Wanyuan Song and Jana Tauschinski work for the British Broadcasting Corporation.
 Image source, BBC; Getty Image; Nasa
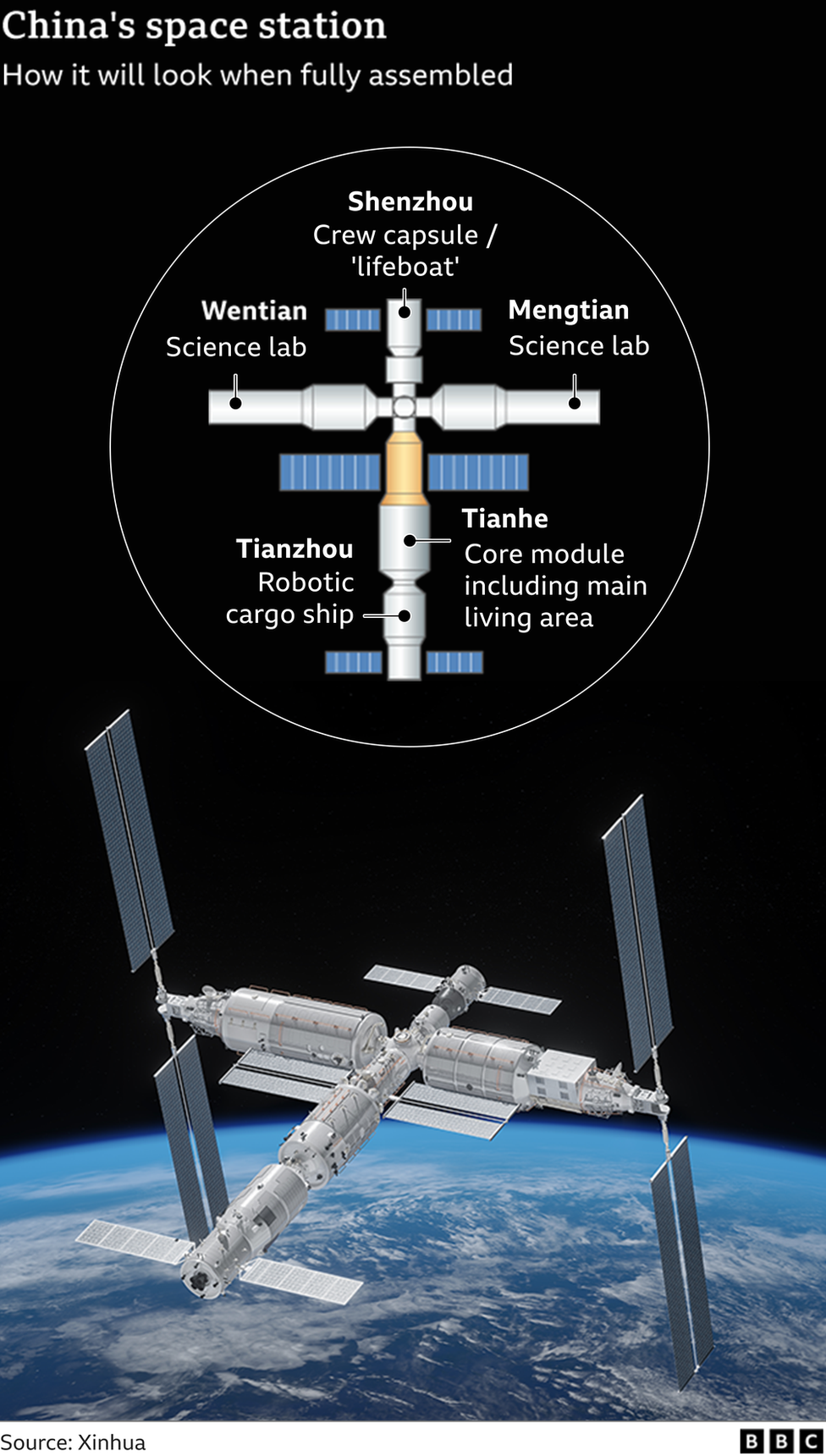
Image source, BBC; Getty Image; NasaThe country's new space station is being worked on by three Chinese astronauts.
It is the latest step in China's plan to become a space power in the future.
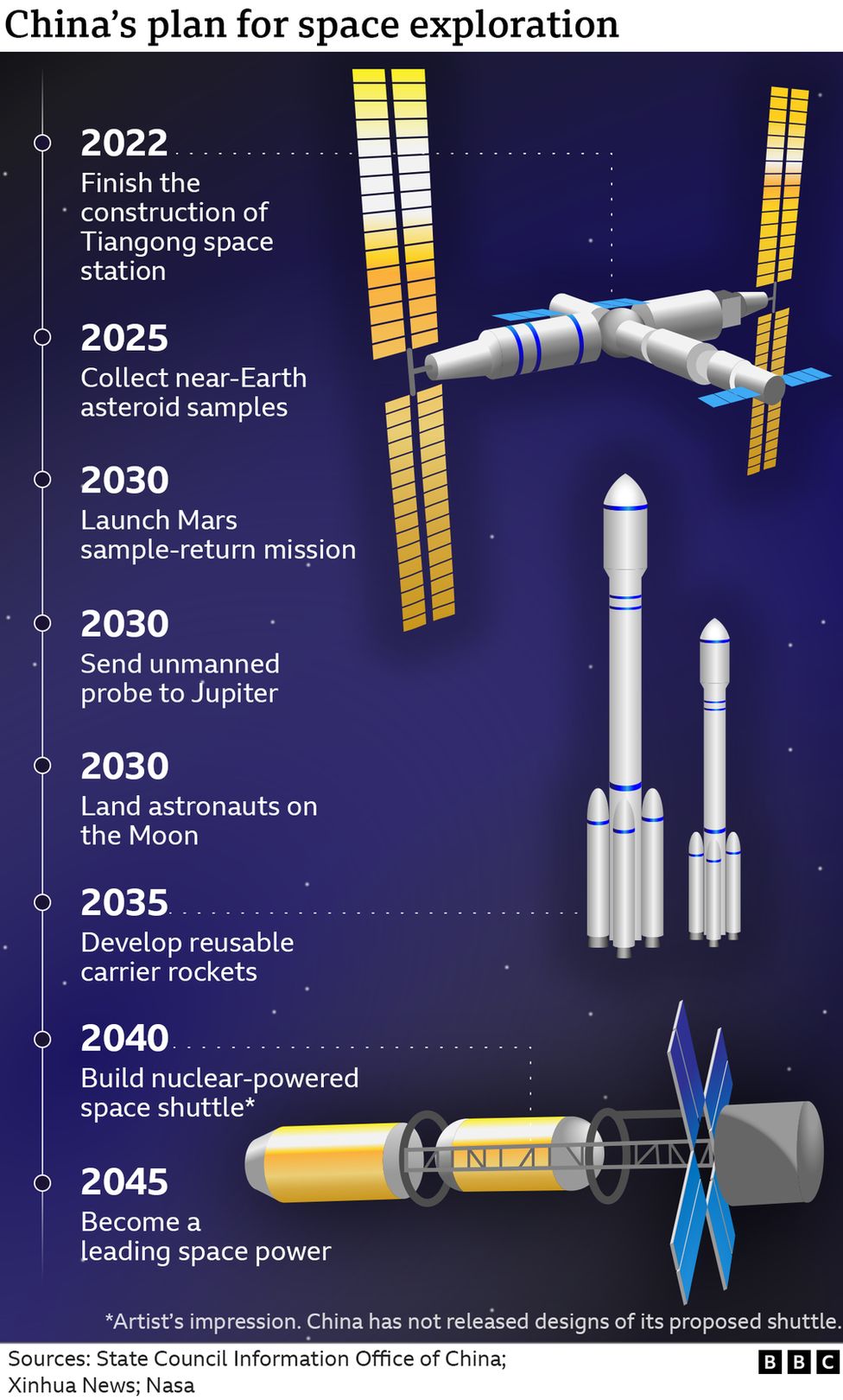
The first module of China's space station was launched last year. The modules will be added by the end of the year.
It will launch a telescope next year. This will dock with the space station for servicing and replenishment.
It will have its own living quarters.
After the Soviet Union and the US, China is the third country to have put humans into space.
The International Space Station is due to be dismantled in 2031.
US law forbids the sharing of data between the US and China.
China does not stop there.
It wants to take samples from asteroids in the future.
It wants to have its first astronauts on the moon by the year 2030.
Several countries are trying to get to the moon as China expands its role.
The new giant SLS rocket was rolled out at the Kennedy Space Center and will be used to return astronauts to the moon.
Japan, South Korea, Russia, India, the United Arab Emirates, and others are working on their own lunar missions.
India wants to have its own space station by the year 2030.
The Cultural Revolution disrupted the launch of China's first satellite.
The US, the Soviet Union, France, and Japan all went into space by that point.
China has launched more than 200 rockets in the last decade.
Chang'e 5 was sent to the Moon to collect and return rocks. The Chinese flag was larger than previous US flags.
China has put 14 astronauts into space, compared with the US and the Soviet Union, which put more than 130 in the past.
There have been challenges. Part of a Chinese rocket fell out of the sky and crashed into the ocean.
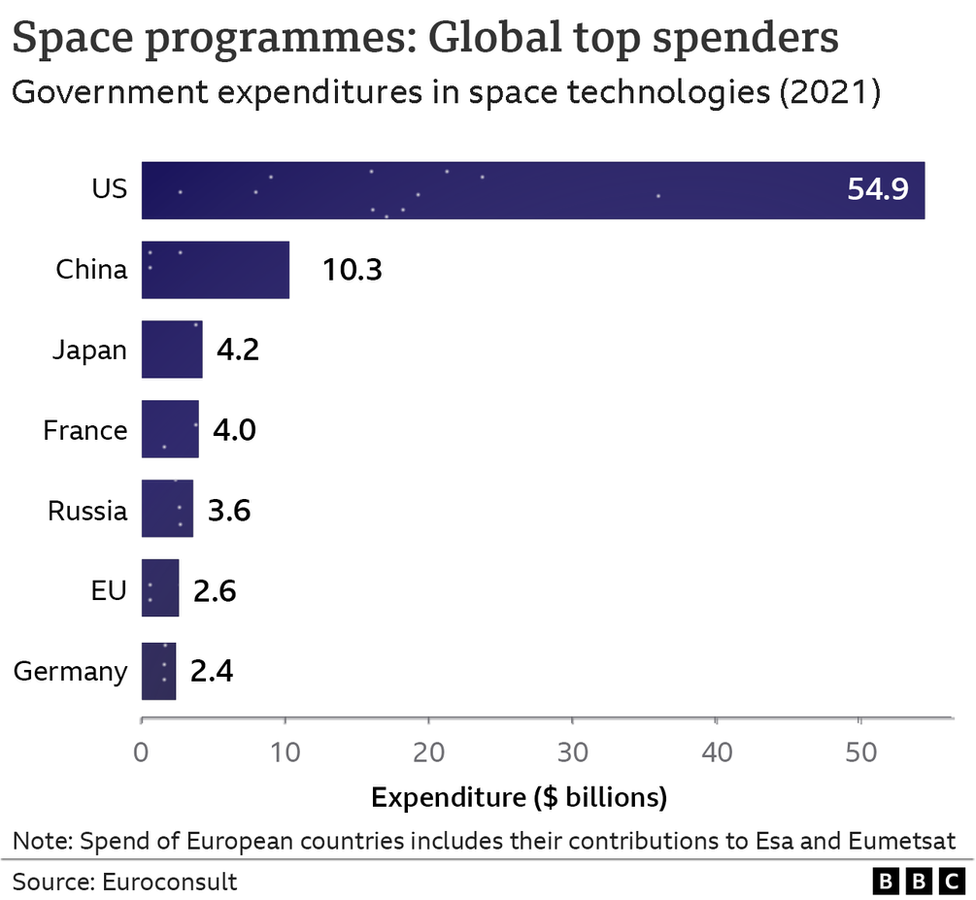
According to the Chinese state media, at least 300,000 people have worked on China's space projects, which is 18 times the number of people currently working for the US space agency.
The Chinese National Space Administration has an annual budget of two billion dollars.
According to Chinese media, in 2016 China opened its space industry to private companies, and they are now investing more than 10 billion dollars a year.

China is interested in developing its satellite technology for a wide range of applications.
Many of its satellites have military uses. They can help it spy on rivals.
China is prolific in all aspects of space and is not just focused on high-profile space missions. The resources and political motivation allow them to fund their plans.
There are opportunities to extract rare earth metals from the Moon.
Prof Sa'id Mosteshar is the director of the London Institute of Space Policy and Law at the University of London.
He claims that China's space programme is more about impressing the rest of the world. It's a demonstration of power and technology.
The additional reporting was done by Jeremy and Tim.