Radio waves, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and microwaves are some of the forms ofEM radiation. Most human eyes can see the wavelengths that are visible to visible light.
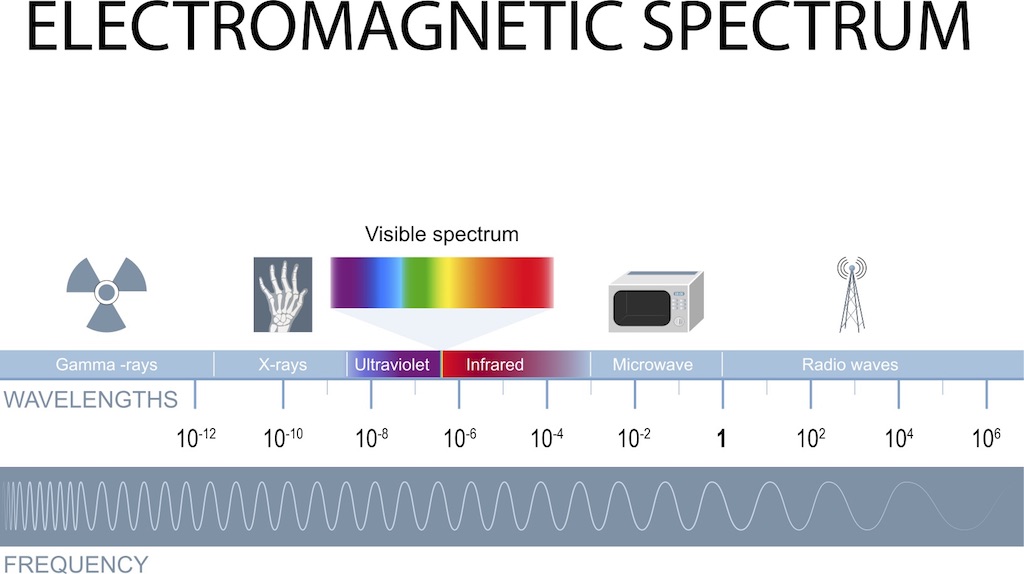
There are different types of visible light, which are transmitted in waves or particles at different frequencies. The range of wavelength is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum is usually divided into seven regions in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy. These are the regions.
The range of the EM spectrum is between theIR and UV. It has frequencies between 4 and 8 and cycles per second or hertz.
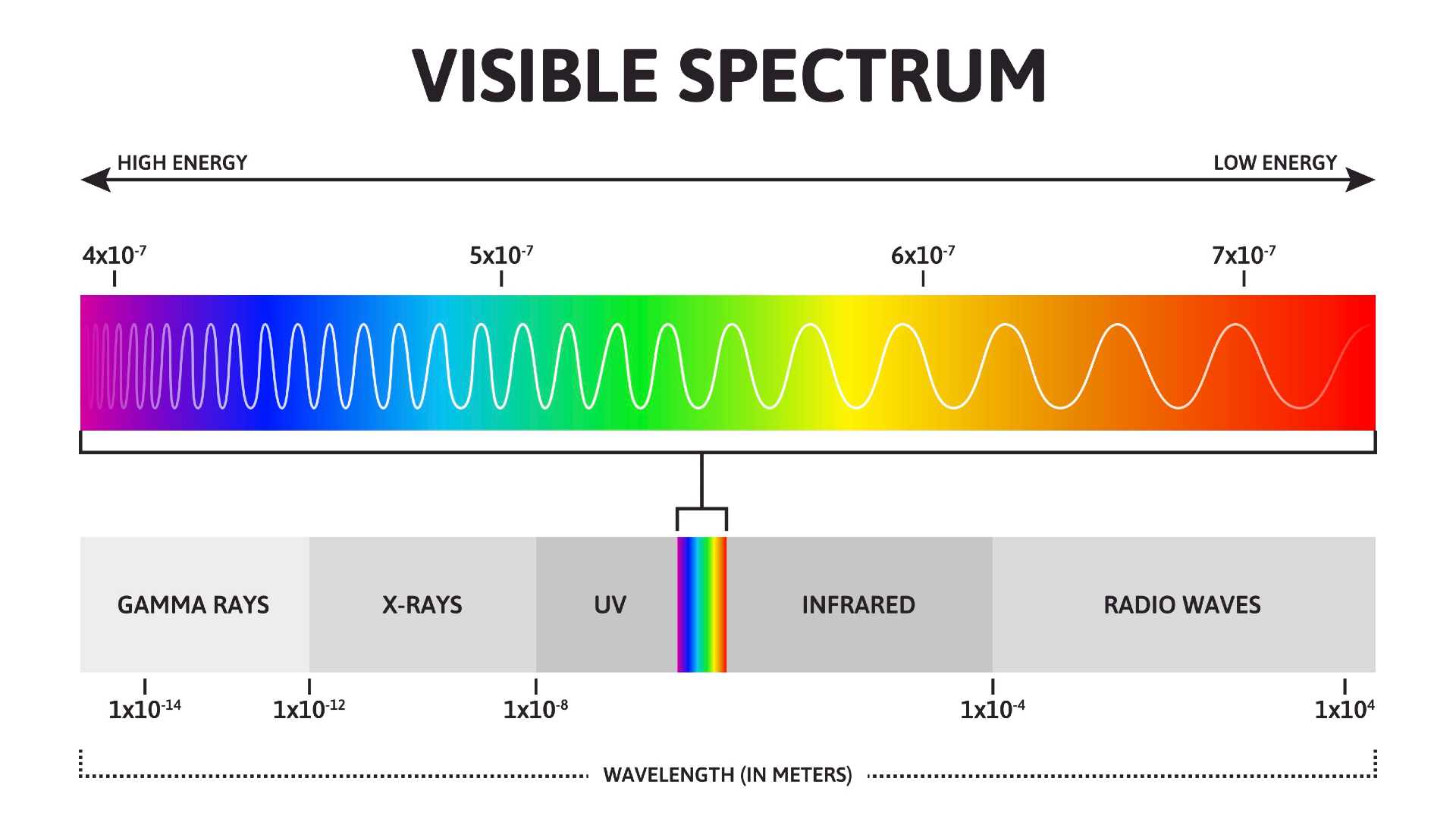
The most important feature of visible light is color. Light and the cells in the human eye make up color. According to The Physics Hypertextbook, objects don't have color. They give off light that appears to be a color. Elert writes that color is only seen in the mind of the beholder.
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU...
The cones in our eyes are specialized and can be used to tune the wavelength of the narrow band of the EM spectrum. Humans see light at the lower end of the visible spectrum, which has a wavelength of about 740 nm, as red, while we see light at the upper end of the spectrum, which has a wavelength of about 380 nm. The colors that we see are combinations of these colors.
The visible light spectrum has red and green regions and a mixture of red and blue. White light has all colors in it. Black has no light. According to the website of Michael Fowler, a physics professor at the University, the first person to realize that white light was made up of the colors of the rainbow was IsaacNewton, who in 1666 passed sunlight through a narrow slit and then a prism to project the colored spectrum onto a wall
As objects grow hotter, they emit energy dominated by shorter wavelength, which we perceive as changing colors. The flame of a blowtorch can be adjusted to burn hotter. According to theIDEA website, incandescence is the process of turning heat energy into light energy.
Incandescent light is produced when hot matter releases a portion of its thermal vibration energy. The energy from an object reaches the IR at about 1,472 degrees Fahrenheit. As the temperature increases, the energy moves into the visible spectrum and the object appears to have a reddish glow. The object gets hotter and the color changes to white hot and blue.

The color of hot objects, such as stars, can be used to estimate their temperatures. The surface temperature of the sun is about 5,800 kelvin. The light has a peak wavelength of about 500 nm, which we think is white light.
The star Betelgeuse would look reddish if the sun's surface temperature were cooler. It would look like the star Rigel if it were hotter.
Astronomers can determine what objects are made of by looking at the absorption spectrum. Calculating the chemical composition of stars, dust clouds and other distant objects can be done with the help of spectroscopes.

National Geographic has a video about how the human brain sees light. Light: The Visible Spectrum and Beyond, written by Black Dog and Leventhal, or do your own visible light experiments at home, can be found on the Ducksters website.
The article was updated on May 23, 2022, by Live Science managing editor.