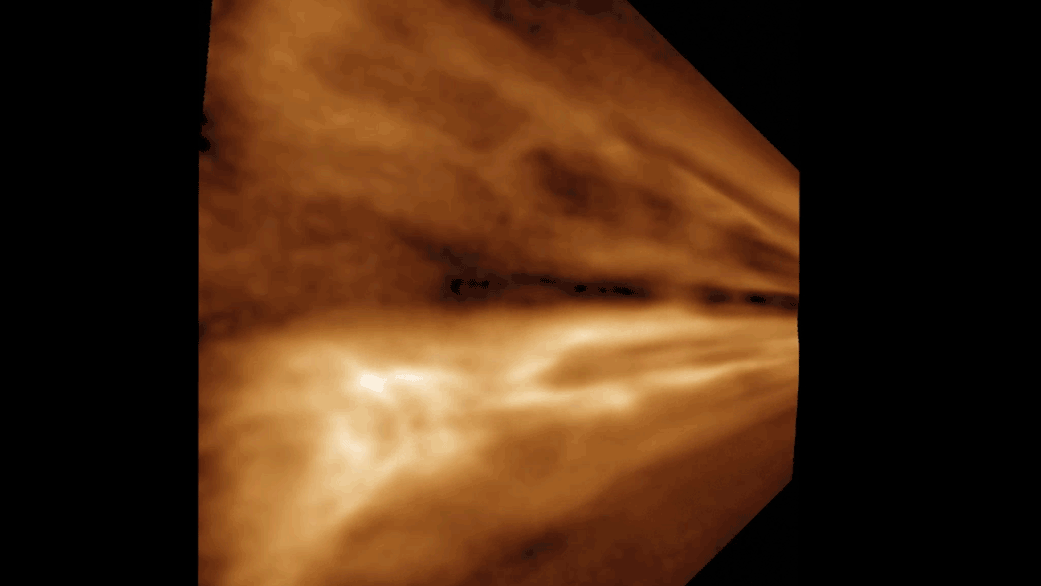
The density and speed of the solar wind varies throughout the 11-year cycle of activity. Sunspot numbers, radiation levels, and ejected material ebb and flow from a solar maximum to a solar minimum. The properties of the solar wind are affected by these alterations.
According to the space weather forecast website SpaceWeatherLive.com, the average solar wind speed is 190 miles per second.
Things are being put into perspective.
The solar wind is travelling at an average speed of over one million mph. A Category 5 storm can reach speeds of over 200 km/h.
During the flyby of Venus, the spacecraft detected the presence of solar wind and identified two separate streams of solar wind, one fast and the other slow. The fast stream was said to be travelling at twice the speed of the slow stream.
X-ray images taken from the sun's corona were used to identify the origin of the solar wind. The solar wind is caused by the cooler regions of the sun with an open magnetic field line structure.
There can be abnormal fast solar winds. According to SpaceWeatherLive.com, wind speeds can go up to more than 1000 km per second in a single day.
The slower solar wind has got scientists scratching their heads despite the impressive speeds.
According to a NASA statement (opens in new tab), the solar wind is a larger mystery.
The origin of the slow wind stream when it flew around the sun's poles has already been discovered by NASA. It found that the sun's equator is where the solar wind comes from.
"As the solar cycle progresses towards its maximum, the structure of the solar wind changes from two distinct regimes, fast at the poles and slow at the equator, to a mixed, inhomogeneous flow."
During its seven-year mission, the solar probe will investigate the mystery. It has promise for revealing new understanding.
Our star has an effect on the solar system.
"If the sun sneezes, Earth catches a cold, because we always feel the impact of what happens on the sun thanks to the solar wind," said Nicky Fox, the division director for heliophysics at NASA Headquarters.
The sun's solar wind creates a bright light show in the polar regions. The southern lights are called theaurora australis whereas the northern lights are called theaurora borealis. If solar wind speeds are high enough geomagnetic storms can be triggered which can lead to Auroras expanding closer to the equator than is1-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-6556 is1-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-65561-6556
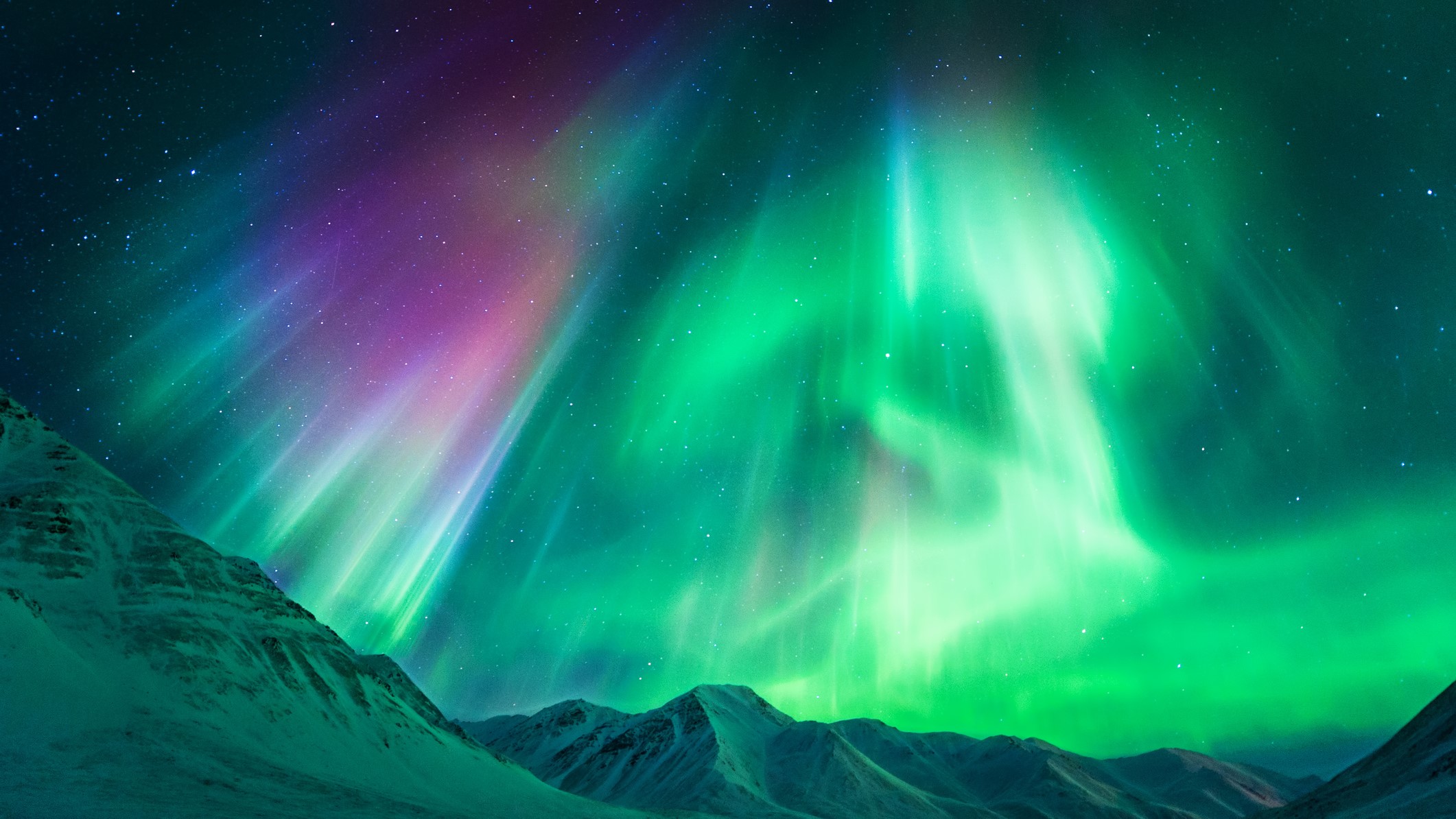

Astronauts in space can be threatened bymagnetic storms. During storms, astronauts on the International Space Station need to seek shelter and all spacewalks are paused and sensitive satellites are powered down until the storm passes.
When a storm destroyed up to 40 Starlink satellites worth over $50 million, it was the first time that the company had seen the damage space weather can cause. When Starlink satellites are released into a very low altitude, they rely on onboard engines to raise themselves to a final altitude of about 350 miles.
During a storm, the Earth's atmosphere absorbs energy from the storms, heats up and expands upwards, leading to a denser thermoosphere that extends from 50 miles to 1000 miles above the Earth's surface. Satellites can be affected by a denser thermoosphere. The Starlink satellites failed to overcome the increased drag from the storm and fell back to Earth.
It is important to increase our understanding, monitoring and predictions of solar weather because it can be very costly. Scientists are studying solar wind in order to better understand the space weather environment.
NASA says we can't ignore space weather but we can protect ourselves.
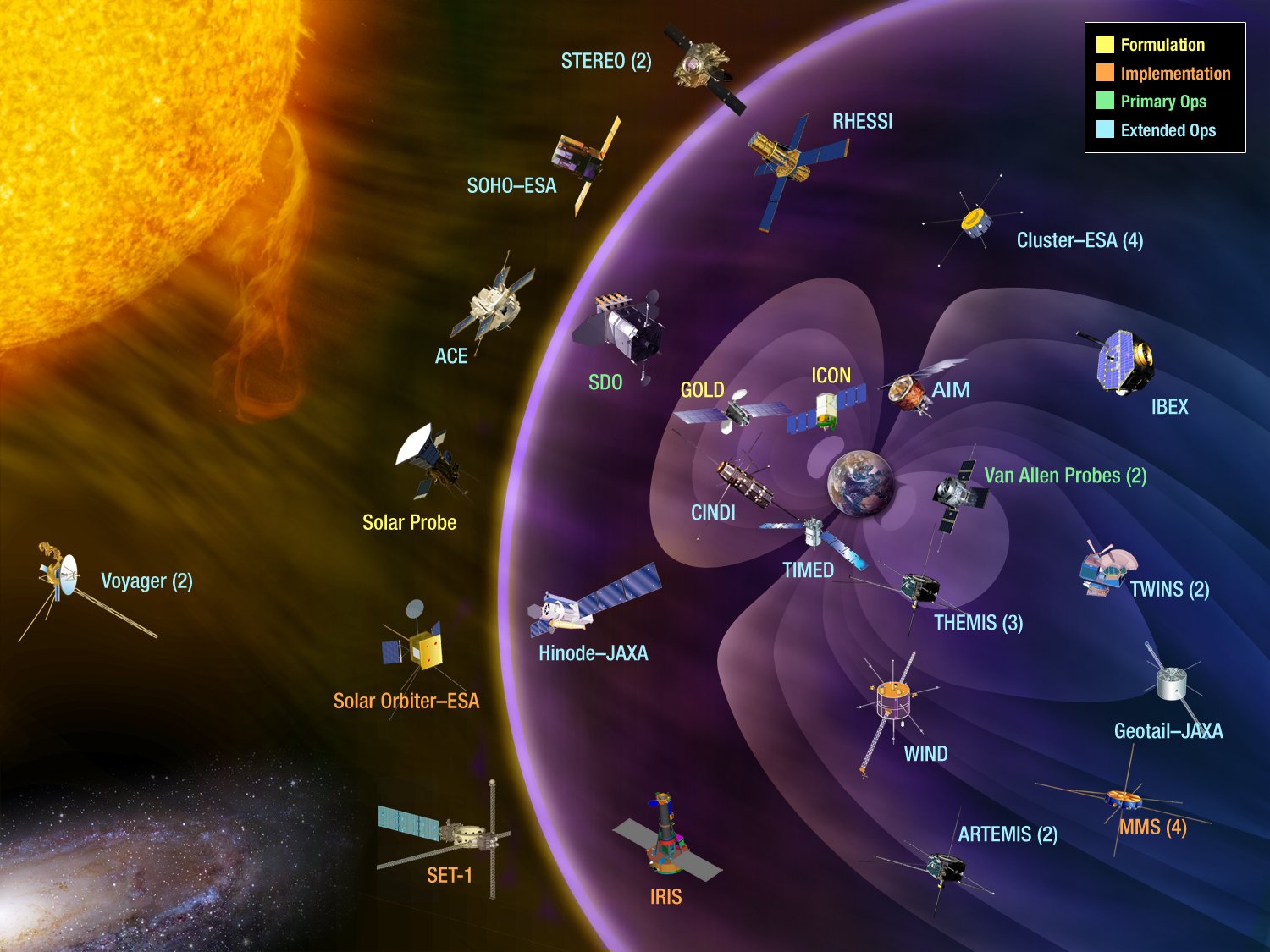
The sun's influence on the solar system is studied by mission.
The goal of these missions is to understand everything from how planetary atmospheres have formed to how space weather can affect astronauts and technology near Earth.
There are a lot of space missions dedicated to understanding the sun's behavior. The mission can be thought of as a single observatory.
The HSO consists of several solar, heliospheric, geospace and planetary spacecraft including theParker Solar Probe on a daring mission to "touch" the sun.
If you would like to see how the solar wind interacts with other objects in the solar system, check out this NASA Infographic. You can explore the heliospheric missions with NASA. The University of Chicago published an explainer article about solar wind. You can see real-time solar wind speed and density with the space weather prediction center.
Richardson, Wang, and Paularena were part of the research team. There is a solar wind from minimum to maximum. The article "Advances in Space Research" can be found at www.sciencedirect.com.
There are holes The space weather prediction center is run by the National Weather Service. On June 15, 2022, from www.swpc.noaa.gov/phenomena/coronal- holes.
There are impacts of solar flares. May 13th, NASA. Flare-impacts.html was published on June 15, 2022, from the NASA website.
Solar wind causes light shows. In October 2015, NASA. Fast-solar-wind-causes-aurora-light-shows is an image feature on the NASA website.
There is aosphere. September 1, 2019, is the date of the science and technology event. On June 15, 2022, from www.ulysses.com, "The Heliosphere" was added.
The name of the solar probe is named after a legendary figure in solar science. The University of Chicago news was published in March. The story was published on June 15, 2022, from thenews.uchicago.edu/story/eugene-parker-legendary-figure-solar-science- and-namesake-parker-solar-probe-1927-2022.
There is a space agency called NASA. The effects of the sun's rays. There is a space agency called NASA. The effects of the solar-wind were reported in June.
There is a space agency called NASA. Science of solar wind. NASA space technology is used. On June 15, 2022, from www.jpl.nasa.gov/nmp/st5/SCIENCE/solarwind.
There is a space agency called NASA. There is a solar wind. The sun's rays have a solar physics. There is a space flight center. On June 15, 2022, from www.solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/SolarWind.
The sun is shining. There is a website called SpaceWeather Live.com. The Solar-wind can be found at https://www.spaceweatherlive.com/en/help/ the-solar-wind.
There is a solar wind There is a forecast forAurora. On June 15, 2022, from www.auroraforecast.is/solar-wind.
There is a solar wind The space weather prediction center has a solar wind. On June 15, 2022, from www.swpc.noaa.gov/phenomena/solar-wind.
H. Zell was published on March 19th. The effects of the sun on space There is a space agency called NASA. On June 15, 1942, from www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sunearth/missions/index.html.