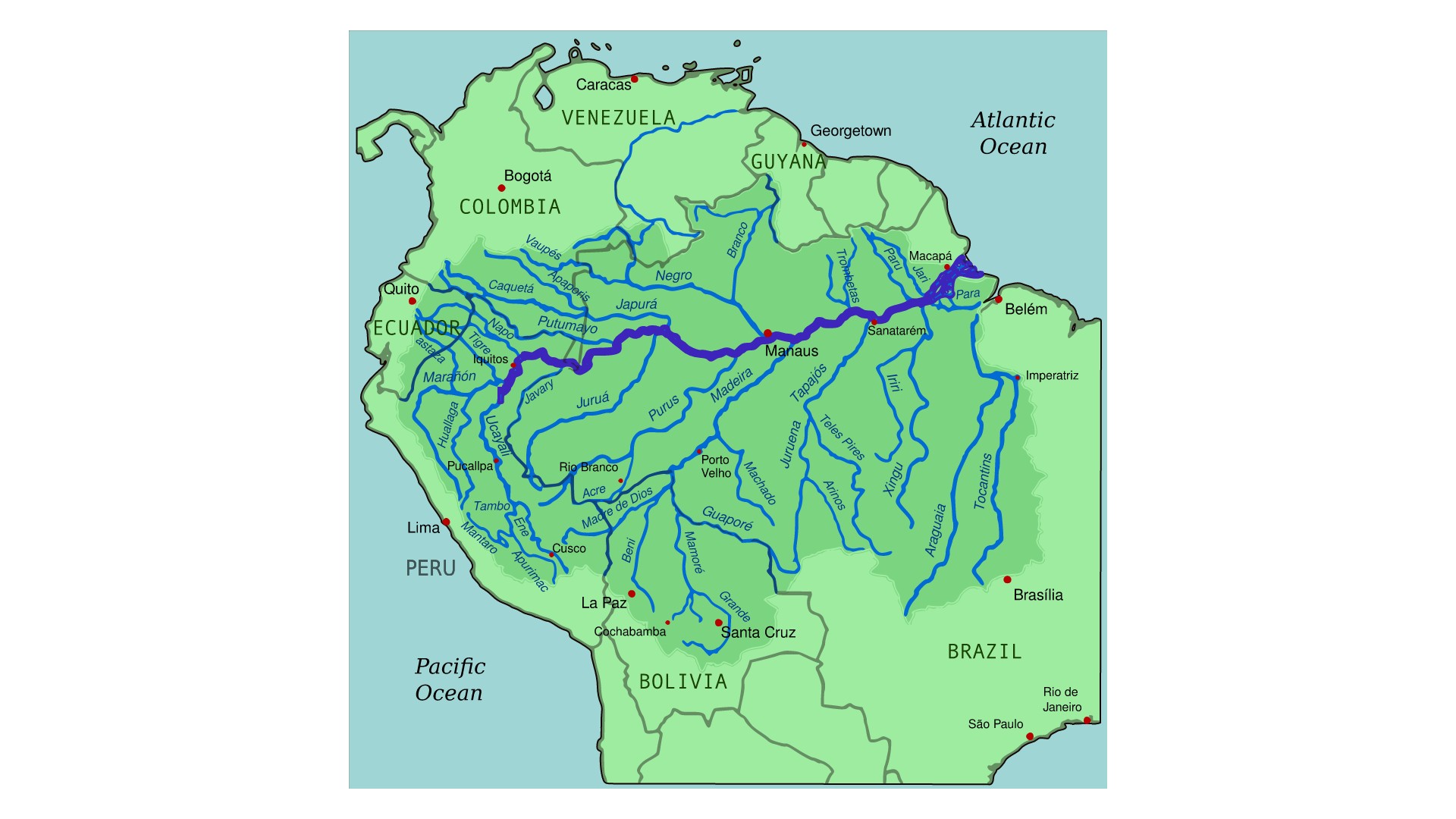
The Amazon River is the second-longest river in the world and one of the most significant waterways. It contains more fresh water by volume than any other river and is home to the largest river dolphin in the world.
There is something that cannot be found on the Amazon River, and that is bridges.
According to the World Wildlife Fund, more than 30 million people live in the basin of the Amazon and no bridges span it. Why is this the case? Is it difficult to build structures in a rainforest with swaps, wetlands and deep undergrowth? Is there any financial barriers? Is it worth the effort?
What is the world's longest bridge?
The lack of bridge crossing on the Amazon is odd compared to other rivers. More than 100 bridges have been completed in the last 30 years across the Yangtze, Asia's premier river, while Europe's Danube is only one-third as long.
So what's the deal with the Amazon?
"There is no sufficiently pressing need for a bridge across the Amazon," Walter Kaufmann, chair of Structural Engineering (Concrete Structures and Bridge Design) at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich, told Live Science in an email.
There are very few major roads for any bridge to connect to in the Amazon because it is a meandering 4,300-mile (6,920 kilometer) length. There is no need for bridges to be built in the cities and towns that border the river because boats and ferries are an established means of moving goods and people.
There are also technical and logistical difficulties.
The Amazon is not an ideal location for bridge builders as it has an array of natural stumbling blocks that need to be conquered by engineers and construction workers.
It would require a lot of financial investment to build a multi-span bridge crossing extended lower areas because of its extensive marshes and soft soils. The changing positions of the river's course across the seasons would make construction extremely demanding.
These issues are not unique to the Amazon, but they are particularly severe there.
The environment at the Amazon is among the most difficult in the world.
Kaufmann said that floating structures are not a solution that would work in most parts of the Amazon because of seasonal fluctuations. During the dry season between June and November, the Amazon has a width of between 2 and 6 miles, while in the wet season December through April has a width of between 2 and 9 miles.
Kaufmann said that the challenge would be unique.
There is no immediate need for a bridge across the Amazon, as well as the processes involved in building one would be considerable.
What is the biggest freshwater fish in the world?
There is a bridge that crosses the Negro River, which is the main tributary of the Amazon. The only major bridge that crosses the Amazon is the Ponte Rio Negro, which was completed in 2011.
While there are no concrete plans for a bridge over the Amazon, it doesn't mean it won't happen, says Philip Fearnside, an American scientist who has spent much of his career in Brazil.
The president of Brazil declared that he wanted a bridge across the Amazon to be built as part of his Rio Branco Project, but so far there has been no progress.
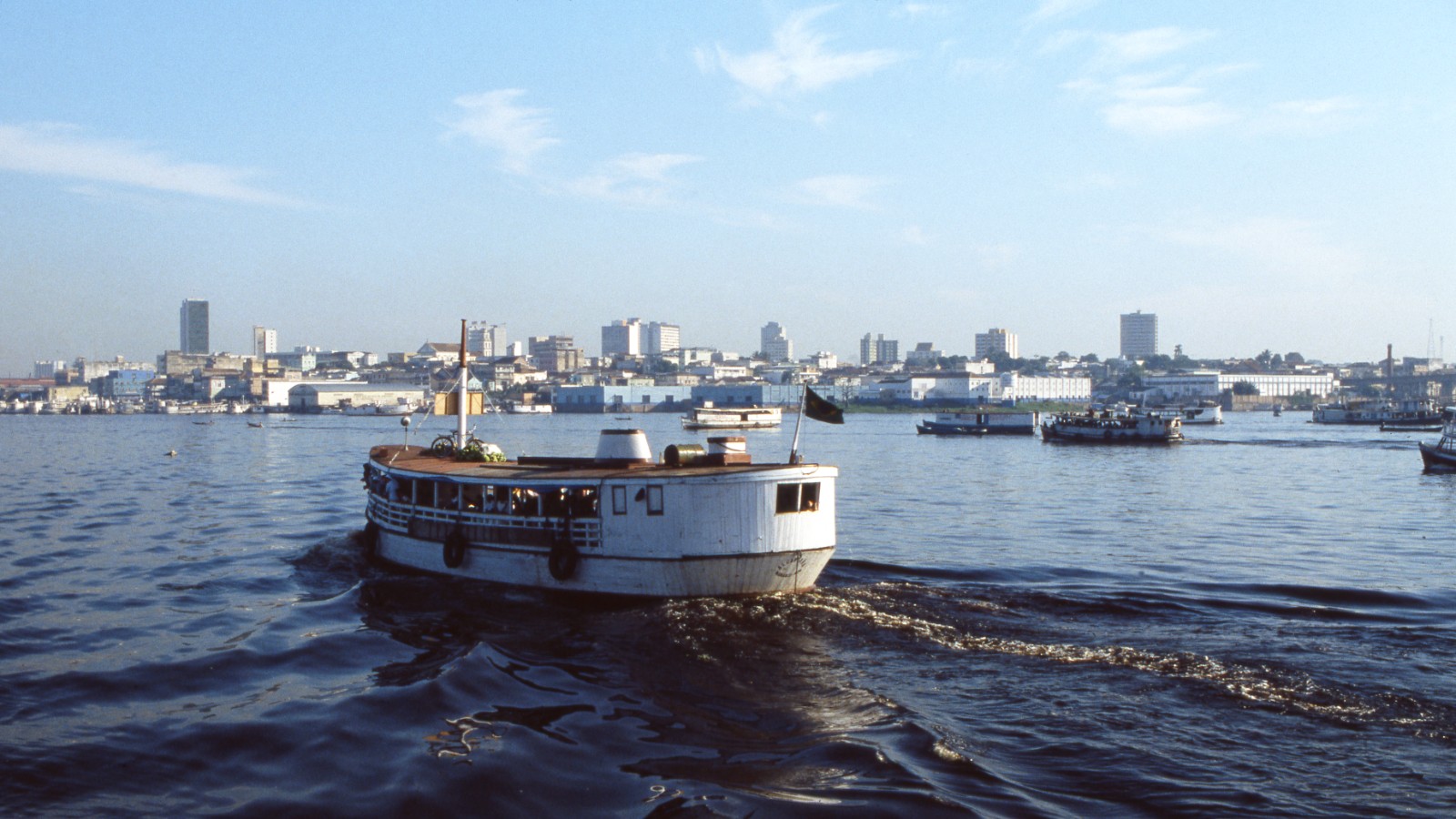

Plans were drawn for a bridge across the SolimF5;es River to connect the BR-319 highway.
BR-319 is a high political priority, but it does not have an economic justification.
The creation of such a bridge would give deforesters access to about half of what remains of the BR-319, as was stated in a 2020 commentary by Fearnside.
Is there a chance that a bridge could be built across the Amazon in the near future?
If the need dominates over the difficulties and cost, a bridge will be built.
It was originally published on Live Science.